Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
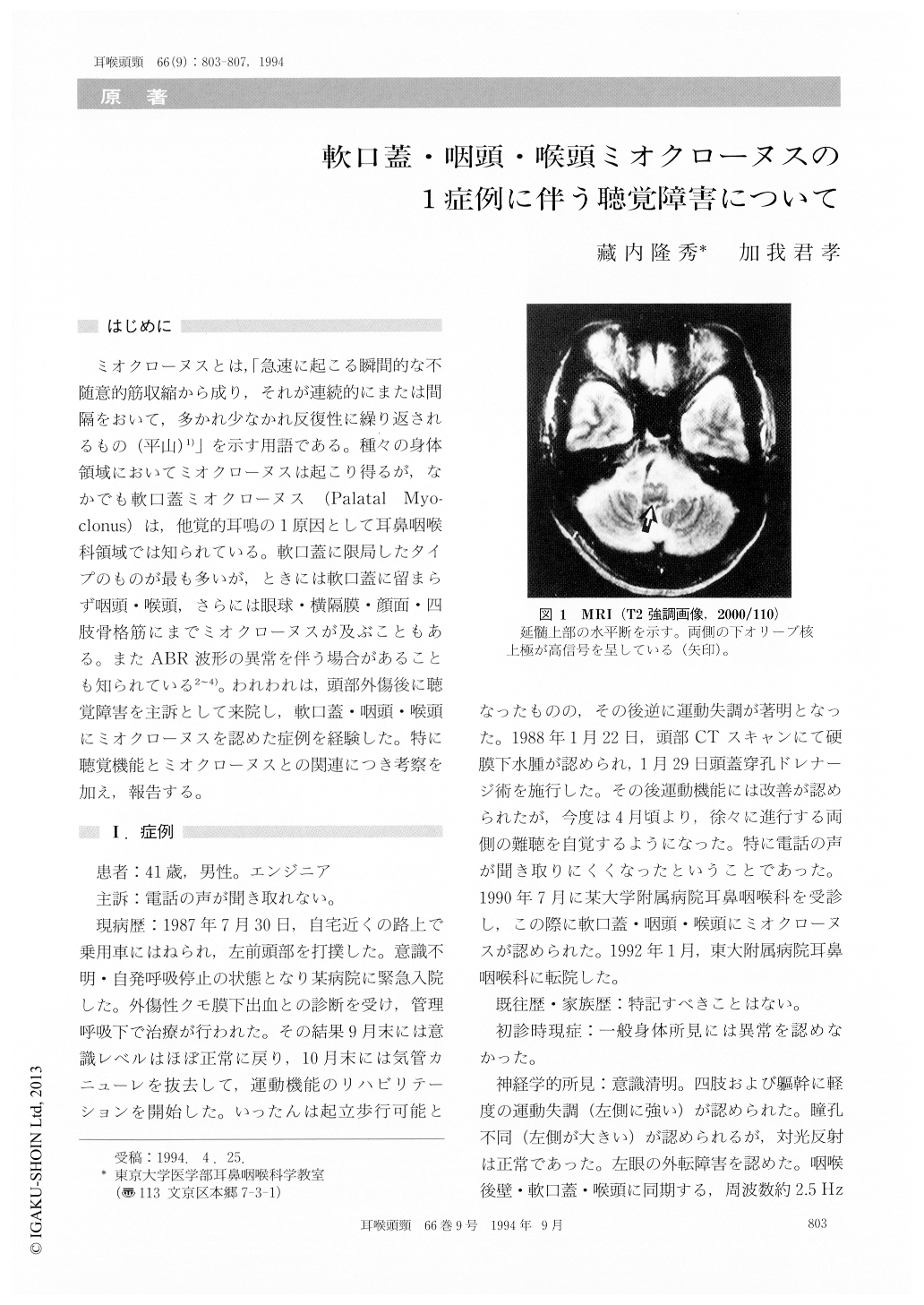
ミオクローヌスとは,「急速に起こる瞬間的な不随意的筋収縮から成り,それが連続的にまたは間隔をおいて,多かれ少なかれ反復性に繰り返されるもの(平山)1)」を示す用語である。種々の身体領域においてミオクローヌスは起こり得るが,なかでも軟口蓋ミオクローヌス(Palatal Myo-clonus)は,他覚的耳鳴の1原因として耳鼻咽喉科領域では知られている。軟口蓋に限局したタイプのものが最も多いが,ときには軟口蓋に留まらず咽頭・喉頭,さらには眼球・横隔膜・顔面・四肢骨格筋にまでミオクローヌスが及ぶこともある。またABR波形の異常を伴う場合があることも知られている2〜4)。われわれは,頭部外傷後に聴覚障害を主訴として来院し,軟口蓋・咽頭・喉頭にミオクローヌスを認めた症例を経験した。特に聴覚機能とミオクローヌスとの関連につき考察を加え,報告する。
A 41-year-old man, who manifested palato-phar-yngo-laryngeal myoclonus and hearing disturbance secondary to head trauma, was audiologically stud-ied. MRI showed a high intensity signal in thebilateral inferior olivary complex. Pure tone audiometry was almost normal, but ABRs showed a low amplitude of wave V bilaterally. The dichotic listening test revealed a decrease with the scores in both ears. The interaural time difference discrimina-tion test showed negative result.
These results suggested that the lesion around the triangle of Guillain-Mollaret, which is located near the auditory brainstem pathway, could result in abnormal perception of hearing in this case.
Copyright © 1994, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


