Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
Ⅰ.緒論
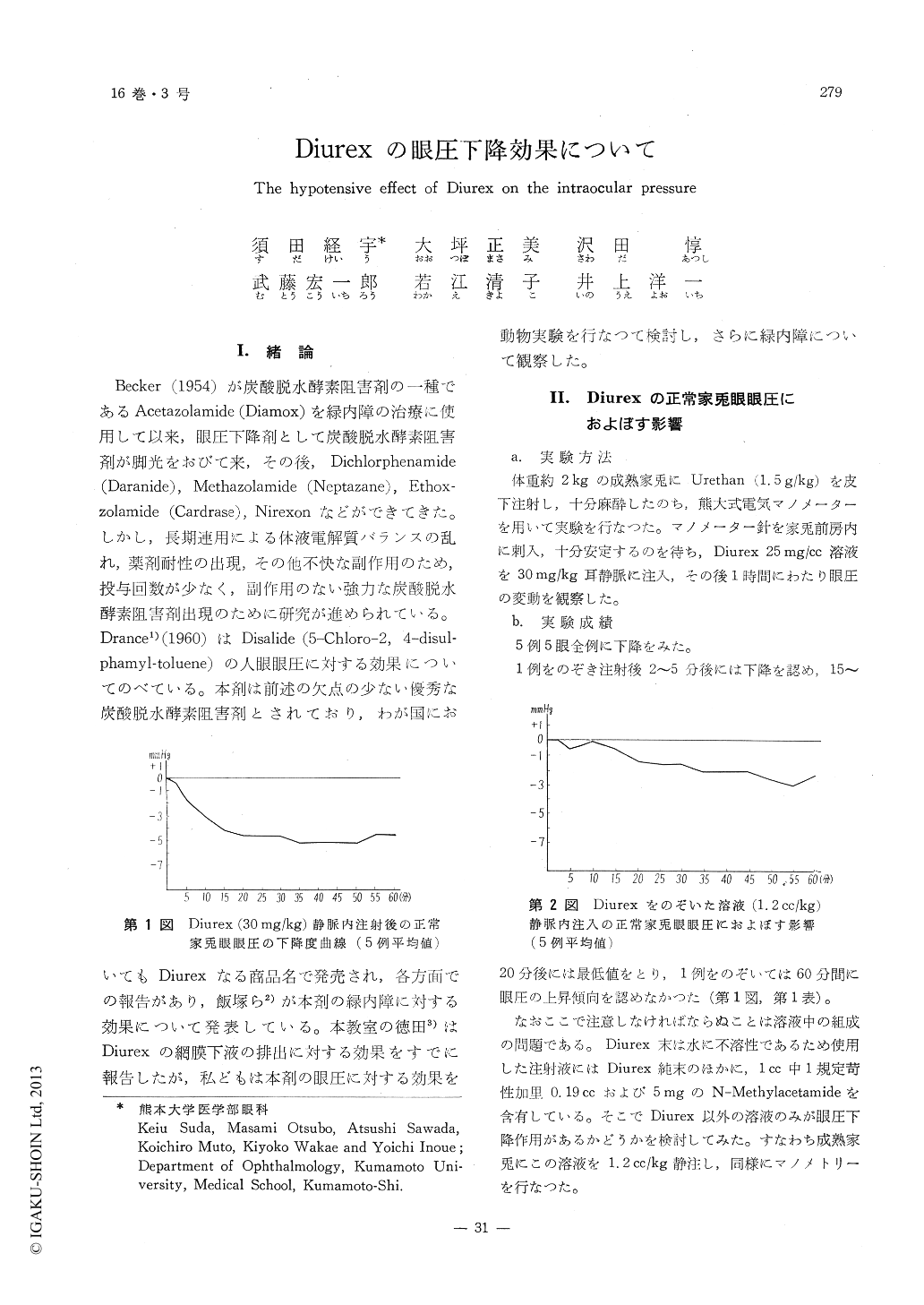
Becker (1954)が炭酸脱水酵素阻害剤の一種であるAcetazolamide (Diamox)を緑内障の治療に使用して以来,眼圧下降剤として炭酸脱水酵素阻害剤が脚光をおびて来,その後,Dichlorphenamide(Daranide),Methazolamide (Neptazane),Ethox—zolamide (Cardrase),Nirexonなどができてきた。しかし,長期連用による体液電解質バランスの乱れ,薬剤耐性の出現,その他不快な副作用のため,投与回数が少なく,副作用のない強力な炭酸脱水酵素阻害剤出現のために研究が進められている。Drance1)(1960)はDisalide (5—Chloro−2,4—disul—phamyl-toluene)の人眼眼圧に対する効果についてのべている。本剤は前述の欠点の少ない優秀な炭酸脱水酵素阻害剤とされており,わが国においてもDiurexなる商品名で発売され,各方面での報告があり,飯塚ら2)が本剤の緑内障に対する効果について発表している。本教室の徳田3)はDiurexの網膜下液の排出に対する効果をすでに報告したが,私どもは本剤の眼圧に対する効果を動物実験を行なつて検討し,さらに緑内障について観察した。
Diurex (5-Chloro-2, 4-disulphamyl-toluene) (a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor) was injected 30 mg./kg. weight intravenously in the rabbits and the changes of the intraocular pressure were ob-served on manometry. A few minutes after injection, the intraocular pressure began to fall in all of 5 cases. Maximal reduction in the intraocular pressure was 5.2mmHg. on the average.
In man, the hypotensive effect of Diurex was studied on 21 glaucomatous eyes (10, 1, 4, 3 and 3 eyes had chronic simple, acute congestive, chronic congestive, congenital and secondary glaucoma respectively). The dose administered daily was varied from 150mg. to 450mg.
Copyright © 1962, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


