Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
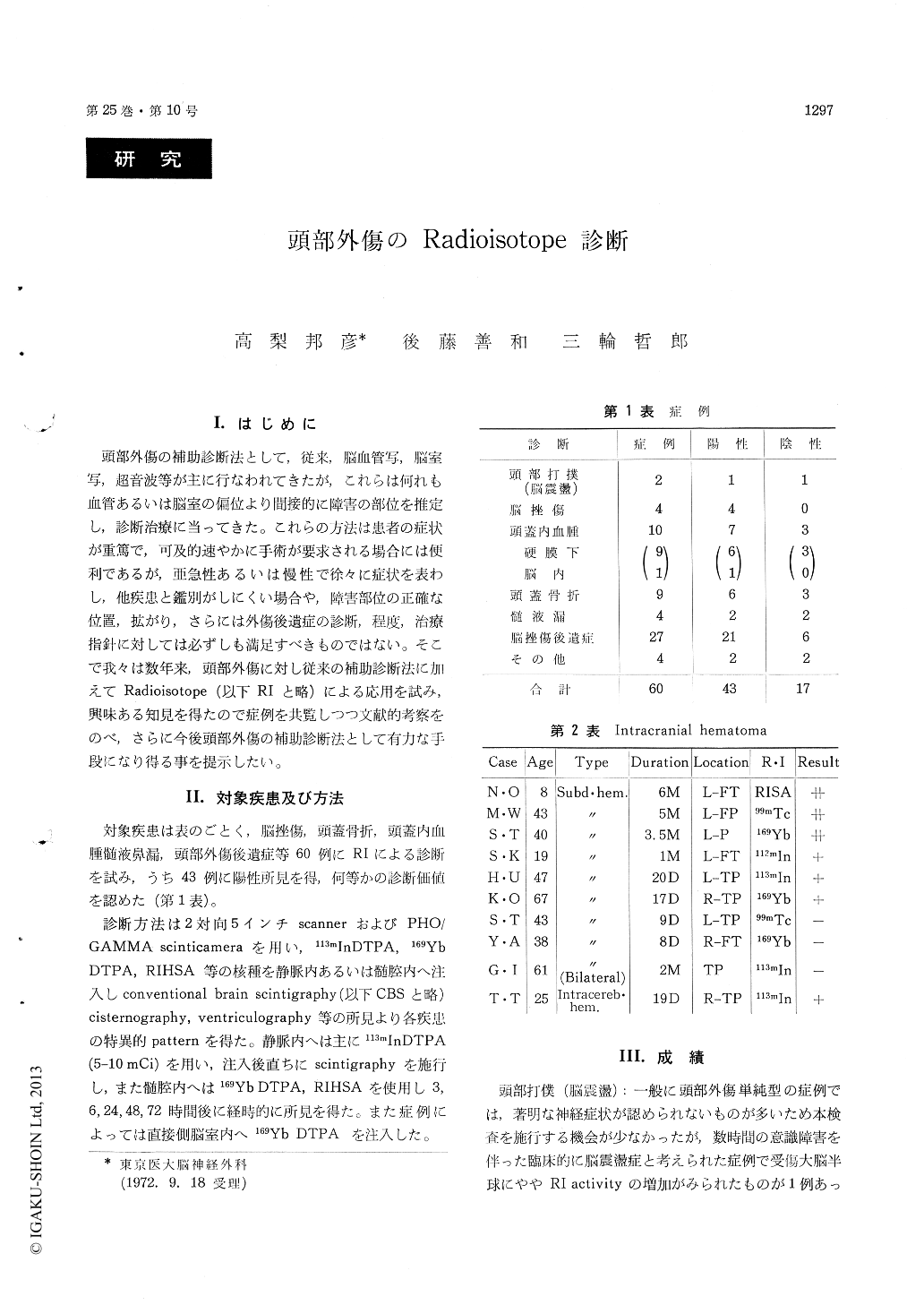
頭部外傷の補助診断法として,従来,脳血管写,脳室写,超音波等が主に行なわれてきたが,これらは何れも血管あるいは脳室の偏位より間接的に障害の部位を推定し,診断治療に当ってきた。これらの方法は患者の症状が重篤で,可及的速やかに手術が要求される場合には便利であるが,亜急性あるいは慢性で徐々に症状を表わし,他疾患と鑑別がしにくい場合や,障害部位の正確な位置,拡がり,さらには外傷後遺症の診断,程度,治療指針に対しては必ずしも満足すべきものではない。そこで我々は数年来,頭部外傷に対し従来の補助診断法に加えてRadioisotope (以下RIと略)による応用を試み,興味ある知見を得たので症例を共覧しつつ文献的考察をのべ,さらに今後頭部外傷の補助診断法として有力な手段になり得る事を提示したい。
As a method of diagnosis in head injury, cerebral angiography, pneumoencephalography, and echo-encephalography have mainly been employed. These methods are convenient in acute type re-quiring emergency operation but are not sufficient for subacute or chronic type with complicated pathological state. In the present study, we have therefore applied methods using radioisotopes (con-ventional brain scintigraphy, cisternography and ventriculography) in addition to these conven-tional methods in 60 cases of brain contusion, skull fracture, intracranial hematoma, CSF rhinorrhea and posttraumatic disorder and obtained some interesting results. Rate of positive diagnosis of more 90% was obtained in intracranial hematoma and these tests were found to be effective in thin hematoma with difficulty in diagnosis even by angiography. As to the mechanism of radioisotope accumulation, discussions were made based on oper-ative finding and cases reported in the literature.
In cases with skull fracture, the results of the tests were correlated with clinical picture such as convulsion and hemiparesis. In operative finding, adhesion and cyst formation were noted in there.
In posttraumatic disorder, severity of the disease was classified into three grade according to the time of suffering from injury and clinical finding. RI tests finding specific to each grade were reported. Especially normal pressure hydrocephalus was classified into three types from the viewpoint of RI ventricular clearance and shunt operation was decided.
Copyright © 1973, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


