Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
Ⅰ.はじめに
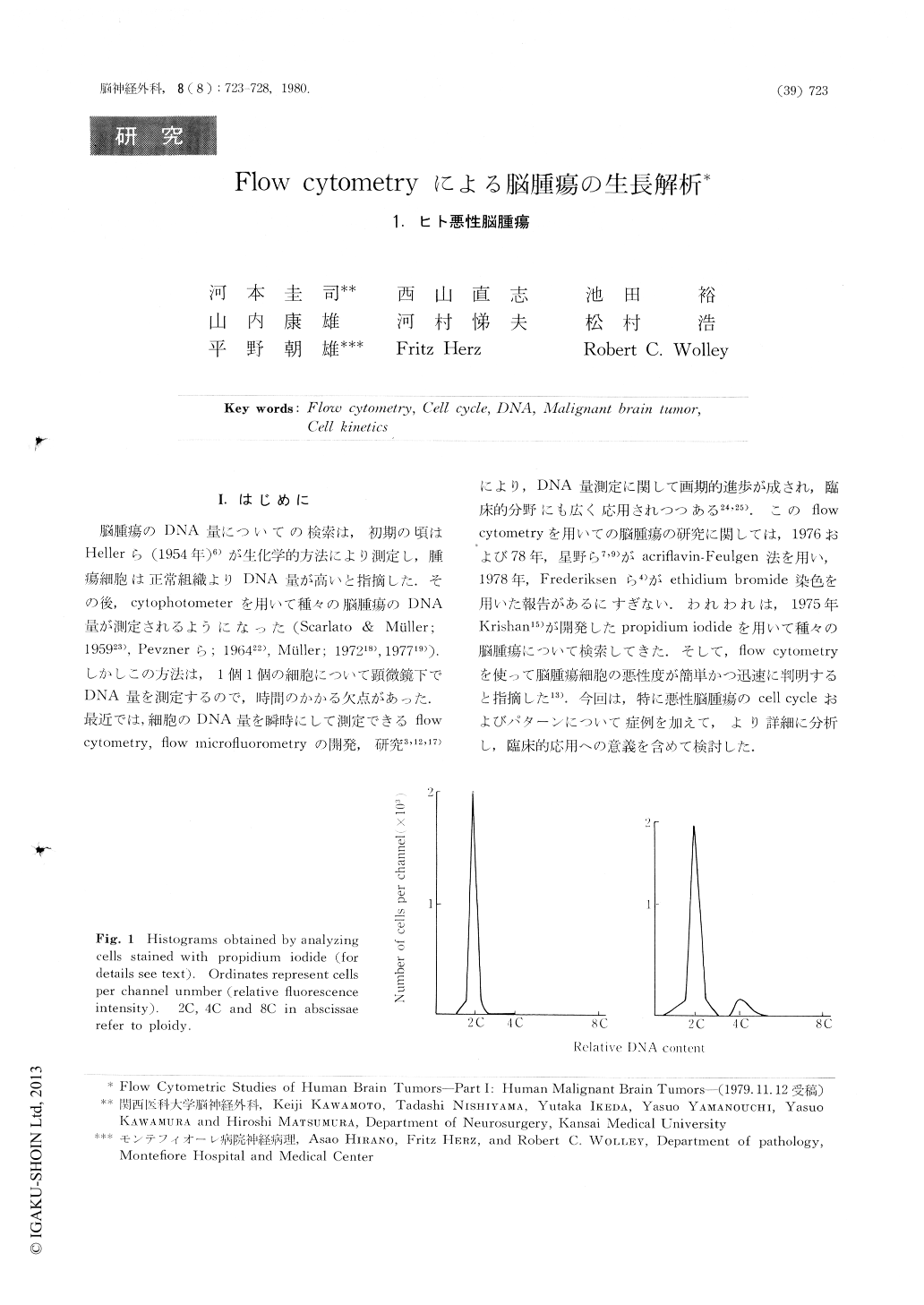
脳腫瘍のDNA量についての検索は,初期の頃はHellerら(1954年)6)が生化学的方法により測定し,腫瘍細胞は正常組織よりDNA量が高いと指摘した.その後,cytophotometerを用いて種々の脳腫瘍のDNA量が測定されるようになった(Scarlato & Müller;195923),Pevznerら;196422),Müller;197218),197719)).しかしこの方法は,1個1個の細胞について顕微鏡下でDNA量を測定するので,時間のかかる欠点があった.最近では,細胞のDNA量を瞬時にして測定できるflow cytometry,flow microfiuorotnetryの開発,研究3,12,17)により,DNA量測定に関して画期的進歩が成され,臨床的分野にも広く応用されつつある24,25).このflow cytometryを用いての脳腫瘍の研究に関しては,1976および78年,星野ら7,9)がacriflavin-Feulgen法を用い,1978年,Frederiksenら4)がethidium bromide染色を用いた報告があるにすぎない.われわれは,1975年Krishan15)が開発したpropidium iodideを用いて種々の脳腫瘍について検索してきた.
This report concerns the distribution of the DNA content in cells obtained from seven nonneoplastic, human brain tissue specimens and from eight different kinds of malignant human brain tumors of 30 patients. Analysis was carried out by flow cytometry using suspensions of single separated cells stained with propidium iodide as DNA-intercalating fluorochrome. Normal, non-stimulated lymphocytes served as diploid controls. An average of 91% of the cells from non-neoplastic brain tissue was diploid (2C) and these cells were presumable in Go or G, stage of the cell cycle.
Copyright © 1980, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


