Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
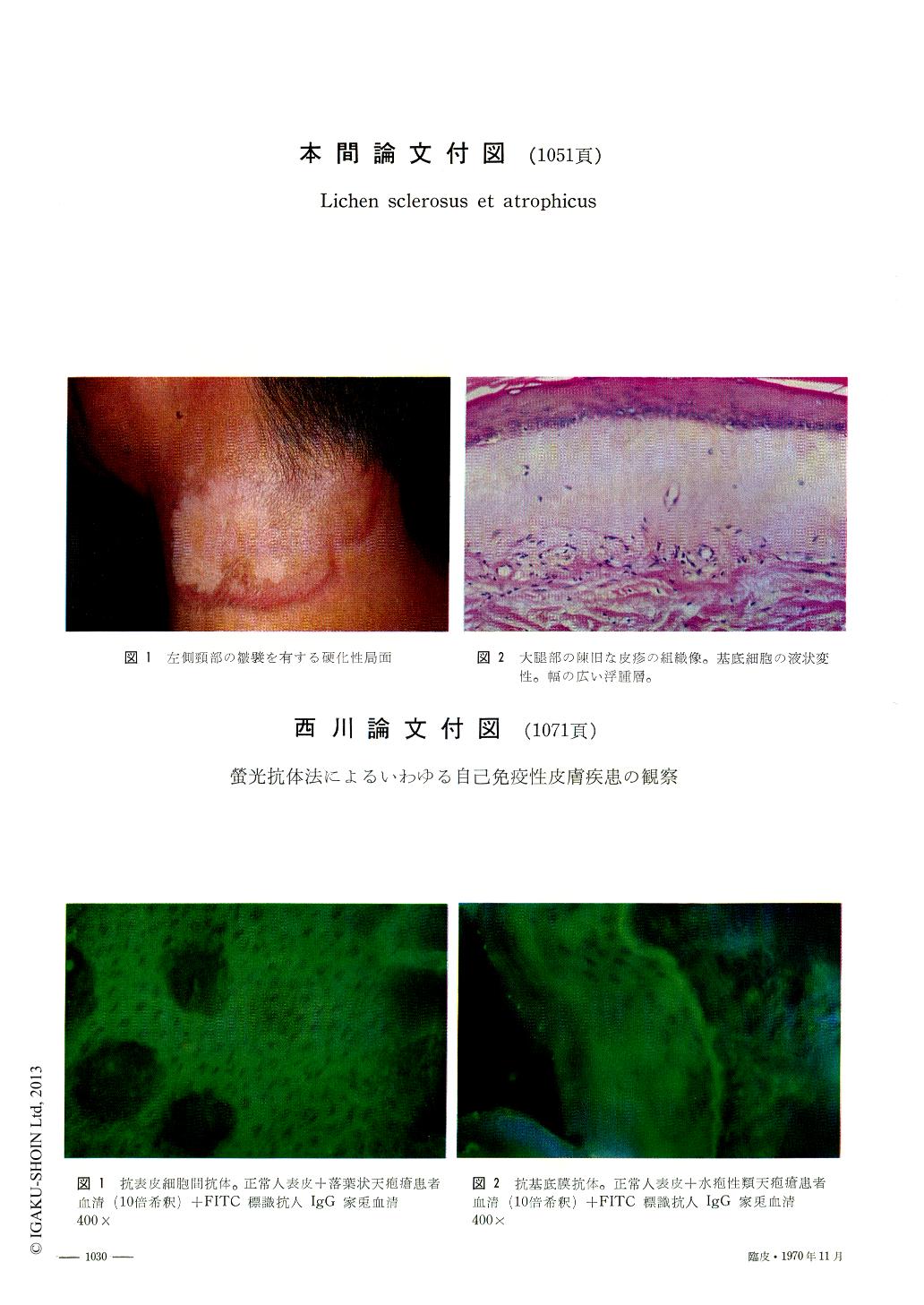
Beutnerら1,2)により尋常性天疱瘡患者血清中に表皮有棘細胞間物質に対する抗体が存在すること,また皮疹部のγ-グロブリンの沈着の事実が螢光抗体法の導入によつて明らかにされて以来,その病因本態を解明するまでには至らないにしても天疱瘡群2),水疱性類天疱瘡3,4),Duhring疱疹状皮膚炎5)などにおける自己免疫現象の関与が相次いで見いだされて注目を浴びるところとなってきた。また,主として内科領域でその自己免疫現象が追求されている全身性紅斑性狼瘡においても皮膚科的には皮膚発疹部あるいは無疹部のγ—グロブリン沈着の存在が患者血清中の抗核抗体とともに補助診断の1つとしてあげられている6,7)。このようないわゆる自己免疫性疾患の病因あるいは診断面での急速な発展はCoons & Kaplan8)により確立された螢光抗体法の導入によるところがきわめて大きい。
われわれは当科で経験した天疱瘡群,水疱性類天疱瘡を中心としたいわゆる自己免疫性皮膚疾患々者の血清中に存在する自己抗体を螢光抗体法を用いて検索した。同時にそのうちの若干の症例については皮疹部に沈着するγ-グロブリン(IgG)をも検索したので報告し,本領域における最近の研究とあわせて,螢光抗体法の応用が皮膚科診断学の一助として,また,経過を観察する上にも有用であることを紹介したい。
Autoantibodies in the patients with autoimmune diseases of the skin were studied by the use of fluorescent antibody technique. Thirty four sera in total served to the test, in which human epidermis was used as a substrate, and FITC labeled rabbit anti-sera to human IgG as a stain-ing reagent. The results confirmed the presence of the disease-specific autoantibody in pemphi-gus group, bullous pemphigoid, lupus erythematosus and generalized morphea. In one of the 3 sera of the patients with dermatitis herpetiformis Duhring, autoantibody to the basement mem-brane was observed.
Skin lesions in 10 cases of the patients were examined for the presence of γ-globulin (IgG) by the direct application of FITC labeled sera. In-vive bound γ-globulin (IgG) was found in one each of pemphigus vulgaris, pemphigus foliaceus, Senear-Usher syndrome, dermatomyositis, and bullous pemphigoid, and 3 of systemic lupus erythematosus.
In addition to the data obtained from our studies, recent investigations on this field were re-viewed. It was suggested that the application of fluorescent antibody technique revealed useful and reliable method in the differential diagnosis and the observation of the clinical course of the patients with autoimmune diseases of the skin.
Copyright © 1970, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


