Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
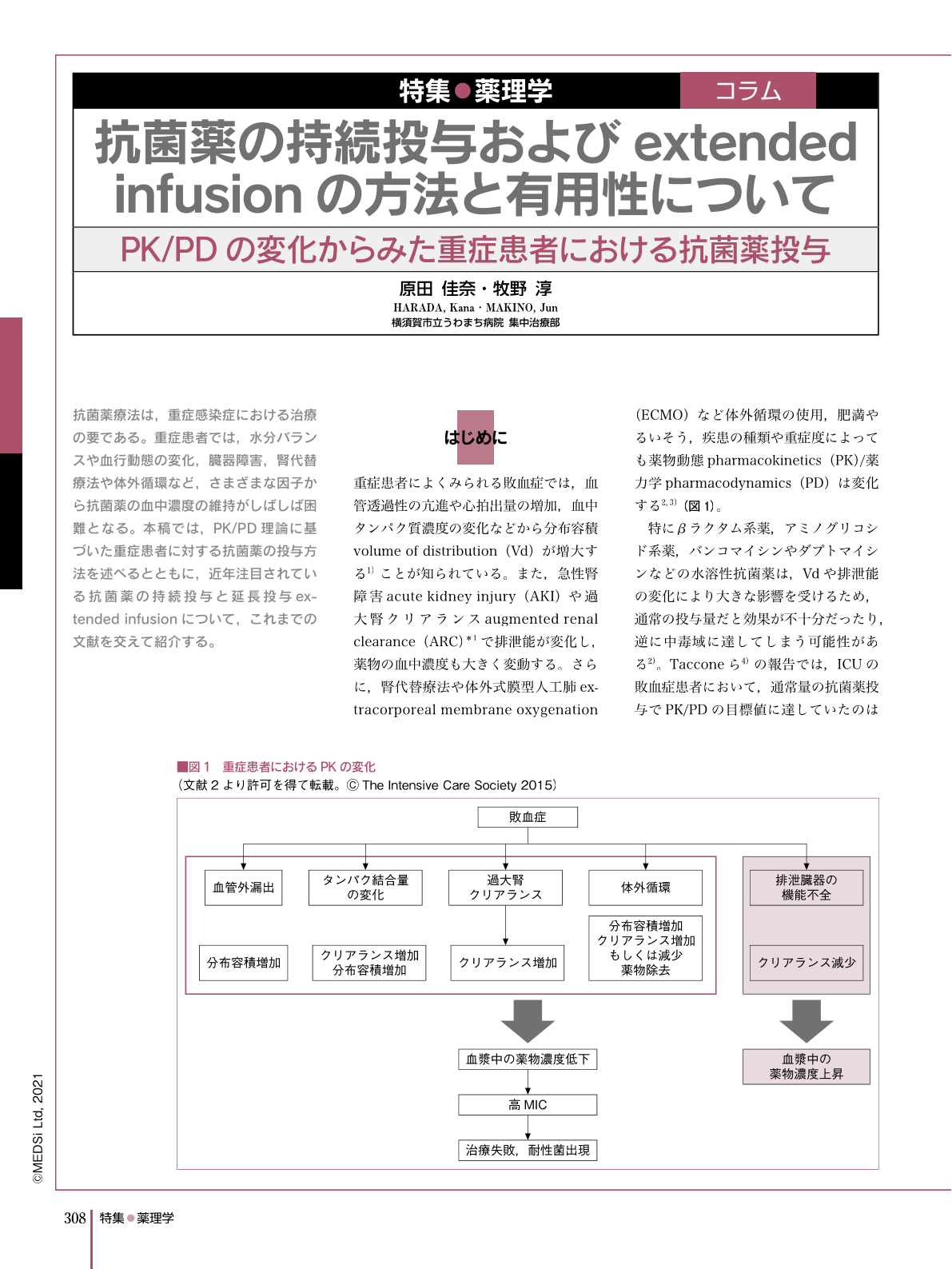
抗菌薬療法は,重症感染症における治療の要である。重症患者では,水分バランスや血行動態の変化,臓器障害,腎代替療法や体外循環など,さまざまな因子から抗菌薬の血中濃度の維持がしばしば困難となる。本稿では,PK/PD理論に基づいた重症患者に対する抗菌薬の投与方法を述べるとともに,近年注目されている抗菌薬の持続投与と延長投与extended infusionについて,これまでの文献を交えて紹介する。
Continuous or prolonged administration of antimicrobial agents has attracted attention in critically ill patients for whom drug administration design is complicated by significant changes in PK-PD. Beta-lactam antibiotics are antimicrobial agents using time over MIC as an index, which was significantly higher with continuous or extended administration than with intermittent administration. Although there was no significant difference in mortality, the French guidelines recommend that critically ill patients receive continuous or extended administration of beta-lactam antibiotics based on TDM data. There are reports that continuous administration of vancomycin was less nephrotoxic than intermittent administration. One possible explanation is that intermittent administration which aims at a high trough value leads to nephrotoxicity. Evidence for the efficacy of continuous administration based on AUC/MIC is expected to accumulate in the future.
Copyright © 2021, MEDICAL SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, LTD. All rights reserved.


