Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
Ⅰ.序
人間では,circadian rhythmは,生後2,3週目頃より認められ1),6か月頃より安定するといわれている2)。また,睡眠中の逆説睡眠(PS)期出現のリズム,ultradian rhythmは,これより早くすでに胎生期より認められるといわれる3)。一方,動物実験において,この睡眠のリズム,とくに睡眠覚醒の調節に脳幹のmonoamine系が重要な役割を持つことが知られている4)。人間については,実験的にセロトニン代謝阻害剤を用いての不眠が知られているが5),カテコールアミン(CA)系代謝異常と睡眠との関係についてはあまり知られていない。
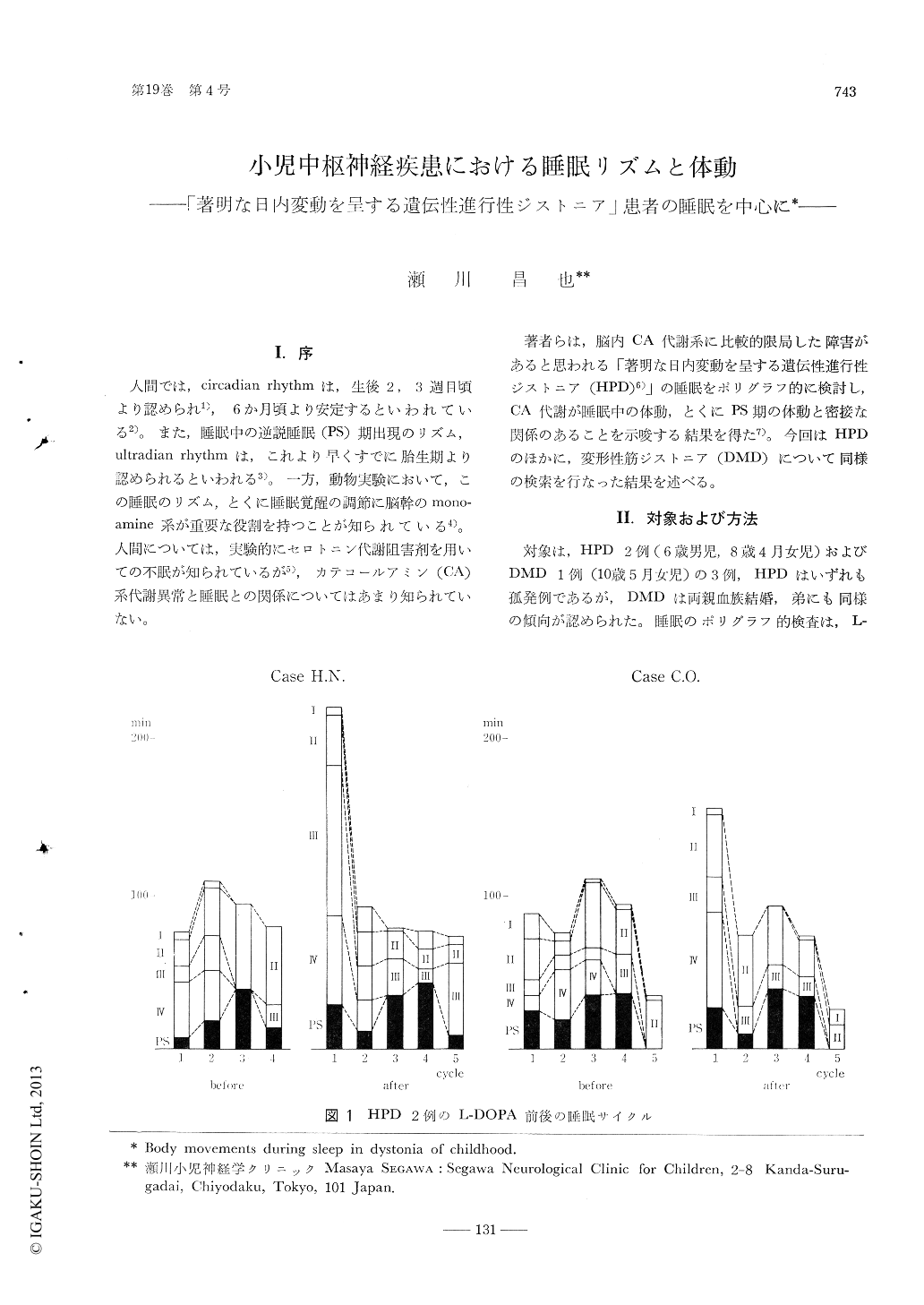
著者らは,脳内CA代謝系に比較的限局した障害があると思われる「著明な日内変動を呈する遺伝性進行性ジストニア(HPD)6)」の睡眠をポリグラフ的に検討し,CA代謝が睡眠中の体動とくにPS期の体動と密接な関係のあることを示唆する結果を得た7)。今回はHPDのほかに,変形性筋ジストニア(DMD)について同様の検索を行なった結果を述べる。
Examinations of body movements during sleepby polygraphical all night EEG studies were performed in two types of childhood hereditary deptonia before and after L-DOPA. One was "hereditary progressive deptonia with diurnal fluctuation (HPD)" and the other was dystonia musculorum deformans (DMD). The former is a hereditary dystonia with onset between three to nine years of age or younger. The trunk and limb muscles are involved with laterality but axial torsion and bulbar signs were very slight or absent.
Copyright © 1975, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


