Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
外傷性後頭蓋窩硬膜外血腫は頭部外傷中の0.3%1,4,5),全硬膜外血腫中,約7%4,6)程度を占めるにすぎず,頻度は少ない.しかもこの診断は比較的難しく,特に小児の場合は一層困難とされてきた.しかしCT導入以来,本症の診断は容易となり,報告例も増え,適切な処置が速やかに行われるようになった.
最近われわれは,本邦の報告例中では最年少と思われる1歳2ヵ月男児の後頭蓋窩急性硬膜外血腫を受傷後2時間目にCTにて診断し,直ちに血腫除去術施行し,救命した.以下,本症例を報告し,今までの報告例を加えて,小児の後頭蓋窩硬膜外血腫の発生頻度,受傷機転,出血部位およびCT所見などについて検討した.
A case of one year and 2-month-old male withtraumatic epidural hematoma in the posterior fossawas reported. He fell from the carriage and hit hisleft occipital area. After one hour, he was drowsy.On admission, there was neither preretinal bleedingnor motor weakness.
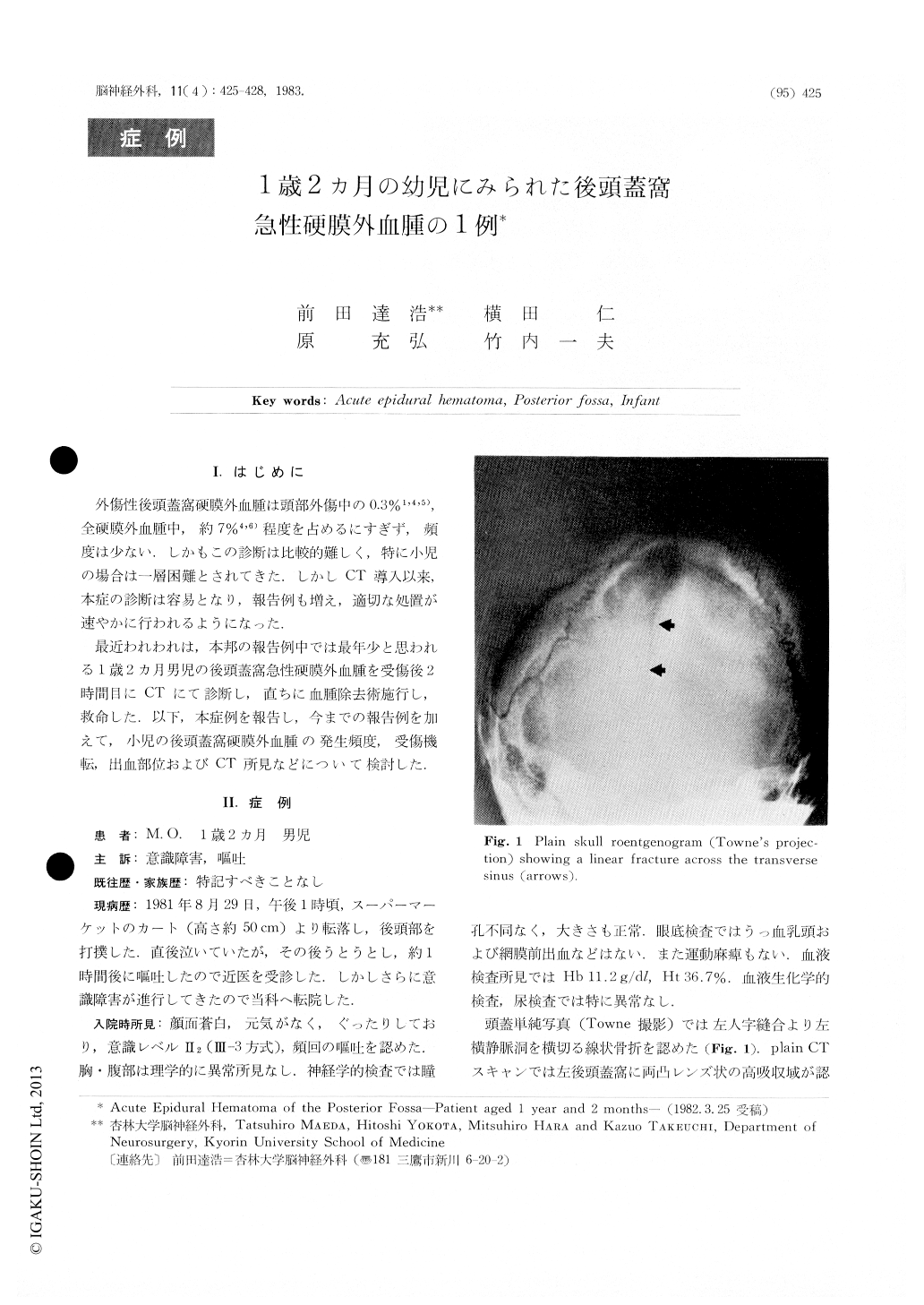
A skull roentgenogram showed a linear fractureacross the transverse sinus. A plain CT scan showeda lenticular high density area in the left posterior fossa.The cisterna ambiens was not observed and the fourthventricle was slightly compressed.
In the operation which took place immediately, amassive epidural clot of ca. 15g was evacuated.
Copyright © 1983, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


