Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
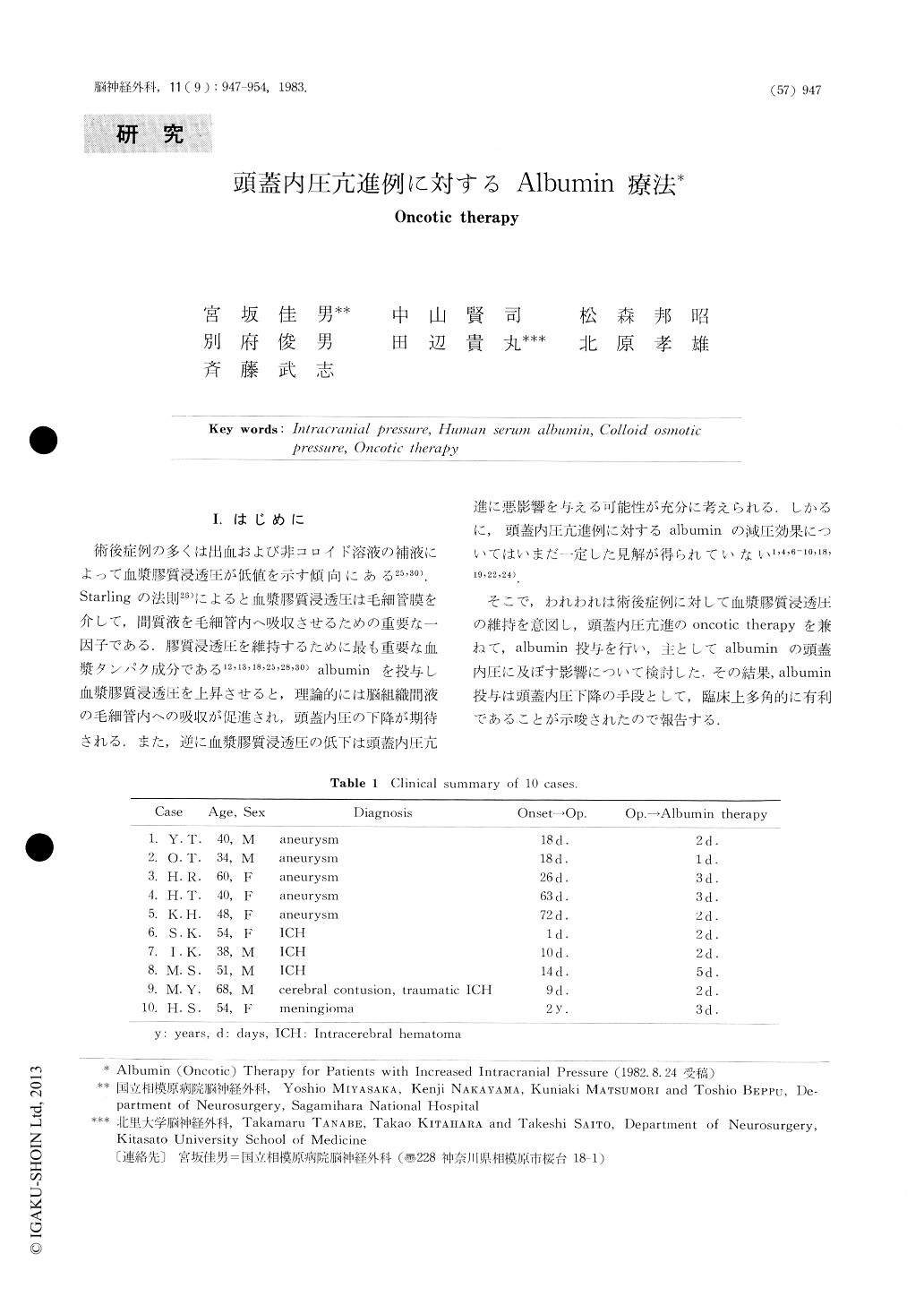
術後症例の多くは出血および非コロイド溶液の補液によって血漿膠質浸透圧低値を示す傾向にある25,30).Starlingの法則25)によると血漿膠質浸透圧は毛細管膜を介して,間質液を毛細管内へ吸収させるための重要な一因子である.膠質浸透圧を維持するために最も重要な血漿タンパク成分である12,13,18,25,28,30)albuminを投与し血漿膠質浸透圧を上昇させると,理論的には脳組織間液の毛細管内への吸収が促進され,頭蓋内圧の下降が期待される.また,逆に血漿膠質浸透圧の低下は頭蓋内圧亢進に悪影響を与える可能性が充分に考えられる.しかるに,頭蓋内圧亢進例に対するalbuminの減圧効果についてはいまだ一定した見解が得られていない1,4,6-10,18,19,22,24).
そこで,われわれは術後症例に対して血漿膠質浸透圧の維持を意図し,頭蓋内圧亢進のoncotic therapyを兼ねて,albumin投与を行い,主としてalbuminの頭蓋内圧に及ぼす影響について検討した.その結果,albumin投与は頭蓋内圧下降の手段として,臨床上多角的に有利であることが示唆されたので報告する.
Albumin plays an important role in maintaining anadequate plasma colloid osmotic pressure (COP).On the basis of the Starling's law, we postulatedthatelevation of plasma COP produced by infusion ofserum albumin would result in the withdrawal ofcerebral interstitial fluid. To test the hypothesisthat an oncotic gradient would produce cerebraldehydration and result in reduction of intracranialpressure (ICP), we infused intravenously 25%solutionof salt-poor human serum albumin, 2g/kg over 60minutes for 10 patients with increased ICP.
Copyright © 1983, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


