Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
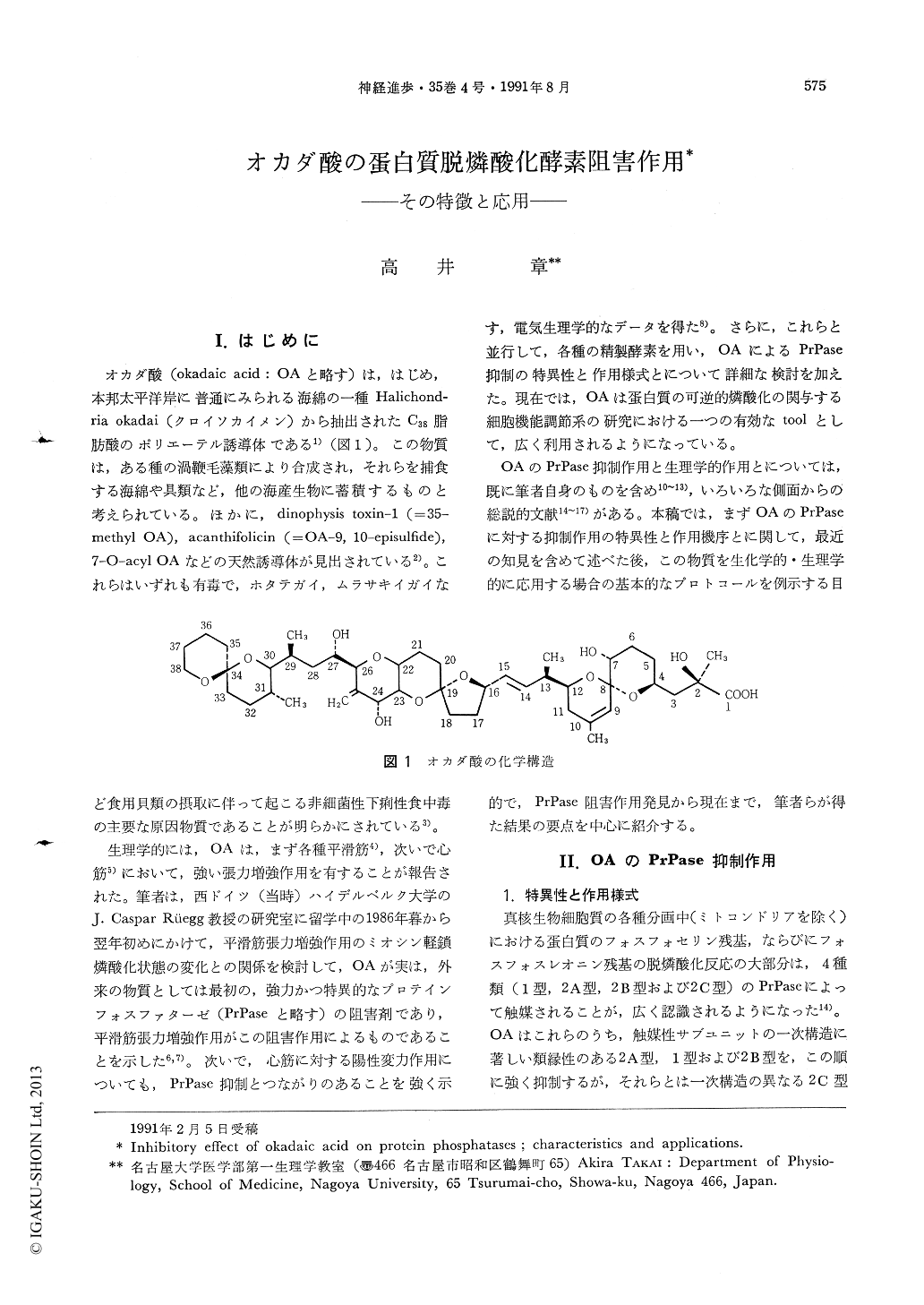
オカダ酸(okadaic acid:OAと略す)は,はじめ,本邦太平洋岸に普通にみられる海綿の一種Halichondria okadai(クロイソカイメン)から抽出されたC38脂肪酸のポリエーテル誘導体である1)(図1)。この物質は,ある種の渦鞭毛藻類により合成され,それらを捕食する海綿や具類など,他の海産生物に蓄積するものと考えられている。ほかに,dinophysis toxin-1(=35-methyl OA),acanthifolicin(=OA-9,10-episulfide),7-O-acyl OAなどの天然誘導体が見出されている2)。これらはいずれも有毒で,ホタテガイ,ムラサキイガイなど食用貝類の摂取に伴って起こる非細菌性下痢性食中毒の主要な原因物質であることが明らかにされている3)。
生理学的には,OAは,まず各種平滑筋4),次いで心筋5)において,強い張力増強作用を有することが報告された。筆者は,西ドイツ(当時)ハイデルベルク大学のJ. Caspar Rüegg教授の研究室に留学中の1986年暮から翌年初めにかけて,平滑筋張力増強作用のミオシン軽鎖燐酸化状態の変化との関係を検討して,OAが実は,外来の物質としては最初の,強力かつ特異的なプロテインフォスファターゼ(PrPaseと略す)の阻害剤であり,平滑筋張力増強作用がこの阻害作用によるものであることを示した6,7)。
Okadaic acid is the first exogenous substance that has been described to have a potent and specific inhibitory effect on protein phosphataes. The dissociation constants for the interaction of okadaic acid wih type 2A-, type 1- and type 2B-protein phosphatases are 30pM, 300nM and 5μM respectively. Enzyme-kinetic studies have shown that okadaic acid acts as a non-competitive or mixed inhibitor on these okadaic acid-sensitive phosphatases, which are structurally related enzymes, having 50% amino acid sequence homology in the catalytic domain. The following enzymes are not affected by up to 10 μM okadaic acid: type 2C-protein phosphatase, phosphotyrosyl phosphatase, inositol-1, 4, 5-trisphosphate phosphatase, acid phosphatases, alkaline phosphatases, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase, myosin light-chain phosphatase, cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Because of the especially high affinity for type 2A-phosphatase, combined use of okadaic acid with inhibitor 2, an intrinsic inhibitory factor of type 1-phosphatase, provide a new method for analysing the protein phosphatase composition in a relatively small amount of tissue extract. Okadaic acid, being membranepermeable, can effectively be used for investigating possible roles of protein phosphorylation in regulation of ionic channels.
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


