Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
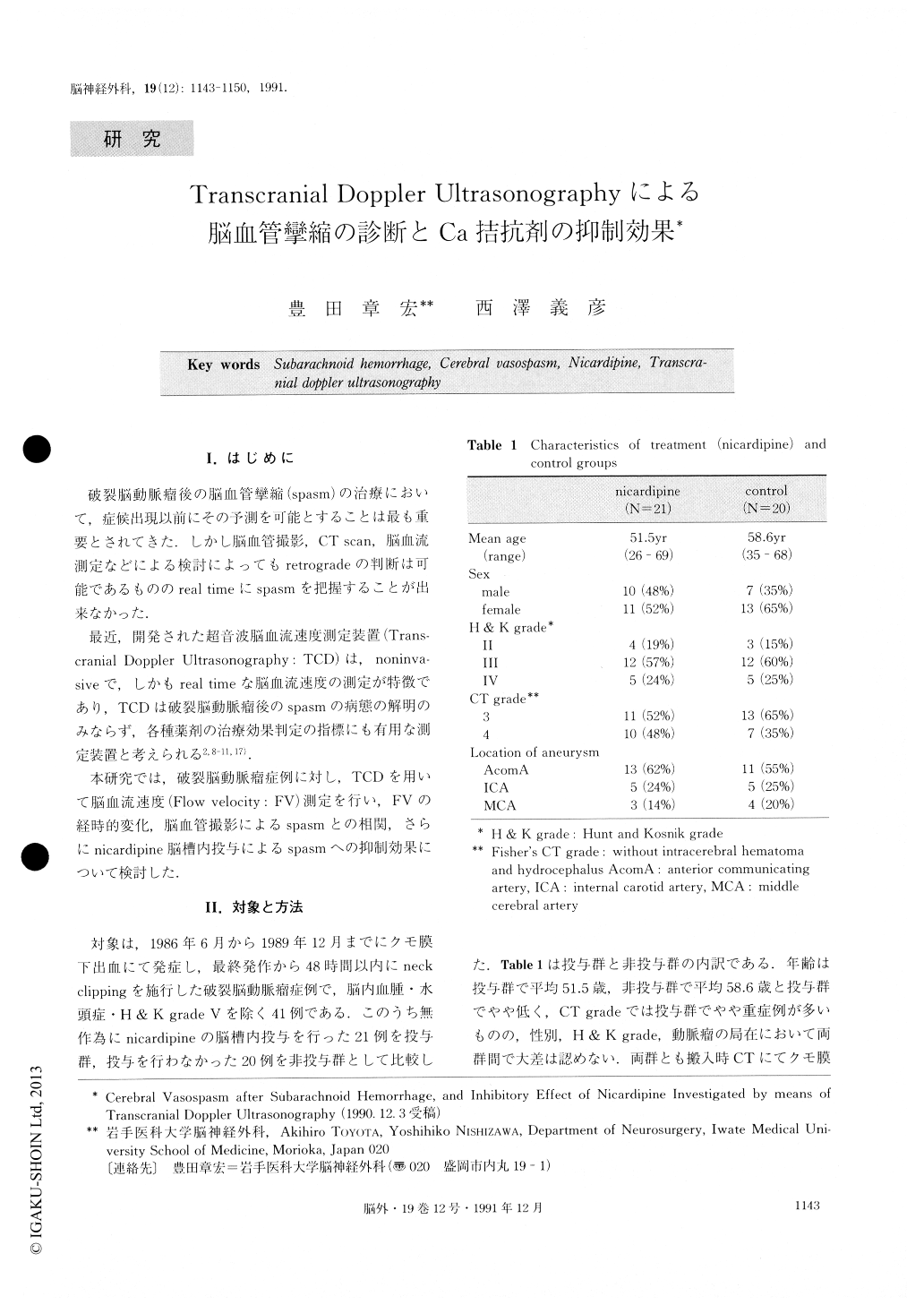
破裂脳動脈瘤後の脳血管攣縮(spasm)の治療において,症候出現以前にその予測を可能とすることは最も重要とされてきた.しかし脳血管撮影,CT scan,脳血正流測定などによる検討によってもretrogradeの判断は可能であるもののreal timeにspasmを把握することが出来なかった.
最近,開発された超音波脳血流速度測定装置(Trans—cranial Doppler Ultrasonography:TCD)は,noninva—siveで,しかもreal timeな脳血流速度の測定が特徴であり,TCDは破裂脳動脈瘤後のspasmの病態の解明のみならず,各種薬剤の治療効果判定の指標にも有用な測定装置と考えられる2,8-11,17).
本研究では,破裂脳動脈瘤症例に対し,TCDを用いて脳血流速度(Flow velocity:FV)測定を行い,FVの経時的変化,脳血管撮影によるspasmとの相関,さらにnicardipine脳槽内投与によるspasmへの抑制効果について検討した.
Cerebral vasospasm is a major complication associ-ated with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). However, real-time evaluation of vasospasm is very difficult via angiography, CT scan, and cerebral blood flow. In this study, for the evaluation of the arterial narrowing, the flow velocity in the middle cerebral artery (MCAFV) was measured with transcranial Doppler ultrasonogra-phy (TCD) in 41 patients with ruptured cerebral aneurysms which were repaired surgically within 48 hours after SAH. MCAFV was measured daily until the 25th clay after onset. All patients underwent CT scan, angiography, and neurological assessments upon admission. To clarify the morphological changes of the cerebral vessels due to SAH, angiography was per-formed again about 10 days after surgery. For evaluation of the efficacy of treatment for vaso-spasm, 21 out of 41 cases were administered a calcium antagonist (4mg of nicardipine) through the cisternal drain every 12 hours for an average of 10 days. The other 20 cases did not receive nicardipine and served as controls.
15 patients with clinical symptoms had a rapid in-crease in MCAFV from the 3rd to 6th day after onset, and a high velocity of more than 150cm/sec continued for 7.6 ± 3.6 days on the average. In marked contrast, 26 patients without clinical symptoms showed only a small increase in MCAFV of less than 110cm/sec.There was a significant correlation between the arterial narrowing of MCA and MCAFV (γ=0.72, p<0.01)except for 5 cases (12%).In addition, there was a differ-ence between the daily increase in MCAFV from Day 3 to Day 5 and the morphological type of angiographic-al vasospasm. Based on a rapid increase in MCAFV of more than 25cm/sec during the 3rd to 5th day, it was possible to predict the occurrence of clinical symptoms with an 82.4% accuracy. Moreover, all of the patients with a high velocity (over 150cm/sec) which continued for more than 3 days after the initial rapid increase in MCAFV developed clinical symptoms. By administra-tion of nicardipine, 1) the rapid increase in MCAFV was decreased to less than 25cm/sec, 2) the duration of the high velocity (more than 150cm/sec) was signifi-cantly reduced (p<0.03), and 3) a favorable prognosis was verified.
In conclusion, serial measurement using TCD has made possible the realtime evaluation of vasospasm, especially for the prediction of the occurrence of clinic-al symptoms. In addition, this method may also be em-ployed to evaluate the efficacy of various treatments for vasospasm.
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


