Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
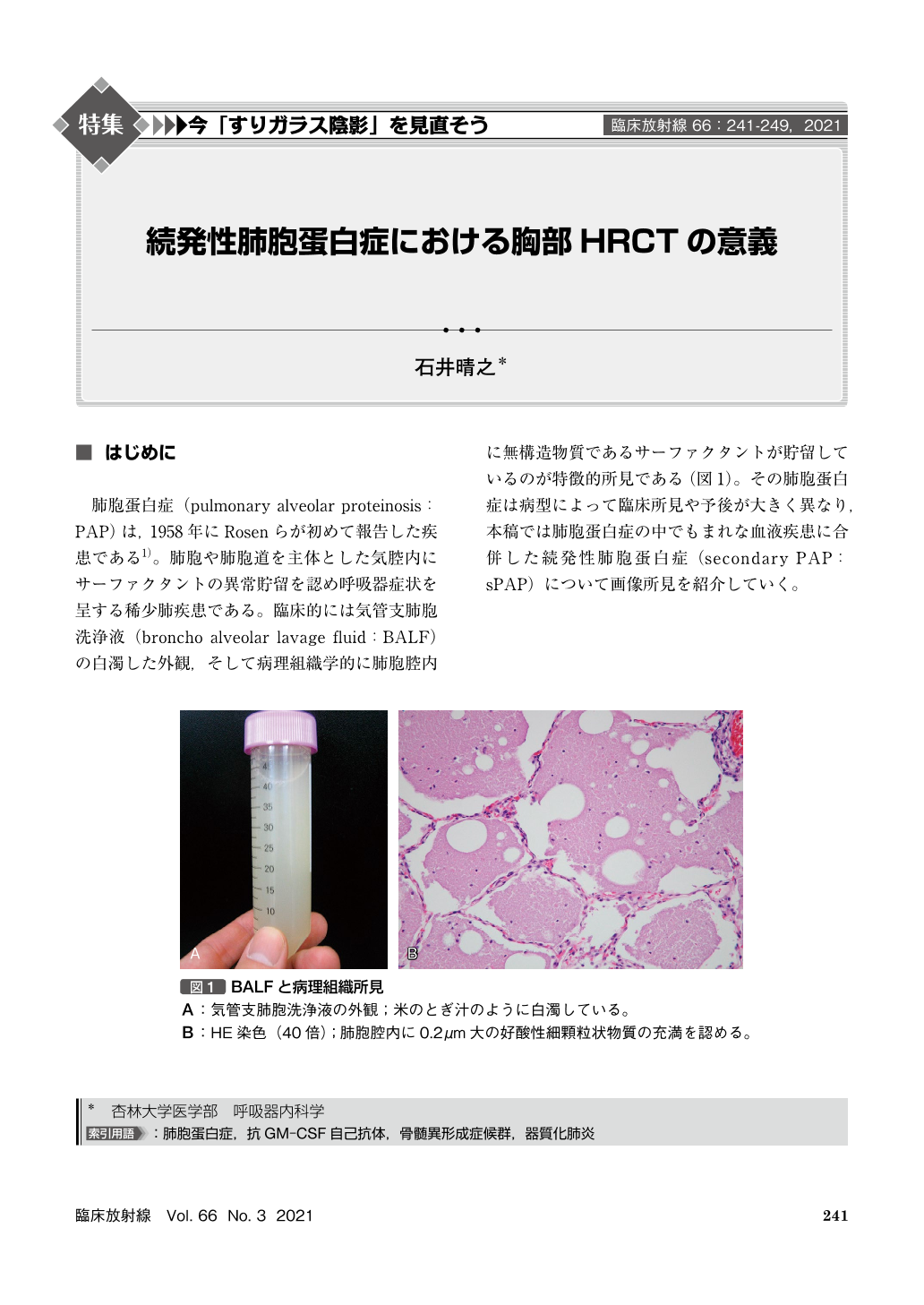
肺胞蛋白症(pulmonary alveolar proteinosis:PAP)は,1958年にRosenらが初めて報告した疾患である1)。肺胞や肺胞道を主体とした気腔内にサーファクタントの異常貯留を認め呼吸器症状を呈する稀少肺疾患である。臨床的には気管支肺胞洗浄液(broncho alveolar lavage fluid:BALF)の白濁した外観,そして病理組織学的に肺胞腔内に無構造物質であるサーファクタントが貯留しているのが特徴的所見である(図1)。その肺胞蛋白症は病型によって臨床所見や予後が大きく異なり,本稿では肺胞蛋白症の中でもまれな血液疾患に合併した続発性肺胞蛋白症(secondary PAP:sPAP)について画像所見を紹介していく。
Secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis(sPAP)is extremely rare lung disease with poor prognosis. Because there is little information for diagnostic management, the definitive diagnosis of sPAP is often delayed in many cases. Therefore, we should consider the characteristic HRCT findings of sPAP to early diagnose as it. Ground glass opacities(GGOs)typically shows a diffuse distribution in sPAP, whereas GGOs shows a geographic distribution in autoimmune PAP. Crazy-paving appearance and subpleural sparing are less frequently seen in sPAP. There are a few cases with interlobular septal thickening, complication of organizing pneumonia, or multiple tiny nodules in patients with sPAP. We should to differential diagnose with sPAP if these findings are detected in some disease, especially hematological disorders.
Copyright © 2021, KANEHARA SHUPPAN Co.LTD. All rights reserved.