Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
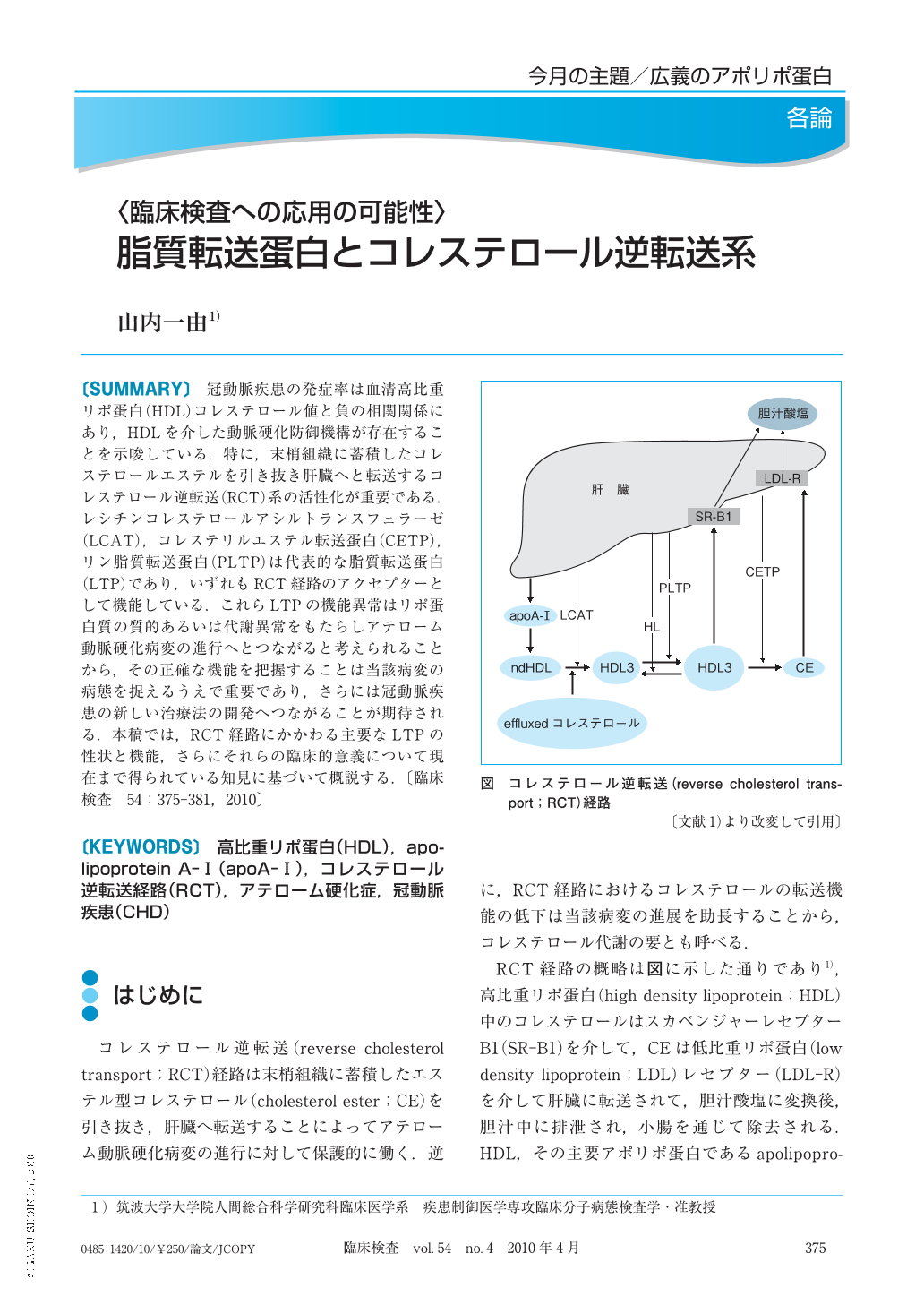
冠動脈疾患の発症率は血清高比重リポ蛋白(HDL)コレステロール値と負の相関関係にあり,HDLを介した動脈硬化防御機構が存在することを示唆している.特に,末梢組織に蓄積したコレステロールエステルを引き抜き肝臓へと転送するコレステロール逆転送(RCT)系の活性化が重要である.レシチンコレステロールアシルトランスフェラーゼ(LCAT),コレステリルエステル転送蛋白(CETP),リン脂質転送蛋白(PLTP)は代表的な脂質転送蛋白(LTP)であり,いずれもRCT経路のアクセプターとして機能している.これらLTPの機能異常はリポ蛋白質の質的あるいは代謝異常をもたらしアテローム動脈硬化病変の進行へとつながると考えられることから,その正確な機能を把握することは当該病変の病態を捉えるうえで重要であり,さらには冠動脈疾患の新しい治療法の開発へつながることが期待される.本稿では,RCT経路にかかわる主要なLTPの性状と機能,さらにそれらの臨床的意義について現在まで得られている知見に基づいて概説する.
Many studies demonstrated that the incidences of coronary heart disease, accompanied by atherosclerotic vascular disease, are negatively correlated with serum high density lipoprotein(HDL)cholesterol levels;therefore, HDL plays a protective role against atherosclerosis in blood vessels. In particular, reverse cholesterol transport(RCT)is the most important pathway by which accumulated cholesterol is delivered from the peripheral tissues to the liver for excretion, thus preventing atherosclerosis. Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase(LCAT), cholesterol ester transfer protein(CETP), and phospholipid transfer protein(PLTP)are the major lipid transfer protein(LTP). As well as HDL and apolipoprotein AI, these LTPs are the crucial constituents of RCT, and play the role as acceptor for this pathway. Because the functional abnormalities of these LTPs and its related abnormalities I the lipoprotein metabolism are considered to be lead to the progression of atherosclerosis lesions, understanding the actual function of these LTPs on the development of atherosclerosis can help clarify those pathophysiological mechanism of atherosclerosis, and provide new therapeutic approaches to atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. This review presents the state of knowledge on the properties, function, and clinical significance of these LTPs in the RCT pathway.
Copyright © 2010, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.