Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
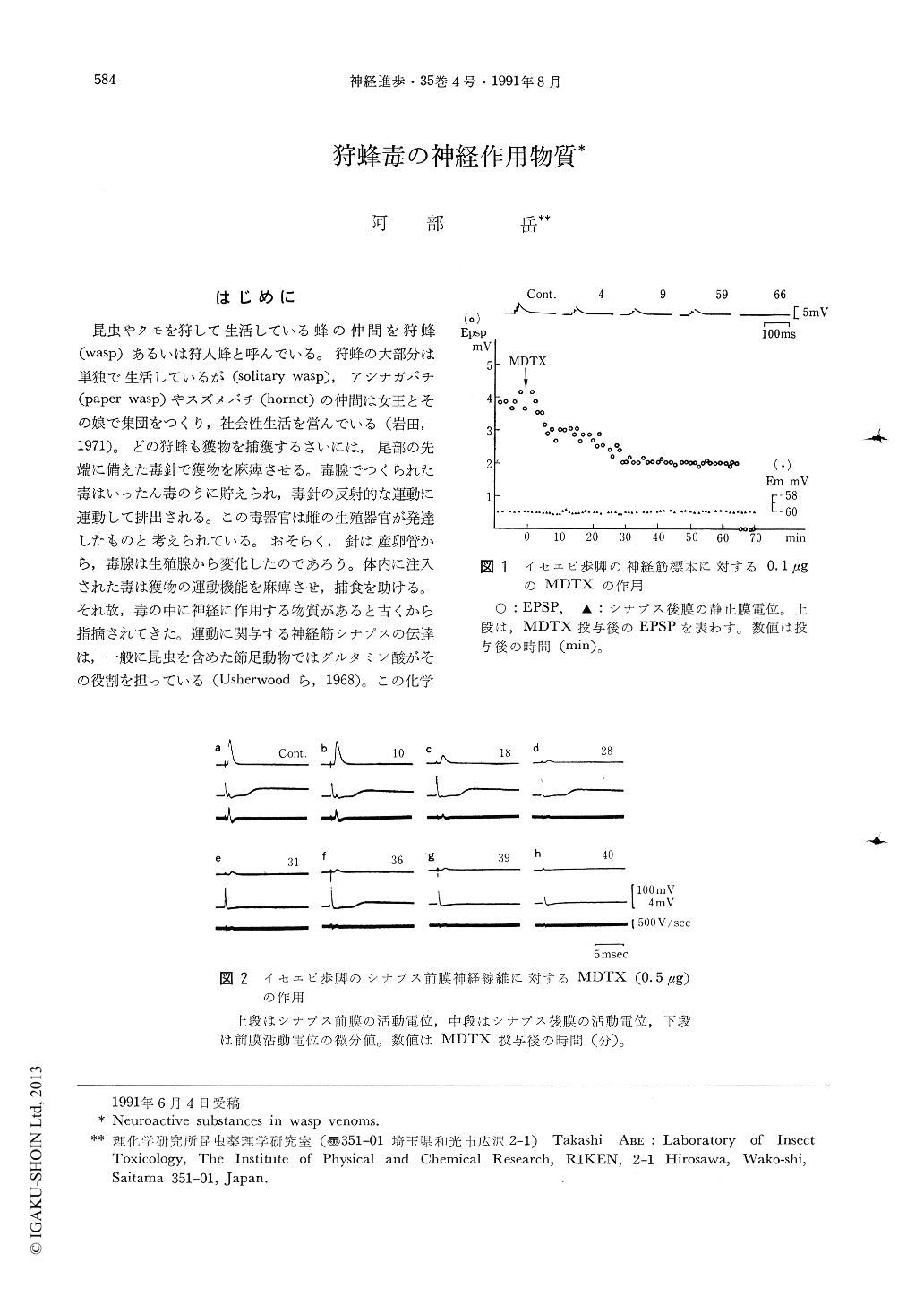
昆虫やクモを狩して生活している蜂の仲間を狩蜂(wasp)あるいは狩人蜂と呼んでいる。狩蜂の大部分は単独で生活しているが(solitary wasp),アシナガバチ(paper wasp)やスズメバチ(hornet)の仲間は女王とその娘で集団をつくり,社会性生活を営んでいる(岩田,1971)。どの狩蜂も獲物を捕獲するさいには,尾部の先端に備えた毒針で獲物を麻痺させる。毒腺でつくられた毒はいったん毒のうに貯えられ,毒針の反射的な運動に連動して排出される。この毒器官は雌の生殖器官が発達したものと考えられている。おそらく,針は産卵管から,毒腺は生殖腺から変化したのであろう。体内に注入された毒は獲物の運動機能を麻痺させ,捕食を助ける。それ故,毒の中に神経に作用する物質があると古くから指摘されてきた。運動に関与する神経筋シナプスの伝達は,一般に昆虫を含めた節足動物ではグルタミン酸がその役割を担っている(Usherwoodら,1968)。この化学伝達物質のリセプターはキスカリン酸型,カイニン酸型,およびN-メチル-D-アスパラギン酸型があり,クモの毒をはじめとする多くの昆虫毒がキスカリン酸タイプのリセプターを阻害する(Abeら,1983)。
狩蜂毒の中でも比較的進展のめざましいスズメバチ毒の研究ですら,炎症やアレルギーを起こす物質,そして循環器系への作用が知られてはいるものの,その組成の全体像は未だにつかめていない。ヒトなど大動物に致命的な損傷を与えるごく一部の狩蜂毒を除いて,大部分は種属維持のために昆虫を捕食する場合の道具としていることから,ここでは神経に作用する化合物の中でも神経機能を特異的に阻害する神経毒および化学伝達物質について述べる。
In the venom of wasps is contained neurotoxins such as Mandaratoxin (MDTX) and Philanthotoxin (PTX), and also chemical transmitters, such as acetylcholine, serotonin, glutamic acid and GABA. MDTX purified from the venom of Vespa mandarinia affects presynaptically on the neuromuscular junction of lobster leg, then blocks specifically on the sodium channels of the axon. It has a molecular weight of 20,000 daltones and a basic property, but no enzymatic and hemolytic activities. While a toxin which blocks irreversibly the spontaneous miniature end plate potentials on the presynaptic nerve of Drosophila larvae is found in the venom of Vespa tropica. Its resembled nature is conceived to be a kind of MDTX. The other hand, it is pointed out the similarity between MDTX and Antigen 5, an allergenic protein, isolated from the venoms of Polystes and Vespula, since both have a very close physicochemical properties.
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


