Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
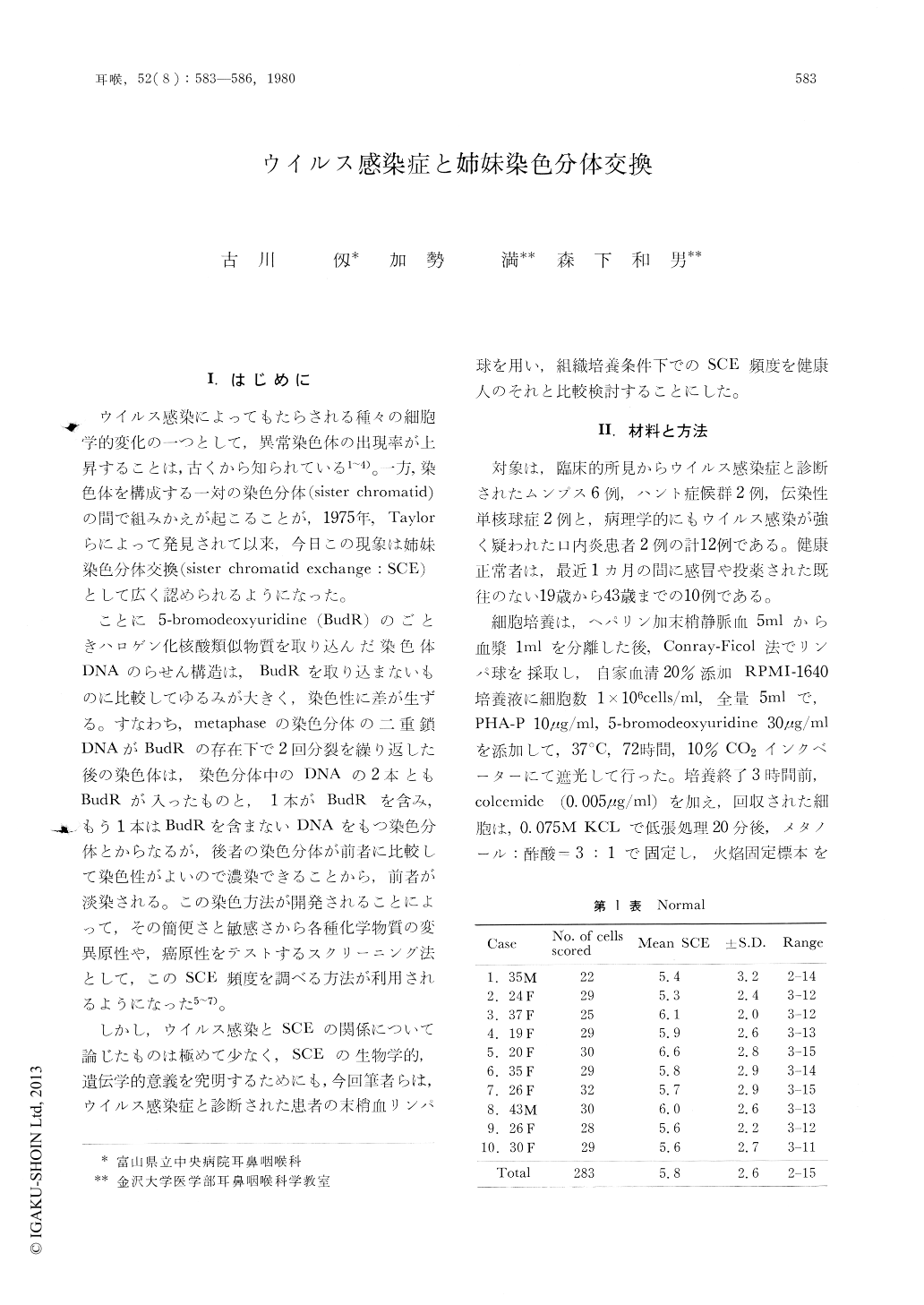
ウイルス感染によってもたらされる種々の細胞学的変化の一つとして,異常染色体の出現率が上昇することは,古くから知られている1〜4)。一方,染色体を構成する一対の染色分体(sister chromatid)の間で組みかえが起こることが,1975年,Taylorらによって発見されて以来,今日この現象は姉妹染色分体交換(sister chromatid exchange:SCE)として広く認められるようになった。
ことに5-bromodcoxyuridine(BudR)のごときハロゲン化核酸類似物質を取り込んだ染色体DNAのらせん構造は,BudRを取り込まないものに比較してゆるみが大きく,染色性に差が生ずる。すなわち,metaphaseの染色分体の二重鎖DNAがBudRの存在下で2回分裂を繰り返した後の染色体は,染色分体中のDNAの2本ともBudRが入ったものと,1本がBudRを含み,もう1本はBudRを含まないDNAをもつ染色分体とからなるが,後者の染色分体が前者に比較して染色性がよいので濃染できることから,前者が淡染される。この染色方法が開発されることによって,その簡便さと敏感さから各種化学物質の変異原性や,癌原性をテストするスクリーニング法として,このSCE頻度を調べる方法が利用されるようになった5〜7)。
The frequency of sister chromatid exchange(SCE) in peripheral lymphocytes derived from patients with viral diseases was examined in order to know the cytological effects induced by viral infections. The mean frequency of SCE from 283 metaphases in the normal healthy subjects was 5.8±2.6 and those of such viral disease, as mumps, Hunt's syndrome, infectious mononucleosis and probably viral stomatitis which were diagnosed by clinical findings, indicated 9.7±5.1, 9.7±5.0, 9.4± 4.3 and 5.5±2.6 respectively. These results suggested that viruses induce SCE, and the further studies will be required to clarify the mechanisms in which viruses may induce SCE.
Copyright © 1980, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


