Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
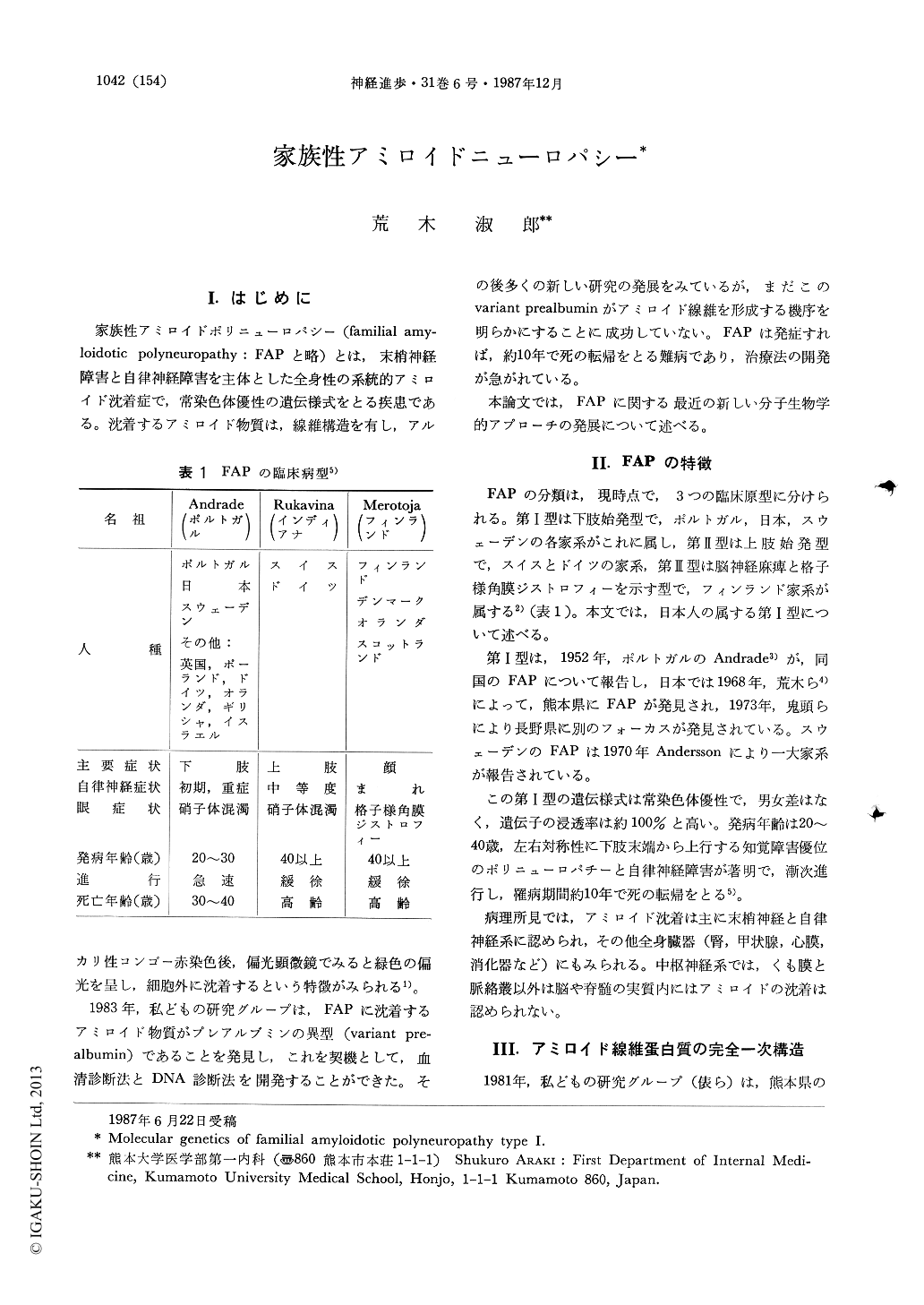
I.はじめに
家族性アミロイドポリニューロパシー(familial amy-loidotic polyneuropathy:FAPと略)とは,末梢神経障害と自律神経障害を主体とした全身性の系統的アミロイド沈着症で,常染色体優性の遺伝様式をとる疾患である。沈着するアミロイド物質は,線維構造を有し,アルカリ性コンゴー赤染色後,偏光顕微鏡でみると緑色の偏光を呈し,細胞外に沈着するという特徴がみられる1)。
1983年,私どもの研究グループは,FAPに沈着するアミロイド物質がプレアルブミンの異型(variant prealbumin)であることを発見し,これを契機として,血清診断法とDNA診断法を開発することができた。その後多くの新しい研究の発展をみているが,まだこのvariant prealbuminがアミロイド線維を形成する機序を明らかにすることに成功していない。FAPは発症すれば,約10年で死の転帰をとる難病であり,治療法の開発が急がれている。
Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP) is an inherited systemic amyloidosis characterized by the extracellular deposition of fibrillar amyloid protein and primarily affects the peripheral and autonomic nervous systems. The inheritance is an autosomal dominant with a high penetrance rate and equal sex ratio. The first symptoms usually appear in individuals between 20 and 45 years of age, and the disease is always progressive and fatal in about 10~20 years. Currently, there is no specific therapy for FAP.
Japanese, Portuguese and Swedish types of FAP all result from a systemic deposition of amyloid fibrils formed by a prealbumin variant containing a methionine-for-valine substitution at the amino acid position 30.
Copyright © 1987, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


