Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
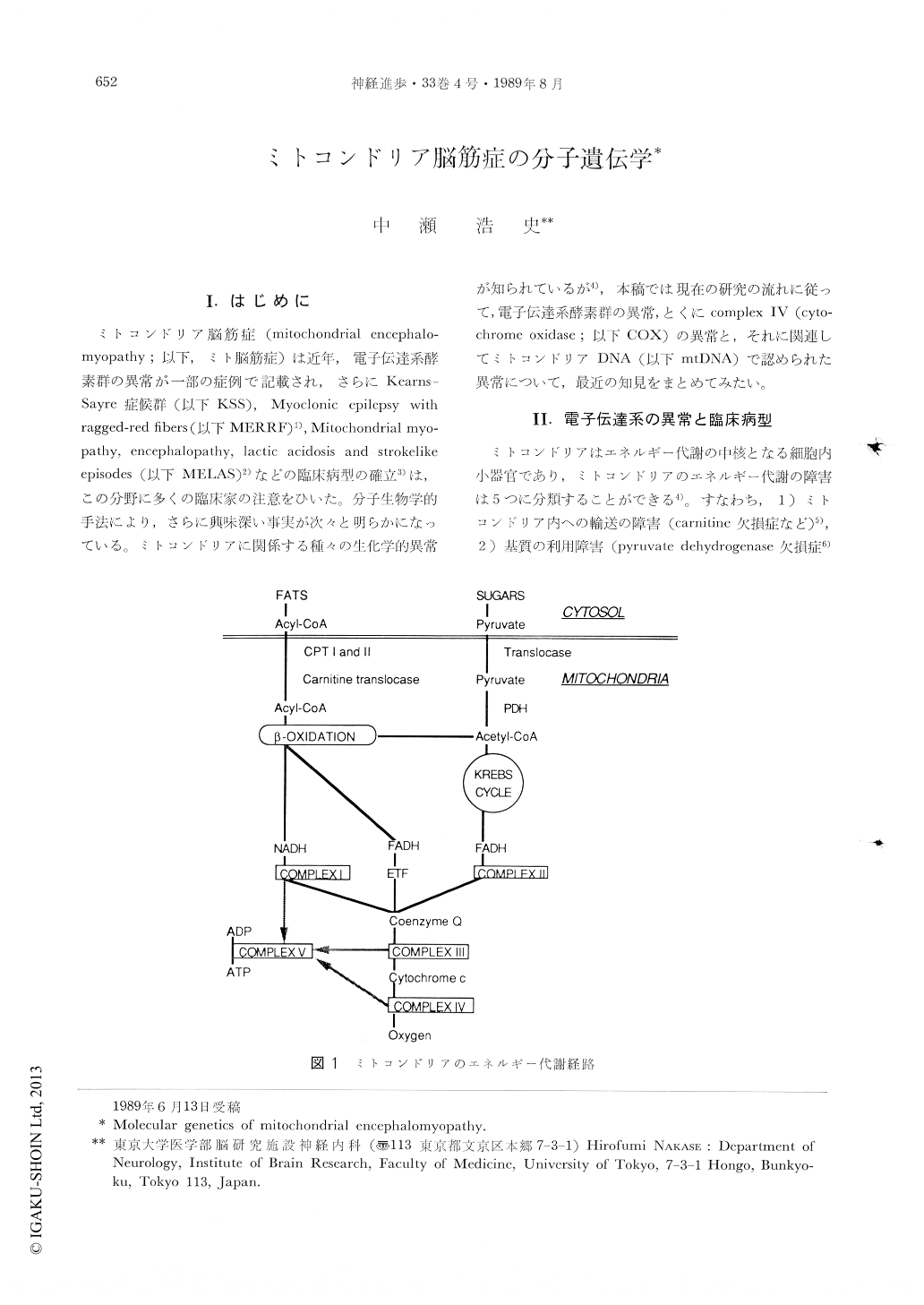
I.はじめに
ミトコンドリア脳筋症(mitochondrial encephalomyopathy;以下,ミト脳筋症)は近年,電子伝達系酵素群の異常が一部の症例で記記され,さらにKearns-Sayre症候群(以下KSS),Myoctonic epilepsy withraggedred fibers(以下MERRF)1),Mitochondriat myopathy,encephalopathy,lactic acidosis and strokelikeepisodes(以下MELAS)2)などの臨床病型の確立3)は,この分野に多くの臨床家の注意をひいた。分子生物学的手法により,さらに興味深い事実が次々と明らかになっている。ミトコンドリアに関係する種々の生化学的異常が知られているが4),本稿では現在の研究の流れに従って,電子伝達系酵素群の異常,とくにcomplex IV(cytochrome oxidase;以下COX)の異常と,それに関連してミトコンドリアDNA(以下mtDNA)で認められた異常について,最近の知見をまとめてみたい。
Disturbance of electron transport system, especially that of complex I, III and IV, has been described among a lot of cases of mitochondrial myopathy. Since mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) encodes 13 subunits of complex I, III, IV and V among some 65 subunits of those complexes, alteration of mtDNA has been studied as a possible cause of these enzymatic disturbance. Human mtDNA is a circular, double stranded 16.6 kb DNA whose sequence identifies 2 rRNA genes, 22 tRNA genes and 13 protein-coding regions, which encode COX I, II and III; ND1, 2, 3, 4, 4L, 5 and 6; and ATPase 6 and 8. mtDNA, which has unique sets of rRNAs and tRNAs, also has another genetic code that is different from the "universal" code. The replication of H-strand and L-strand of mtDNA proceeds from two different undirectional origins separated by 66 % of the genome. Human mtDNA is transcribed into a single polycistronic transcript, from which tRNAs are cleaved to release the rRNAs and mRNAs. High copy number, high mutation rate and cytoplasmic location are features of mtDNA that can explain the substantial different behavior of mitochondrial genes:
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


