Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
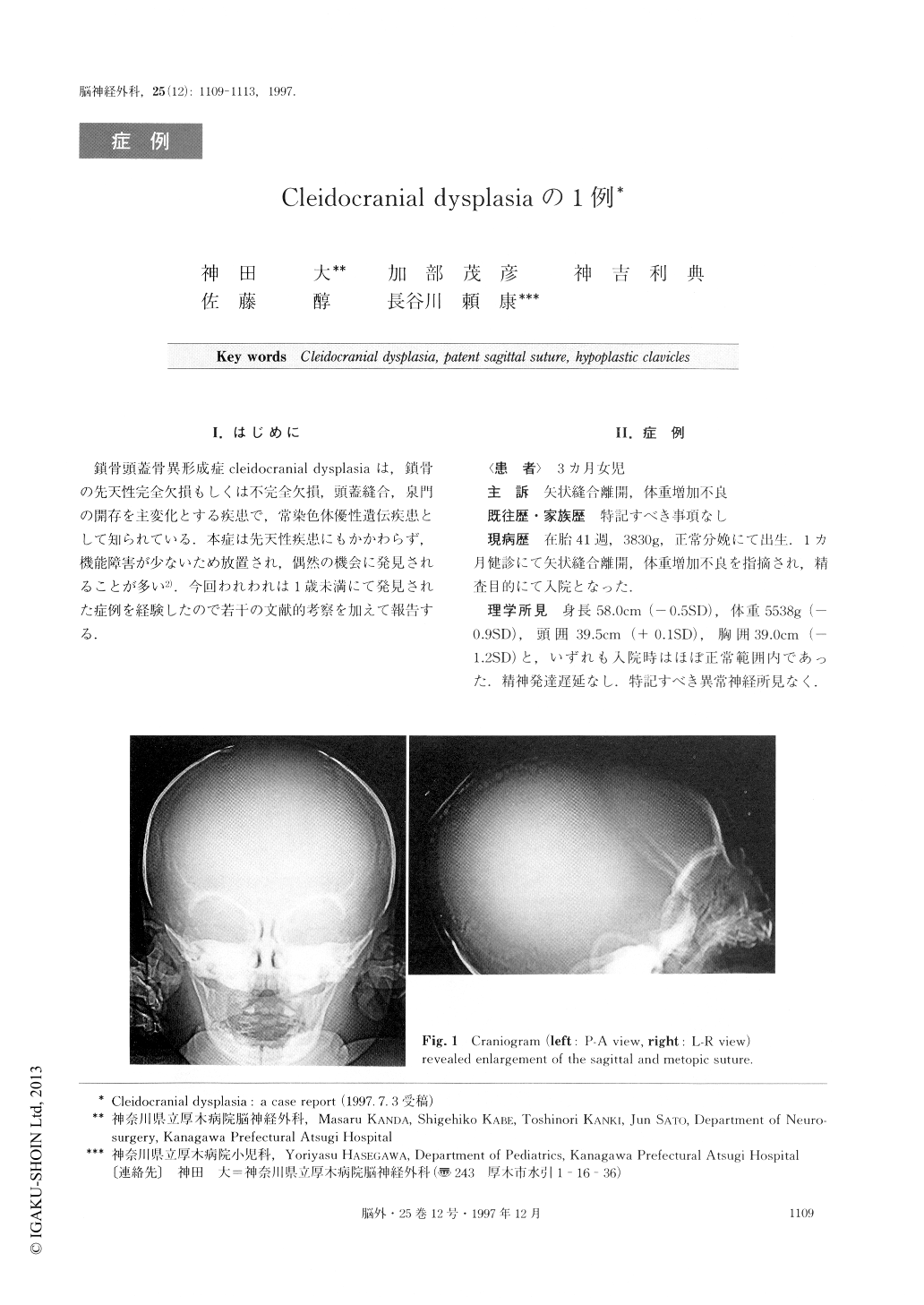
鎖骨頭蓋骨異形成症cleidocranial dysptasiaは,鎖骨の先天性完全欠損もしくは不完全欠損,頭蓋縫合,泉門の開存を主変化とする疾患で,常染色体優性遺伝疾患として知られている.本症は先天性疾患にもかかわらず,機能障害が少ないため放置され,偶然の機会に発見されることが多い2).今回われわれは1歳未満にて発見された症例を経験したので若干の文献的考察を加えて報告する。
A 3-month-old female infant who presented with pa-tent sagittal suture and loss of weight is described. Physical examination revealed a large sagittal and metopic suture showing delayed closure, a high-arched palate, saddle nose, hypertelorism and nonpalpable edges of the bilateral clavicles. The clavicles also showed undue mobility. Radiological investigations of the cranial skeletal abnormalities revealed enlargement of the sagittal and metopic sutures, and the anterior and posterior fontanelles. A chest radiograph showed a small, bell-shaped thoracic rib cage with partial aplasia of both clavicles. On the basis of the clinical findings, cleidocranial dysplasia was diagnosed.
Cleidocranial dysplasia is an uncommon generalized skeletal disorder which, as its name implies, shows striking involvement of the cranial vault and clavicles. The clinical features reflect a generalized defect of both membranous and endochondral bone formation. It is characterized by delayed ossification of the skull, aplas-tic or hypoplastic clavicles, delayed deciduous dentition, and hereditary characteristics. The amount of calvarial growth is generally small, and the shape remains nearly unaltered. In all cases, calvarial bone thickness in-creases with age, but in the midline, the fontanelle area, which is shown to be defective at the first examination, remains open in all cases. The midfrontal area is poorly developed and exhibits a groove in many patients. It is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, with wide variability of expression but a high degree of pene-trance. Cytogenetic abnormalities involving chromo-some 6p21 have been reported with a cleidocranial dys-plasia phenotype.
Although psychosocial disorders associated with the abnormal facial and body features may occur, patients have a good overall prognosis and life expectancy. Skull deformity, and delayed closure of the fontanelles and cranial sutures are the most important problems for neurosurgeons. The postero-lateral fontanelle closes be-fore adulthood, whereas the opening in the midfrontal sutural area may persist. Many children with cleidocra-nial dysplasia whom we have encountered have persist-ing fontanelles and patent sutures, but this does not seem to predispose them to an abnormal calvarial growth pattern, at least in the age groups investigated. Congenital midface retrusion in the presence of relative or absolute mandibular prognathism is also a major de-formity.
Care is supportive, including attention to neurosur-gical, orthopedic, pediatric and dental problems.
Copyright © 1997, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


