Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.Krabbe病とは
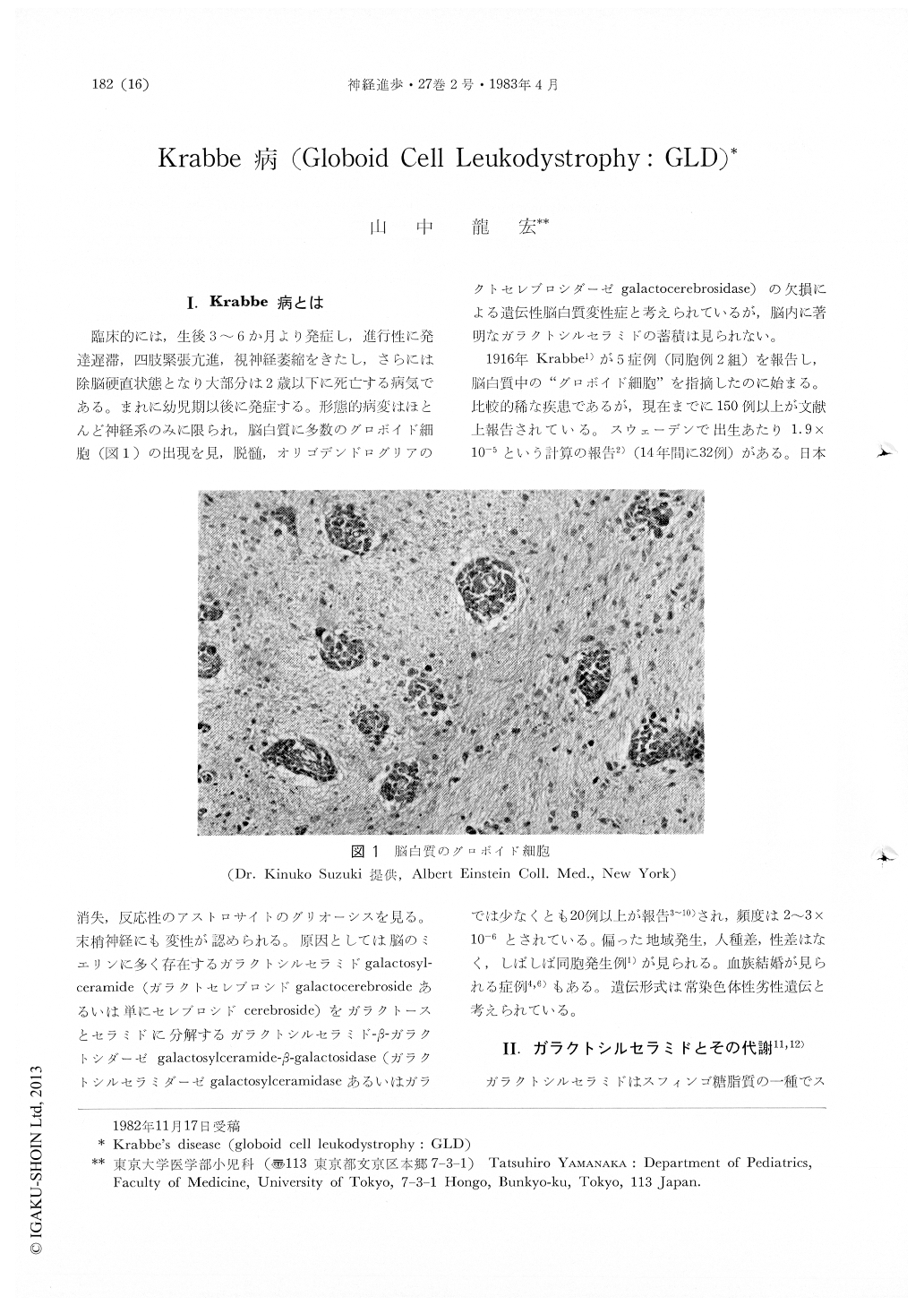
臨床的には,生後3〜6か月より発症し,進行性に発達遅滞,四肢緊張亢進,視神経萎縮をきたし,さらには除脳硬直状態となり大部分は2歳以下に死亡する病気である。まれに幼児期以後に発症する。形態的病変はほとんど神経系のみに限られ,脳白質に多数のグロボイド細胞(図1)の出現を見,脱髄,オリゴデンドログリアの消失,反応性のアストロサイトのグリオーシスを見る。末梢神経にも変性が認められる。原因としては脳のミエリンに多く存在するガラクトシルセラミドgalactosylceramide(ガラクトセレブロシドgalactocerebrosideあるいは単にセレブロシドcerebroside)をガラクトースとセラミドに分解するガラクトシルセラミド-β-ガラクトシダーゼgalactosylceramide-β-galactosidase(ガラクトシルセラミダーゼgalactosylceramidaseあるいはガラクトセレブロシダーゼgalactocerebrosidase)の欠損による遺伝性脳白質変性症と考えられているが,脳内に著明なガラクトシルセラミドの蓄積は見られない。
1916年Krabbe1)が5症例(同胞例2組)を報告し,脳白質中の"グロボイド細胞"を指摘したのに始まる。比較的稀な疾患であるが,現在までに150例以上が文献上報告されている。
Globoid cell leukodystrophy (GLD) is a neurodegenerative disorder, and transmitted as an autosomal recessive trait. Usually clinical course is rapidly progressive and shows only neurological manifestations. Patients rarely survive the second year. Several cases of late onset GLD were reported including the adult case. The pathological finding of multinucleated globoid cell in the white matter is pathognomonic. Other pathological findings include severe myelin loss and astrocytic gliosis.
Copyright © 1983, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


