Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
カエルのM.sartoriusにおける神経筋伝達の,筋伸長によつて起る促通について,細胞内電極を用いて調べた。
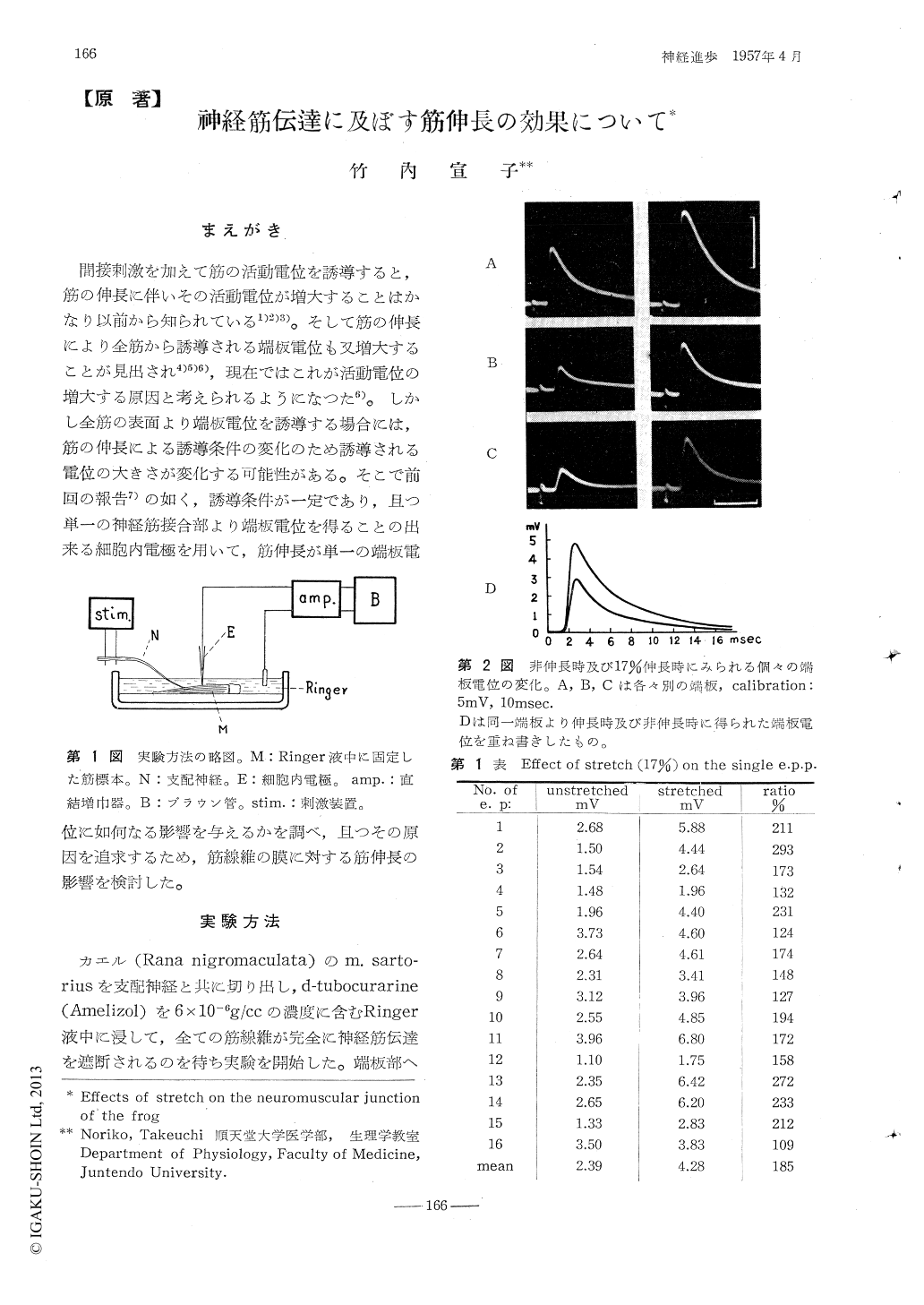
1.筋伸長による端板電位の増大の程度は個々の端板によりかなり異るが,何れの端板においても増大がみられ,17%伸長時の平均増大率は185%であつた。
2.端板電位発生の際,膜を通つて移動する荷電の量は伸長時著明に増し,その時間的経過には著変が認められない。
3.外液中に加えたacetylcholineに対する端板のsensidvityは伸長により変化しない。
4.端板部静止電位も伸長により変らない。
5.神経impulseに対する端板電位発生の確率を低下させた状態で非伸長時と伸長時を比較すると,伸長時著明にその確率が増す。
6.spontaneous miniature potentia1は伸長時頻度を増し,又大きさには著変がない。
7.筋伸長によつて起る端板電位の増大は,その原因の大部分が神経筋接合部の神経側にあり,神経末端からのtransmitterの遊離量が増大することに起因すると結論される。
The effects of stretch on the neuromuscularjunction of the curarized frog's sartorius musclewere studied with intracellular microelectrode.
1.Although the rate of increase in amplitudeof the individual end-plate potentials differed, themean value of the 17% stretched muscle was 185%.
2.The electric charge which was transfered acro-ss a curarized end-plate was remarkably increasedby stretching the muscle,but the change in itstime course was not detected.
3.The sensitivity to externaly applied acetylcho-line was not changed by lengthening the muscle.
4.In preparations treated with low Ca++ andheigh Mg++ Ringer's solution,the probability ofresponses was increased by stretching the muscle.
5.The frequency of the spontaneous miniatureend-plate potentials was remarkably increased bystretching the muscle.
6.It may be concluded that stretch of the mus-cle causes the increase in output of acetylcholinereleased at nerve ending of the neuromuscularjunction.
Copyright © 1957, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


