Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.緒言
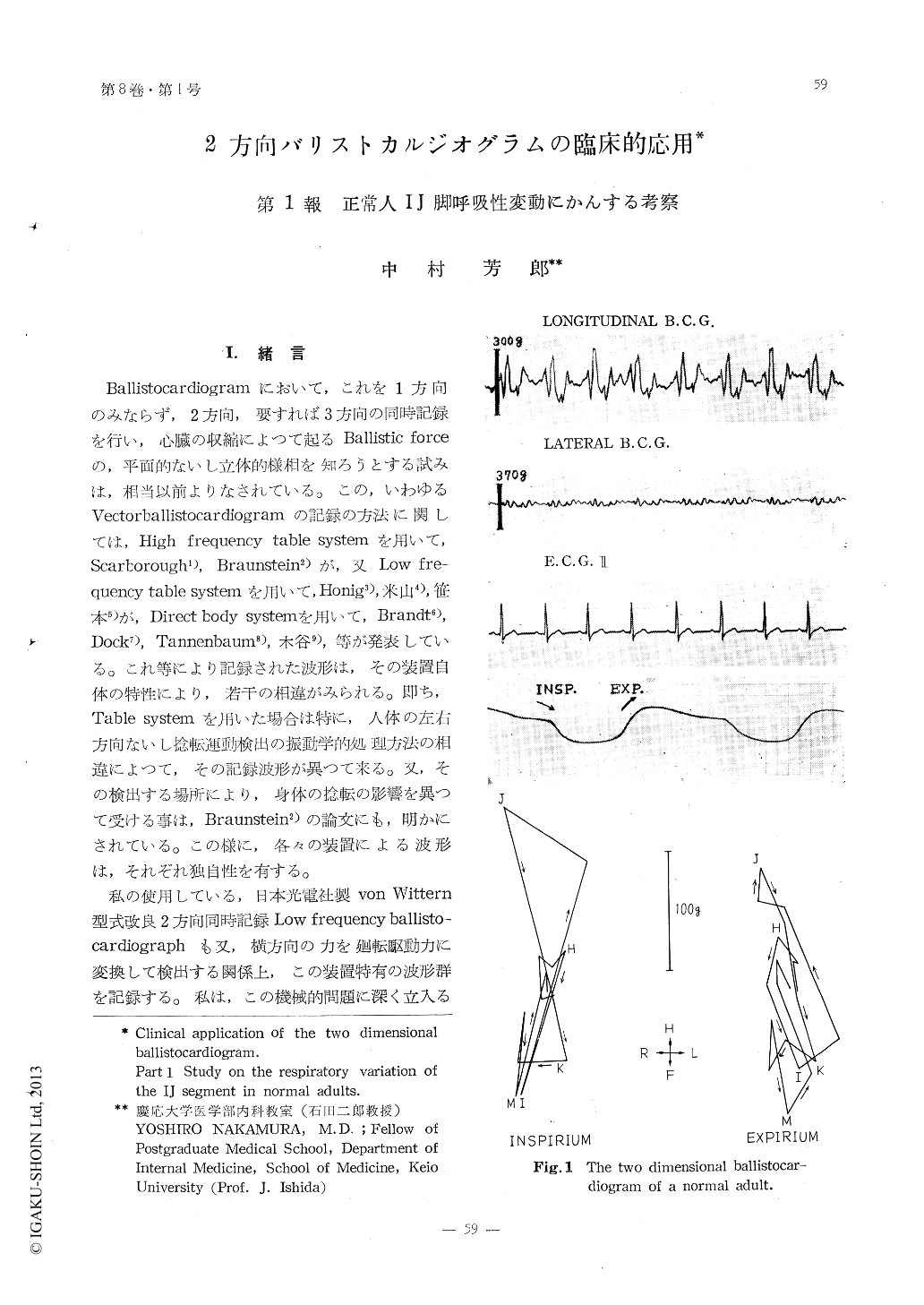
Ballistocardiogramにおいて,これを1方向のみならず,2方向,要すれば3方向の同時記録を行い,心臓の収縮によつて起るBallistic forceの,平面的ないし立体的様相を知ろうとする試みは,相当以前よりなされている。この,いわゆるVectorballistocardiogramの記録の方法に関しては,High frequency table systemを用いて,Scarborough1),Braunstein2)が,又Low fre—quency table systemを用いて,Honig3),米山4),笹本5)が,Direct body systemを用いて,Brandt6),Dock7),Tannenbaum8),木谷9),等が発表している。これ等により記録された波形は,その装置自体の特性により,若干の相違がみられる。即ち,Table systemを用いた場合は特に,人体の左右方向ないし捻転運動検出の振動学的処理方法の相違によつて,その記録波形が異つて来る。又,その検出する場所により,身体の捻転の影響を異つて受ける事は,Braunstein2)の論文にも,明かにされている。この様に,各々の装置による波形は,それぞれ独自性を有する。
Using a modified von Wittern's type two dimensional low frequency ballistocardiograph, the respiratory variation of the IJ segment in 30 normal adults was studied.
The direction of the IJ segment on the frontal plane had a tendency variate with the change in the direction of the cardiac axis by the respiration.
But the change in the ballistic force caused by the respiration was more eminent, and the respiratory variation of the IJ amplitude on the frontal plane was almost same to that of the longitudinal IJ ampli-tude, because the lateral amplitude in normal adults was small.
Hence it was concluded that respiratory variation of the longitudinal IJ amplitude was caused chiefly by that of the IJ amplitude on the frontal plane and very little by the variation of the direction.
Copyright © 1960, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


