Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
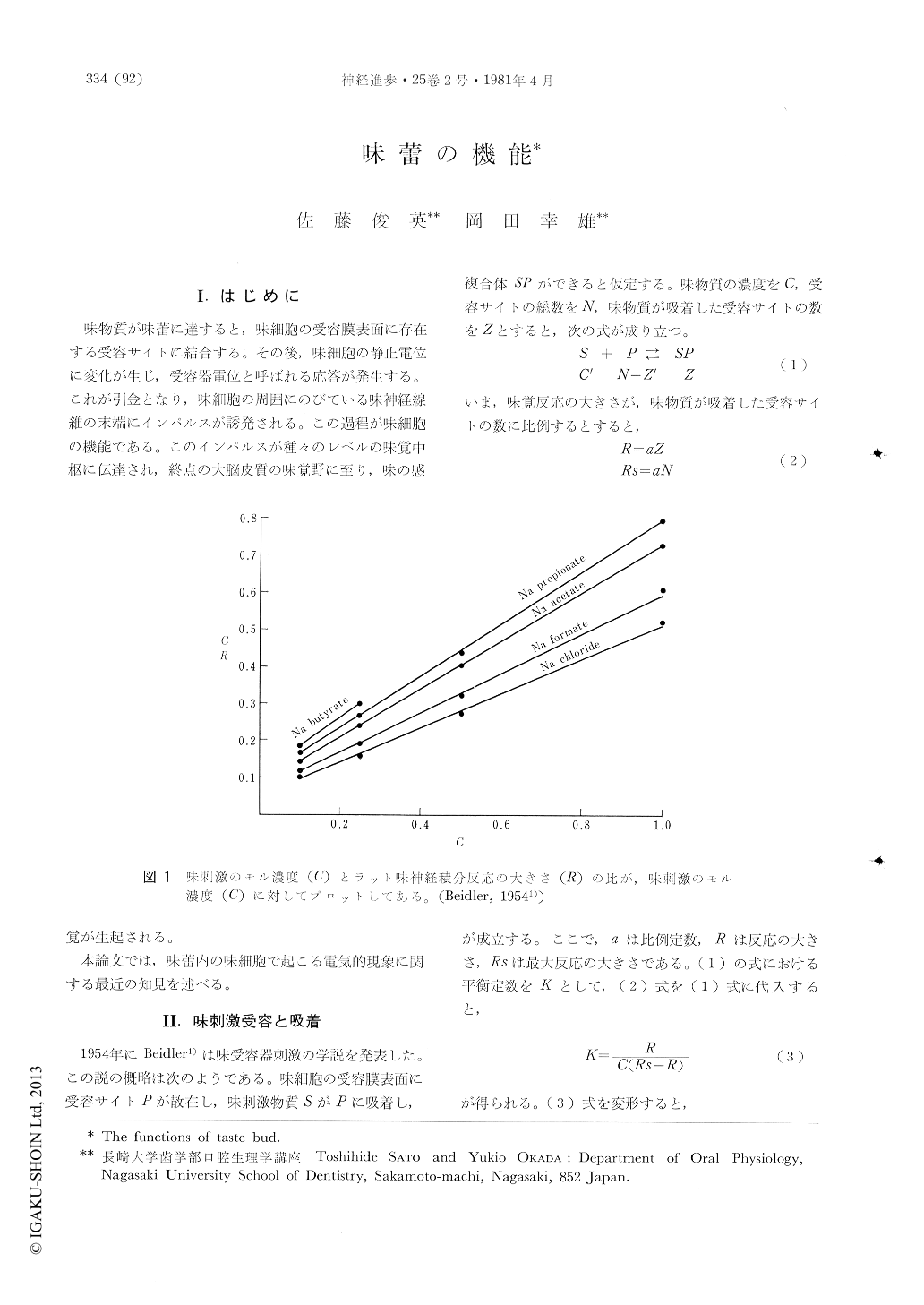
味物質が味蕾に達すると,味細胞の受容膜表面に存在する受容サイトに結合する。その後,味細胞の静止電位に変化が生じ,受容器電位と呼ばれる応答が発生する。これが引金となり,味細胞の周囲にのびている味神経線維の末端にインパルスが誘発される。この過程が味細胞の機能である。このインパルスが種々のレベルの味覚中枢に伝達され,終点の大脳皮質の味覚野に至り,味の感覚が生起される。
本論文では,味蕾内の味細胞で起こる電気的現象に関する最近の知見を述べる。
Abstract
The most important cell in the taste buds is a taste cell.The functions of the taste cell are to receive necessary and unnecessary taste stimuli coming into the mouth and to transduce the receptor potential into gustatory neural impulses.
The mean resting membrane potentials of taste cells in catfish, frog, mudpuppy, rat and hamster range from -18 to -40 mV. Taste stimuli higher than a threshold concentration generally produce a depolarizing receptor potential, but taste stimuli lower than the threshold produce no response or a hyperpolarizing receptor potential in a taste cell.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


