Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
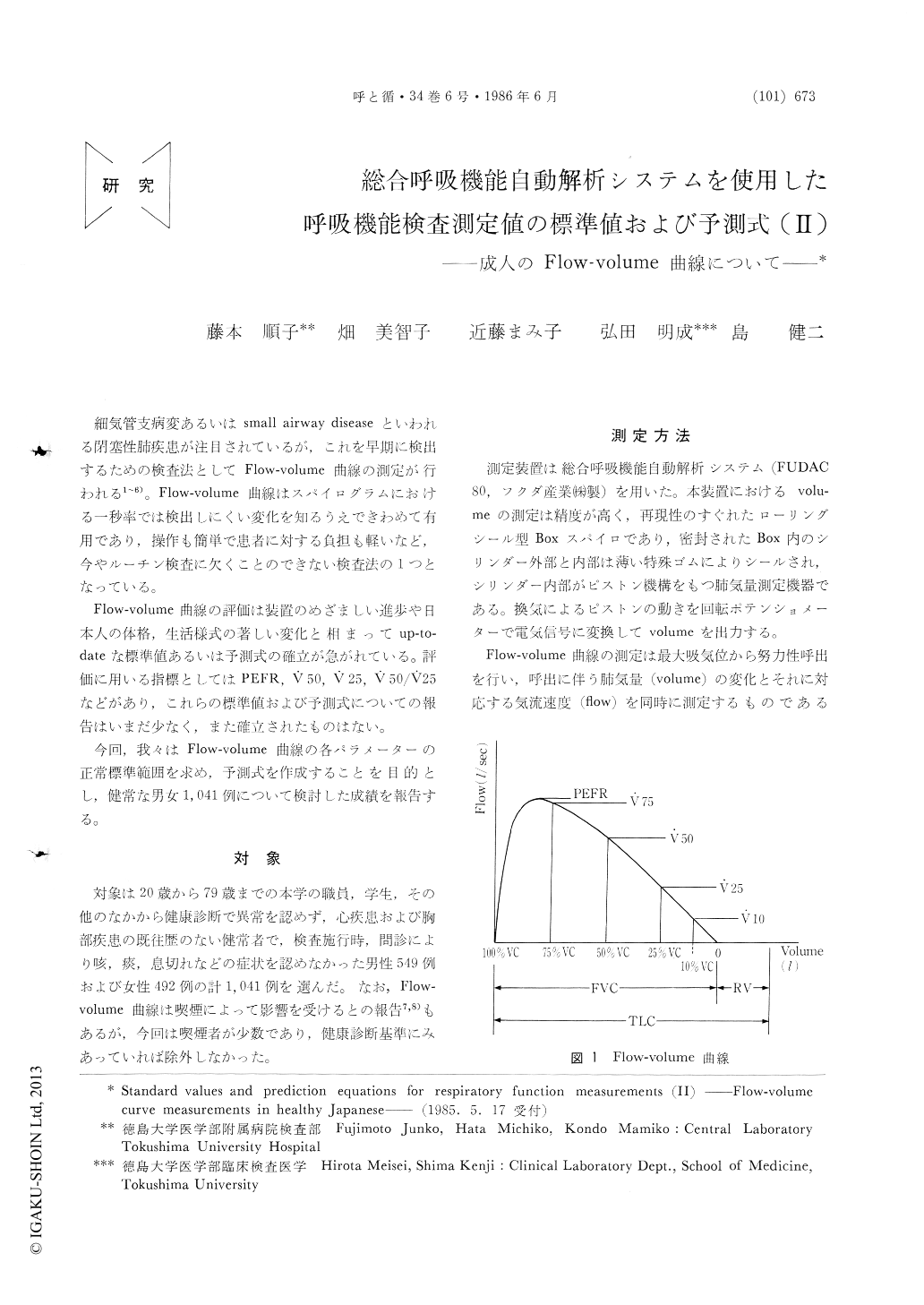
細気管支病変あるいはsmall airway diseaseといわれる閉塞性肺疾患が注目されているが,これを早期に検出するための検査法としてFlow-volume曲線の測定が行われる1〜6)。Flow-volume曲線はスパイログラムにおける一秒率では検出しにくい変化を知るうえできわめて有用であり,操作も簡単で患者に対する負担も軽いなど,今やルーチン検査に欠くことのできない検査法の1つとなっている。
Flow-volume曲線の評価は装置のめざましい進歩や日本人の体格,生活様式の著しい変化と相まってup-to-dateな標準値あるいは予測式の確立が急がれている。評価に用いる指標としてはPEFR,V50,V25,V50/25などがあり,これらの標準値および予測式についての報告はいまだ少なく,また確立されたものはない。
Normal parameters for flow-volume measurement using a computerized spirometer (FUDAC 80) in 1401 healthy subjects ranged from 20 to 79 years of age were reported.
The subjects were separated by sex and grouped by age in decades. The parameters used in this study include maximal flow at 75 per cent (V75), 50 per cent (V50), 25 per cent (V25), 10 per cent (V10), of the forced vital capacity, peakflow (PEFR) and their ratios with vital capacity (VC), and height (Ht). All the values obtained were decreasing in parallel with age in both sexes, and this tendency was higher in male. The flow rates adjusted with vital capacity (V/VC) showed a decrease in the low VC range indicating an increased terminal airway resistance and/or a decreased pulmonary recoil pressure in the aged group. Prediction equations were derived from the measured values with multiple regression analysis and showed a good accordance with the previously reported values from other institutes.
In this study, normal values and prediction equations for flow-volume measurement were obtained, and these parameters were shown to be highly reliable and appli-cable in the clinical field.
Copyright © 1986, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


