Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
アミロイドーシスは,アミロイドと総称される特異な構造の物質が組織間隙に病的に沈着することにより起こる疾患群と定義される。アミロイドは主にアミロイドフィブリル蛋白という線維蛋白からなる。アミロイドフィブリル蛋白は高次構造上,βひだ状シート構造という共通性をもつ反面,一次構造のうえでは多様である1)。従来"原発性アミロイドーシス"および"骨髄腫に合併するアミロイドーシス"と呼ばれた病型のアミロイドフィブリル蛋白は,免疫グロブリンのL鎖に由来する一次構造を有し,ALと呼ばれる。また"続発性アミロイドーシス"のアミロイドフィブリル蛋白は,急性期蛋白であるSAA(serum amyloid A)に由来しAA,遺伝性アミロイドーシスの一病型である家族性アミロイドポリニューロパチー(以下FAP)のアミロイドフィブリル蛋白は変異プレアルブミン(またはトランスサイレチン,TTR)に由来しAFと,それぞれ呼称される1)。この差はアミロイドの臓器分布や沈着様式にも影響し,臨床像を複雑で多彩なものにしている。
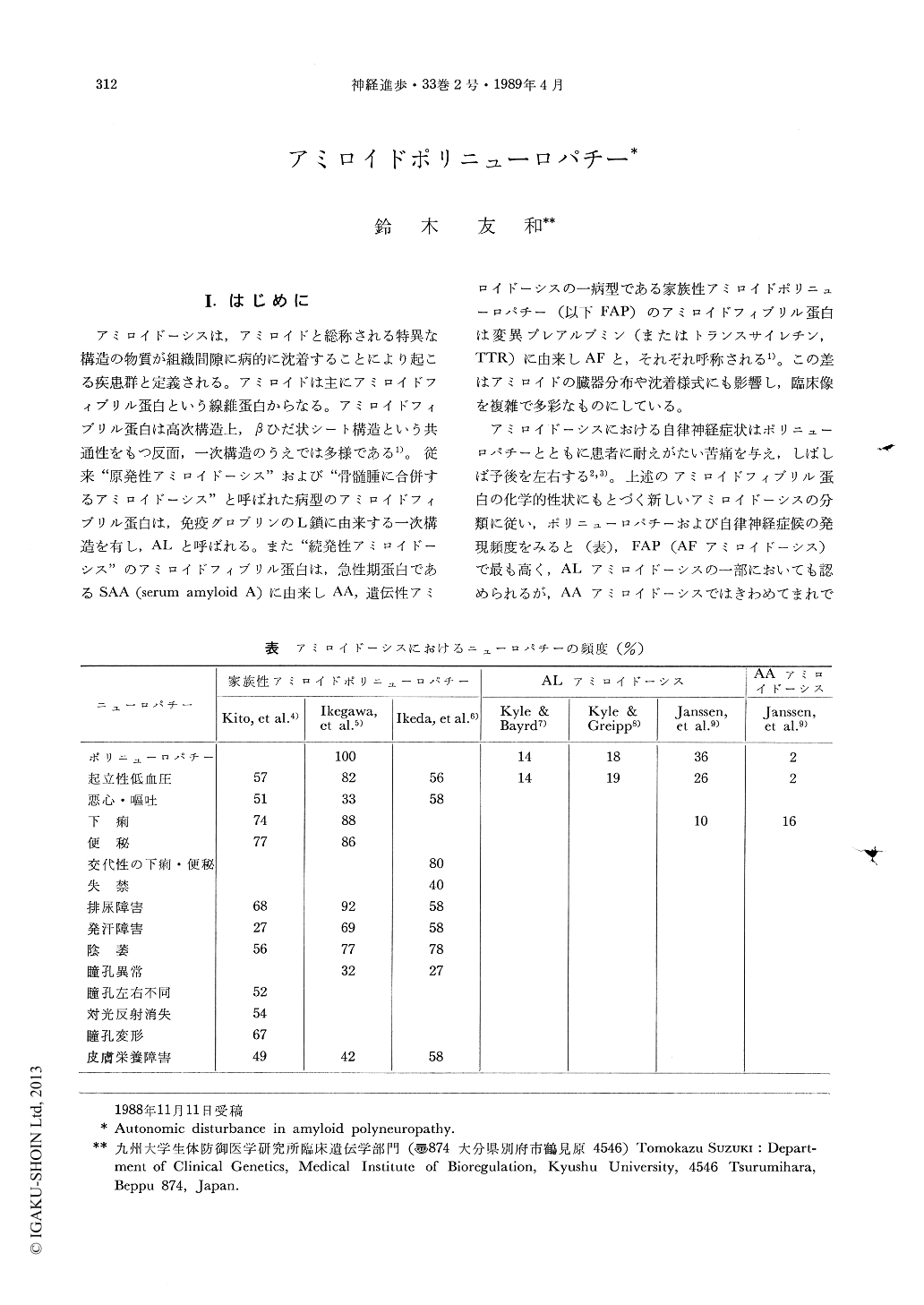
アミロイドーシスにおける自律神経症状はポリニューロパチーとともに患者に耐えがたい苦痛を与え,しばしば予後を左右する2,3)。
Although it was prevalent that amyloid deposition in every organ was wholly responsible for autonomic disturbance in amyloidosis, recent progress of neuropharmacologic and histochemical metho-dology has made it feasible to distinguish autonomic dysfunction from visceral one due to amyloid. In this paper, first of all, clinical feature and neuropathology of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP) were described briefly. Then the results of our biochemical, pharmacologic and physiologic studies on the sympathetic dysfunction in FAP were summarized, and it was concluded that orthostatic hypotension in FAP is pathophysiologically similar to pure autonomic failure. It was also pointed out that autonomic dysfuncton might play an important role in the pathogenesis of various manifestations in amyloidosis. Finally, therapeutic application of L-threo-3, 4-dihydroxyphenylserine (L-threo-DOPS), an immediate precursor of (-)-norepinephrine, was summarized. A multicenter study has recently revealed that L-threo-DOPS is useful to treat orthostatic hypotension and some other autonomic manifestations in FAP.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


