Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
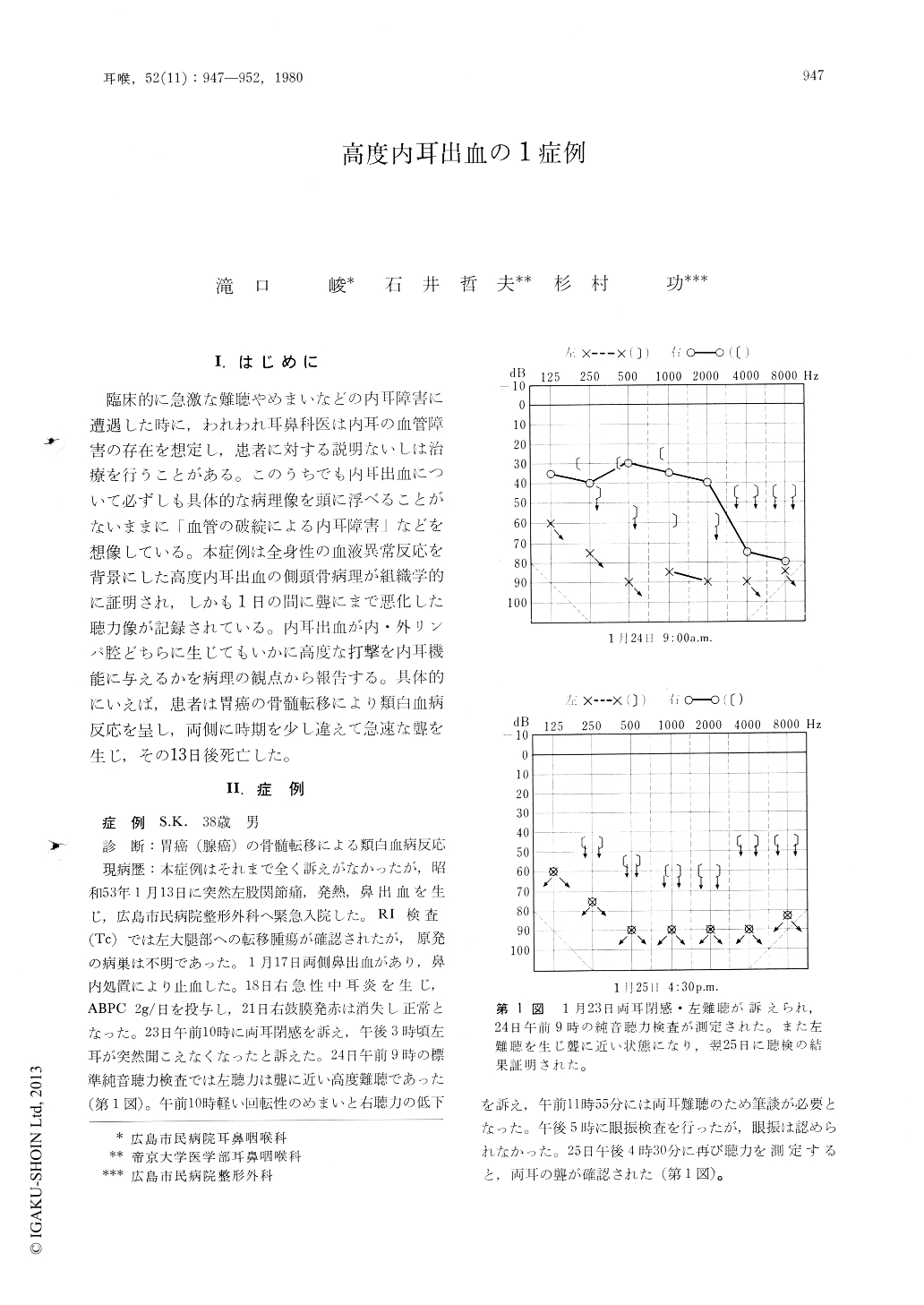
臨床的に急激な難聴やめまいなどの内耳障害に遭遇した時に,われわれ耳鼻科医は内耳の血管障害の存在を想定し,患者に対する説明ないしは治療を行うことがある。このうちでも内耳出血について必ずしも具体的な病理像を頭に浮べることがないままに「血管の破綻による内耳障害」などを想像している。本症例は全身性の血液異常反応を背景にした高度内耳出血の側頭骨病理が組織学的に証明され,しかも1日の間に聾にまで悪化した聴力像が記録されている。内耳出血が内・外リンパ腔どちらに生じてもいかに高度な打撃を内耳機能に与えるかを病理の観点から報告する。具体的にいえば,患者は胃癌の骨髄転移により類白血病反応を呈し,両側に時期を少し違えて急速な聾を生じ,その13日後死亡した。
A 38-year-old man, died of leukemoid reaction caused by metastasis of gastric adenocarcinoma to bone marrow, developed a severe hearing loss of sudden onset 13 days prior to death. Deafness in the left ear occurred first which was followed by hearing loss in the right on the next day. Totaldeafness in all frequencies was recorded in the last audiogram. Histopathological findings of both temporal bones revealed an intense hemorrhage in the endolymphatic space of the cochlea and saccule as well as in the perilymphatic space of the cochlea and vestibule. Hemorrhage and infiltration were observed in the various parts of membranous labyrinth. The authors speculated that deafness of this patient was caused by an acute, intense hemorrhage to perilymphatic and endolymphatic spaces.
Copyright © 1980, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


