Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
arachnoid cystは,全頭蓋内space occupying lesionの1%に見られるに過ぎない.特にintrasellar regionに発生するarachnoid cystは非常に稀で,トルコ鞍部に発生するpituitary adenomaをはじめ,craniopharyn—gioma,empty sella,Rathke's cleft cyst,epidermoidなどとの鑑別が重要である.今回われわれは,頭痛ならびに視野障害にて発症した症例を経験したので報告する.また,intrasellar arachnoid cystの臨床像,検査法,治療法,ならびにその発生機序について若干の文献的考察を加える.
Intrasellar arachnoid cyst is very rare. We report a case of intrasellar arachnoid cyst.
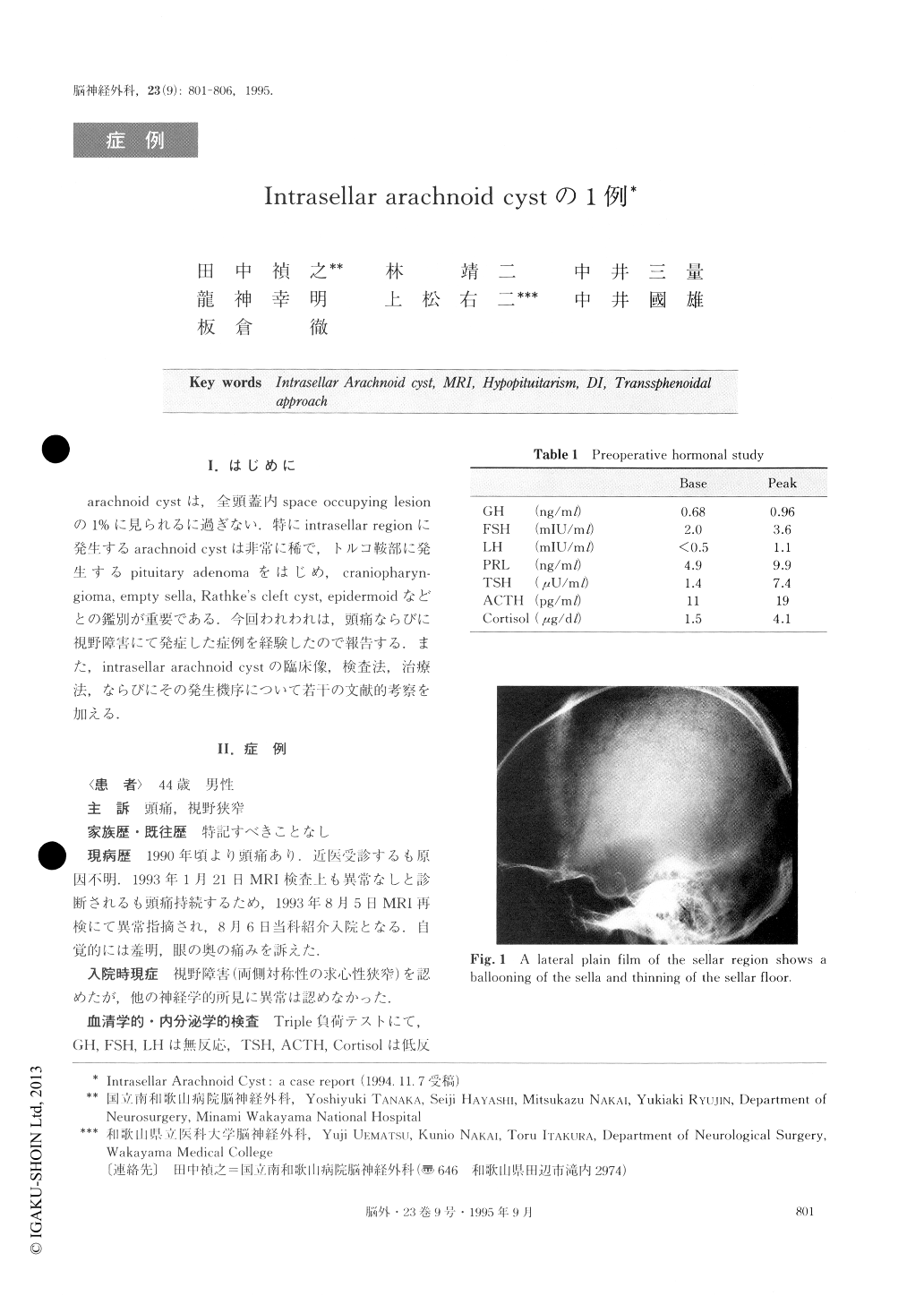
A 44-year-old male was admitted for evaluation of his headache and visual disturbance on August 6, 1993.Neurological examination revealed bilateral decreased visual acuity and visual field defect. Endocrinological examination showed panhypopituitarism. Other neuro-logical findings were normal. X-ray film of the skull showed a ballooning dilation of the sella turcica with thinning of the sellar floor. CT scan showed a cystic le-sion with CSF-density occupied the sella. After in-travenous administration of contrast medium, the cyst showed no enhancement. MRI showed the intrasellar mass had the same characteristics as the surrounding subarachnoid space. Bilateral carotid angiographies de-monstrated that the carotid siphons were stretched and displaced laterally, and the A1 portions of the anterior cerebral arteries were raised. We made a diagnosis of intrasellar cystic lesion. On August 18, the sella turcica was opened via the transsphenoidal rhinoseptal approach. The cyst contained CSF-like fluid, and a part of the cyst wall was resected. The cavity was filled with Gelfoam and the sellar floor was repaired with bone flap. Postoperarively, the patient's visual disturb-ance improved, but diabetis insipidus appeared and re-quired hormonal replacement. The patient was dis-charged on September 27 with improvement of visual acuity and visual field. Histological examination demon-strated that the cyst wall consisted of thick arachnoidal cells with fibrous connective tissue. The arachnoidal cells with oval nuclei was stained with epithelial memb-rane antigen.
Symptoms, signs and radiological findings of intra-sellar arachnoid cyst are similar to those of various sel-lar lesions including pituitary adenoma, craniopharyn-gioma, empty sella, Rathke's cleft cyst, epidermoid et al. Intrasellar arachnoid cyst can be suitably treated by a transsphenoidal approach. The indications for trans-sphenoidal exploration include the following: to relieve the compression to the optic chiasm, the pituitary stalk or gland, and to exclude the possibility of other sellar neoplasms.
Clear differentiation between a true intrasellar arach-noid cyst and arachnoid diverticulum is difficult with-out complete histological examination of the cyst. In this case we presumed that the cyst was arachnoid di-verticulum originated from empty sella because of the radiological appearance and surgical findings. This is the first case to demonstrate with MRI the natural course of the intrasellar arachnoid cyst.
Copyright © 1995, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


