Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
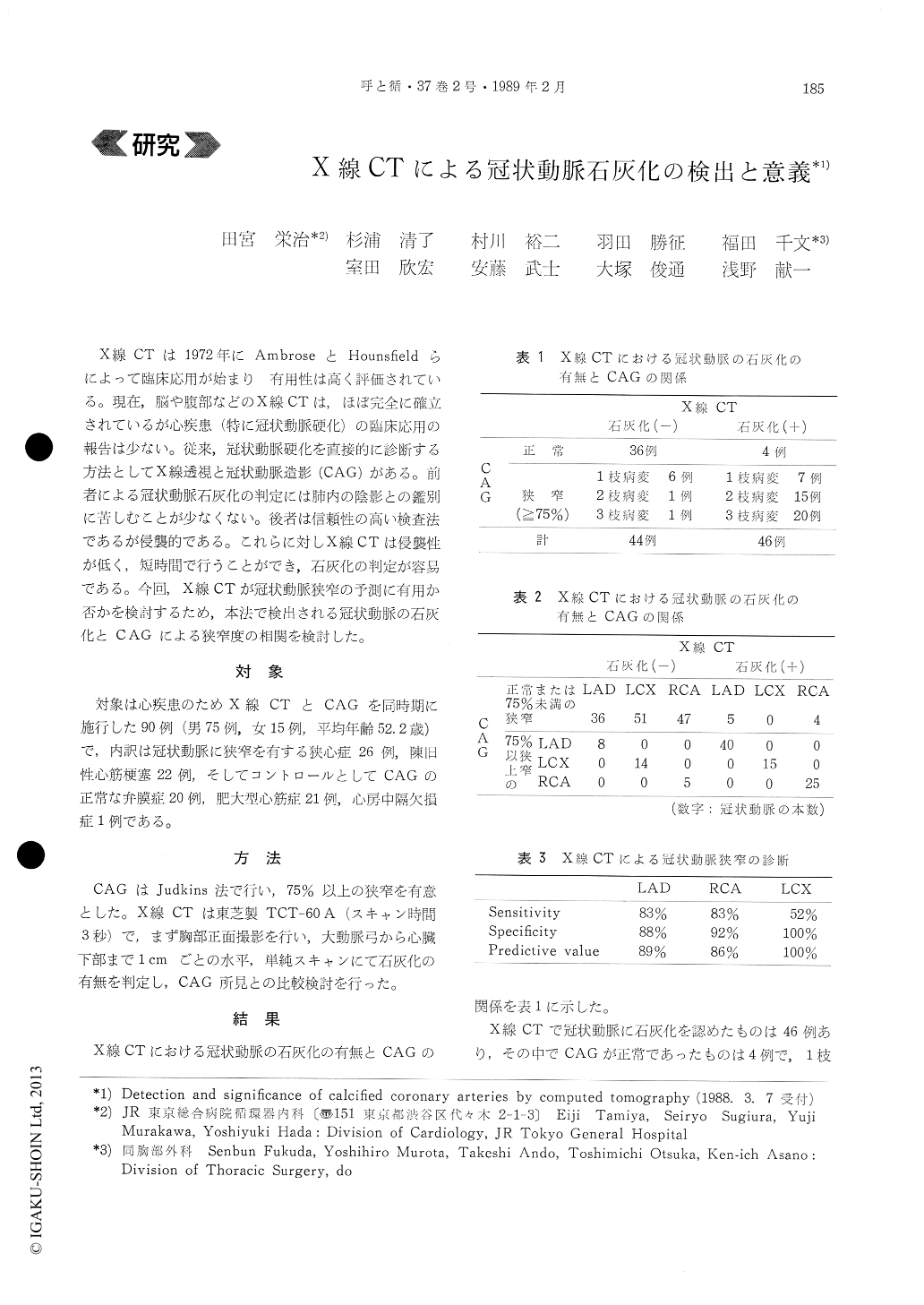
X線CTは1972年にAmbroseとHounsfieldらによって臨床応用が始まり有用性は高く評価されている。現在,脳や腹部などのX線CTは,ほぼ完全に確立されているが心疾患(特に冠状動脈硬化)の臨床応用の報告は少ない。従来,冠状動脈硬化を直接的に診断する方法としてX線透視と冠状動脈造影(CAG)がある。前者による冠状動脈石灰化の判定には肺内の陰影との鑑別に苦しむことが少なくない。後者は信頼性の高い検査法であるが侵襲的である。これらに対しX線CTは侵襲性が低く,短時間で行うことができ,石灰化の判定が容易である。今回,X線CTが冠状動脈狭窄の予測に有用か否かを検討するため,本法で検出される冠状動脈の石灰化とCAGによる狭窄度の相関を検討した。
To investigate whether coronary artery disease is detected noninvasively, we correlated calcification on computed tomography (CT) with coronary angio-graphic (CAG) findings in 90 consecutive patients including 48 with angina pectoris or myocardial in-farction. The mean age was 52.2 years and 83% were men. CT scans without contrast enhancement (3 sec scan time) were obtained at 1cm thickness from the ascending aorta to cardiac apex to identify calcification in coronary arteries.
Results ; CAG revealed of 50 patients, and stenosis was present more often at calcified vessels on CT.
LAD RCA LCX
Sensitivity 83% 83% 52%
Specificity 88% 92% 100%
Predictive value 89% 86% 100%
Calcification occurred more often in 2 or 3 vessel disease. However, stenotic segments were not al-ways calcified.
We conclude that CT is sensitive for the detection of calcification and an important method for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


