Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
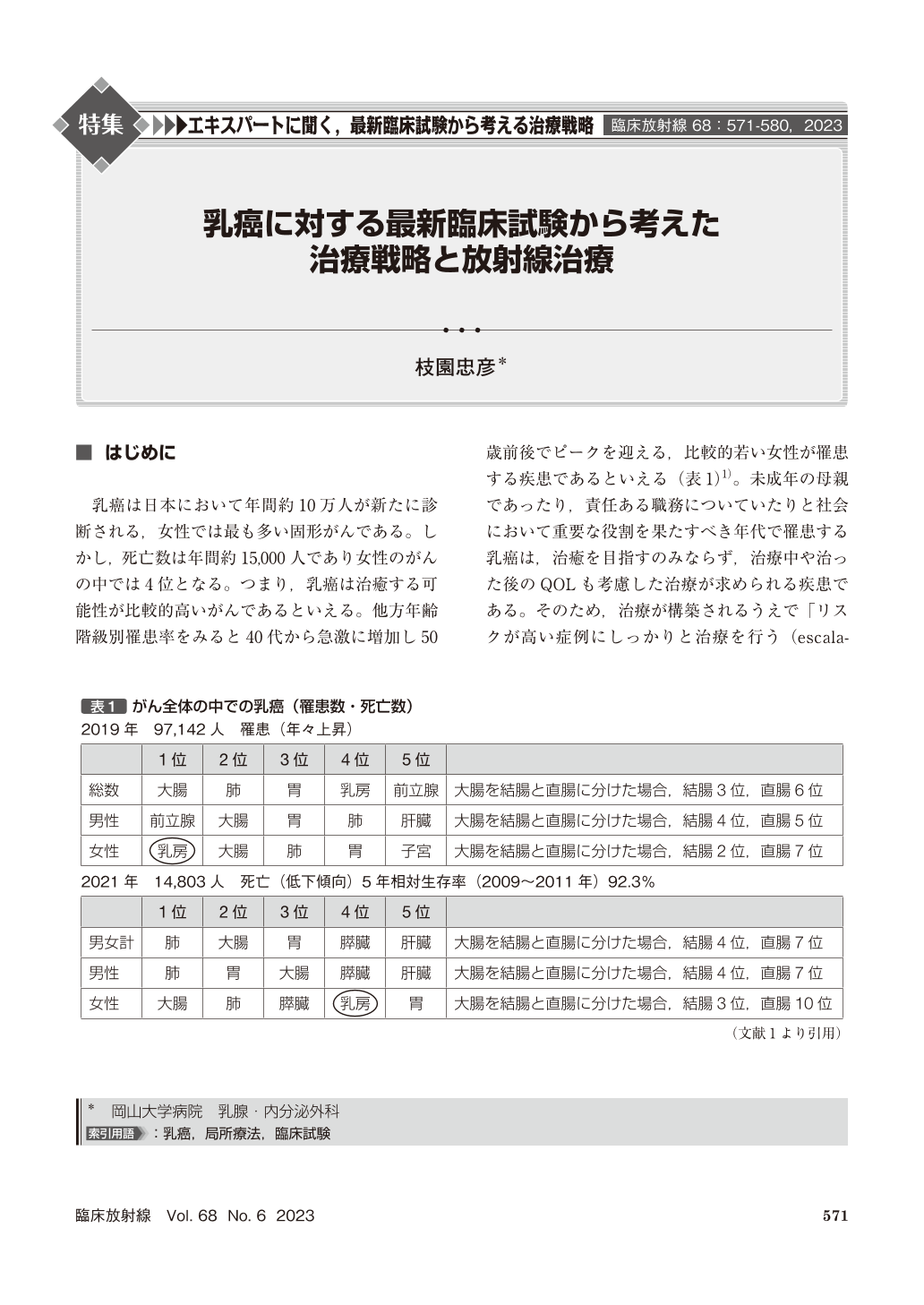
乳癌は日本において年間約10万人が新たに診断される,女性では最も多い固形がんである。しかし,死亡数は年間約15,000人であり女性のがんの中では4位となる。つまり,乳癌は治癒する可能性が比較的高いがんであるといえる。他方年齢階級別罹患率をみると40代から急激に増加し50歳前後でピークを迎える,比較的若い女性が罹患する疾患であるといえる(表1)1)。未成年の母親であったり,責任ある職務についていたりと社会において重要な役割を果たすべき年代で罹患する乳癌は,治癒を目指すのみならず,治療中や治った後のQOLも考慮した治療が求められる疾患である。そのため,治療が構築されるうえで「リスクが高い症例にしっかりと治療を行う(escalation)」と「リスクの低い症例には治療を軽減する(de-escalation)」の考えが重要視される。特に早期乳癌ではde-escalationが,転移乳癌ではescalation治療の流れが認められる。
Breast cancer treatment consists of multidisciplinary treatment with surgery, radiation therapy, and systemic therapy. The significance and role of local therapy are changing with the progress of each therapy. It is necessary to provide optimal multidisciplinary treatment that considers the biology of breast cancer and the degree of progression and that does not over- or under-treat the patient’s wishes. It is important to continue accumulating evidence by verifying each in clinical studies.
Copyright © 2023, KANEHARA SHUPPAN Co.LTD. All rights reserved.