Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.緒言
白内障手術時に眼内圧を下降させておく為に,眼球に指圧を加えることはroutineの処置として現在広く行われているが,眼球に加える圧迫をどの程度にしたらよいかを知る為に,一つの試みとして,普通それ程きつくない状態として500gの圧迫を5分間加えたときには,圧迫除去後90分でも圧迫前の眼内圧に迄戻らない,又少くとも45分間は10mmHg以下の値が保たれることを前の実験5)で明かにされた。
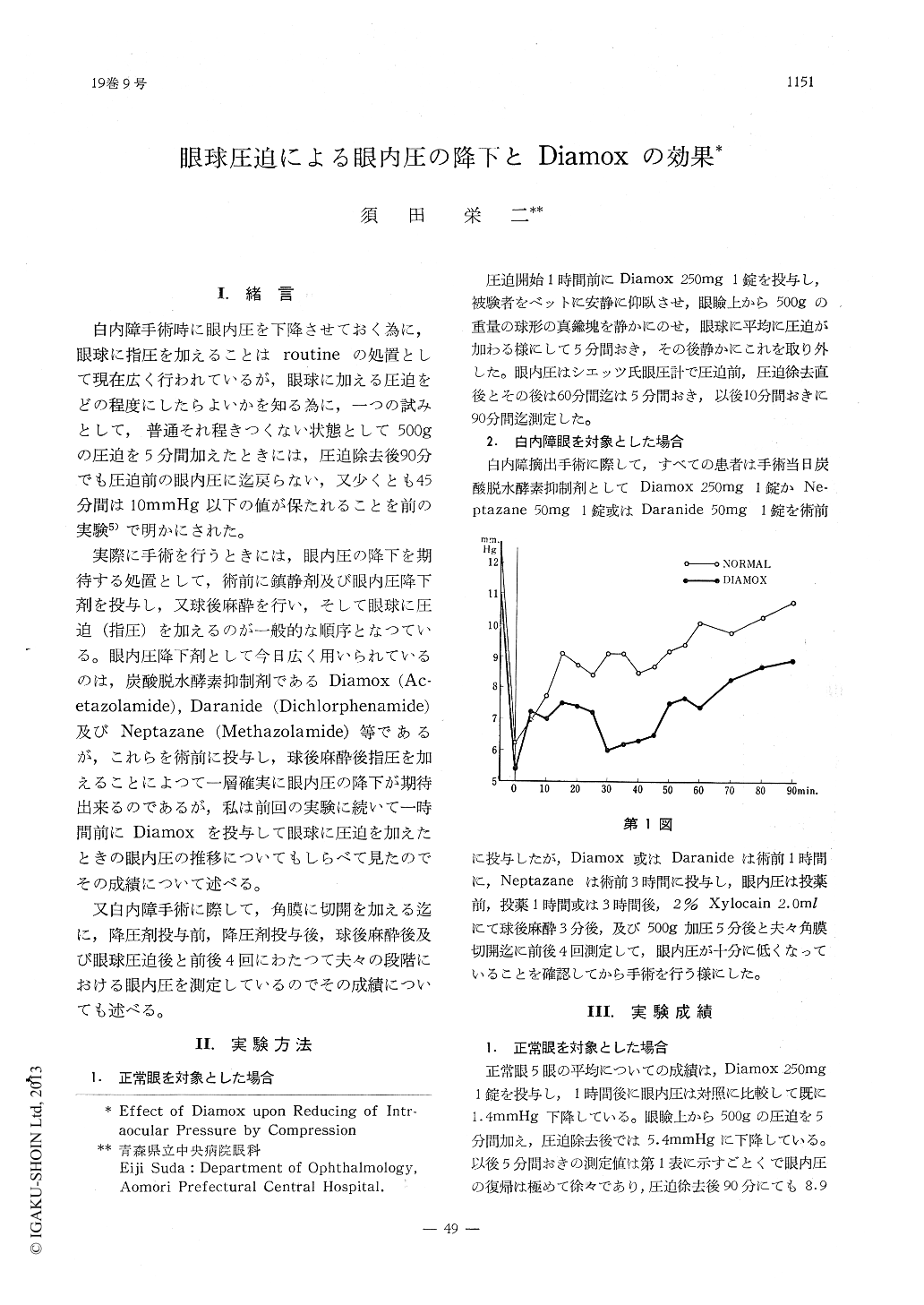
実際に手術を行うときには,眼内圧の降下を期待する処置として,術前に鎮静剤及び眼内圧降下剤を投与し,又球後麻酔を行い,そして眼球に圧迫(指圧)を加えるのが一般的な順序となつている。眼内圧降下剤として今日広く用いられているのは,炭酸脱水酵素抑制剤であるDiamox (Ac—etazolamide),Daranide (Dichlorphenamide)及びNeptazane (Methazolamide)等であるが,これらを術前に投与し,球後麻酔後指圧を加えることによつて一層確実に眼内圧の降下が期待出来るのであるが,私は前回の実験に続いて一時間前にDiamoxを投与して眼球に圧迫を加えたときの眼内圧の推移についてもしらべて見たのでその成績について述べる。
The intraocular pressure is reduced to an average of 5.4mm. Hg. in normal subject byplacing a metal block of 500Gm. for 5 minu-tes upon the palpebrae after 1 hour of the administration of Diamox 250mg. and returns slowly to the initial level, but reaches at only 8.9mm. Hg. even after 90 minutes. The reduc-ing rate is distinctly remarkable as compared with control.
In cataract eyes, the intraocular pressure is also reduced to an average of 5.4mm. Hg. by the administration of Diamox with the retrobulbar anesthesia and the ocular compre-ssion. And the rate of reducing shows an average of 64.5% to the initial level.
Copyright © 1965, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


