Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
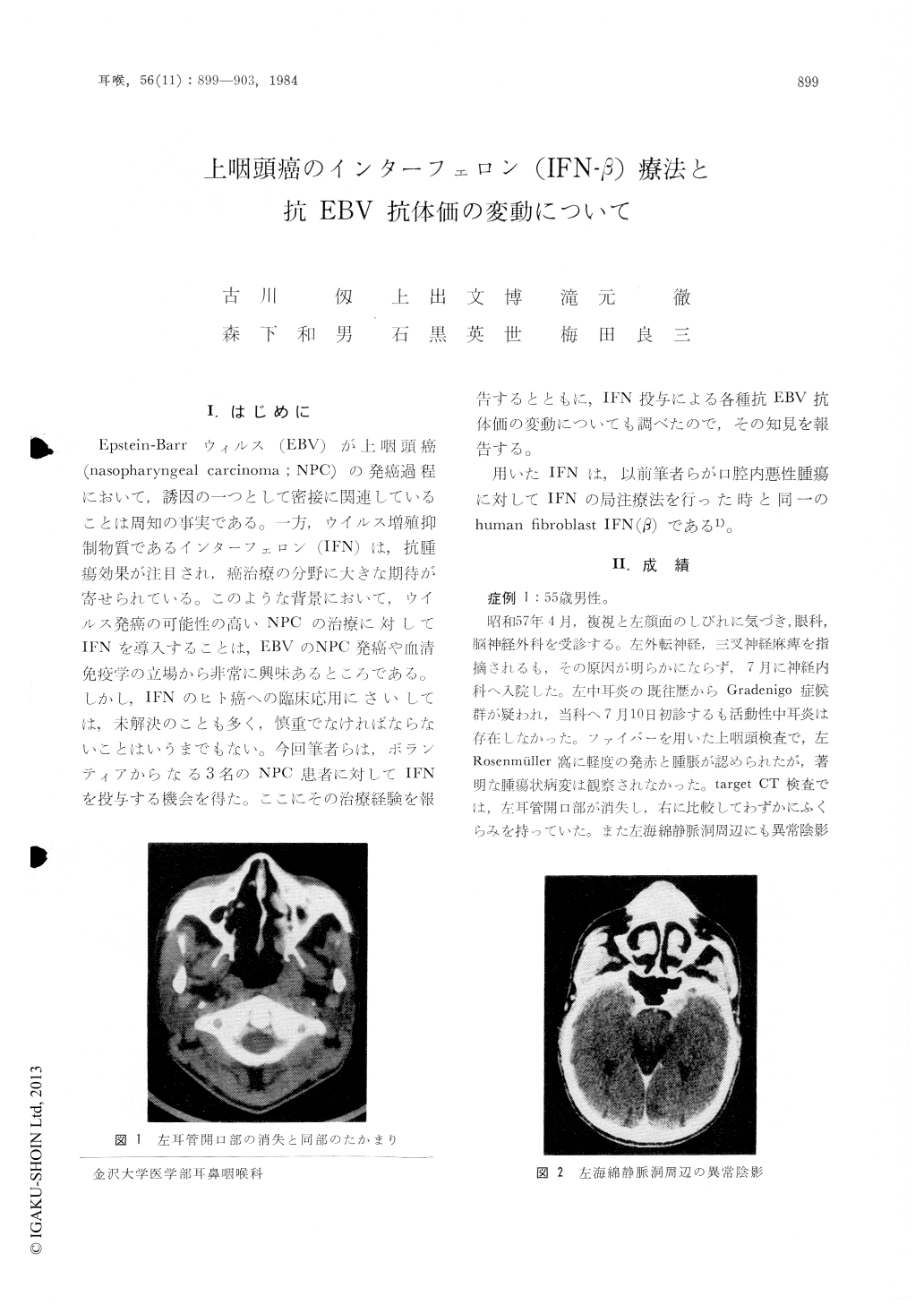
I.はじめに
Epstein-Barrウィルス(EBV)が上咽頭癌(nasopharyngeal carcinoma;NPC)の発癌過程において,誘因の一つとして密接に関連していることは周知の事実である。一方,ウイルス増殖抑制物質であるインターフェロン(IFN)は,抗腫瘍効果が注目され,癌治療の分野に大きな期待が寄せられている。このような背景において,ウイルス発癌の可能性の高いNPCの治療に対してIFNを導入することは,EBVのNPC発癌や血清免疫学の立場から非常に興味あるところである。しかし,IFNのヒト癌への臨床応用にさいしては,未解決のことも多く,慎重でなければならないことはいうまでもない。今回筆者らは,ボランティアからなる3名のNPC患者に対してIFNを投与する機会を得た。ここにその治療経験を報告するとともに,IFN投与による各種抗EBV抗体価の変動についても調べたので,その知見を報告する。
用いたIFNは,以前筆者らが口腔内悪性腫瘍に対してIFNの局注療法を行った時と同一のhuman fibroblast IFN(β)である1)。
The purpose of this study is to determine the efficiency of human fibroblast interferon (IFN-β)in the treatment of NPC and its effect on IgG and IgA anti-EBV viral capsid antigen (VCA), IgA and IgA early antigen (EA). Three patients with NPC were studied. Fibroblast IFN was given at a dose from 1×106 to 10×106 units from 2 to 7 times a week by 60 min intravenous infusion.
No complete remission was obtained, and in 2 patients the effect was considered to be NC, and in the other was PD.
The anti-EBV serologic tests monitored before, during, and after treatment showed no change. It was considered that IFN had some activity against NPC but no effect on EBV serology.
Copyright © 1984, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


