Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
Ⅰ はじめに
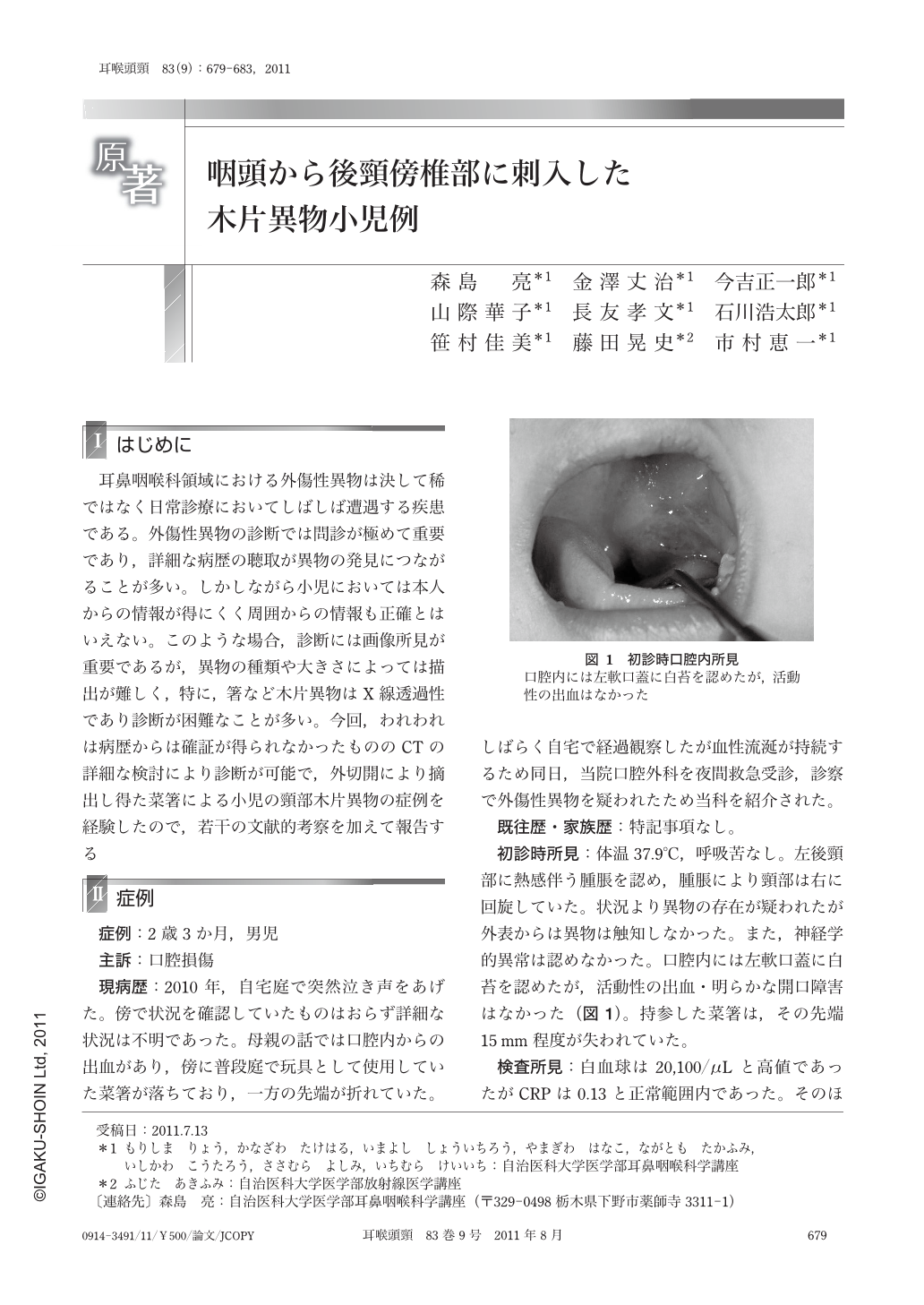
耳鼻咽喉科領域における外傷性異物は決して稀ではなく日常診療においてしばしば遭遇する疾患である。外傷性異物の診断では問診が極めて重要であり,詳細な病歴の聴取が異物の発見につながることが多い。しかしながら小児においては本人からの情報が得にくく周囲からの情報も正確とはいえない。このような場合,診断には画像所見が重要であるが,異物の種類や大きさによっては描出が難しく,特に,箸など木片異物はX線透過性であり診断が困難なことが多い。今回,われわれは病歴からは確証が得られなかったもののCTの詳細な検討により診断が可能で,外切開により摘出し得た菜箸による小児の頸部木片異物の症例を経験したので,若干の文献的考察を加えて報告する。
A 2-year-and-3-month-old boy was suspected that the broken tip of a wooden chopstick penetrated his left soft palate. CT scan revealed that the wooden tip passed nearby the left carotid artery without injury of the arterial wall,and reached to the left posterior cervical region. Furthermore,CT films enabled us to estimate the size,form of the foreign body and the relationship between the foreign body and the main vessels of the neck. Supporting by preoperative CT examination,the foreign body was removed through an external incision from the posterior neck under general anesthesia. The CT value changed in time depending manner because the wooden foreign body absorbed water from surrounding tissues. It was difficult to find the wooden foreign body using radiographic examination including CT scan. In this case,CT scan was very useful to find the foreign body because we took the CT scan immediately after he came and did carefully ckeck the CT examination. Thus,the CT scan should be taken as soon as possible if the wooden foreign body was suspected.
Copyright © 2011, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


