Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
ヒトの大脳の遠心性機能を反映する脳波現象は,求心性機能に比較してまだ解明されない点が多い。ヒトの随意運動に伴う電位変化を頭皮上から初めて記録したのはBates3)(1951)である(重畳法)。そして1965年に,Kornhuberら23)とVaughanら40)がそれぞれ電算機による加算平均法によって随意運動に伴う頭皮上電位を記録した。とくにKornhuberら23)は,磁気テープを逆回転させて加算平均することにより,運動開始前の現象を求めた。
この電位は完全な形では図1のように四つの成分より成る。Vaughanら(196614),196841))は全体を運動電位と考え,運動開始の約1秒前から始まる約10μVの陰性緩電位をN1,運動開始直前に現われる小さい陽性電位をP1,続いて現われる急峻な陰性電位をN2,最後の陽性電位をP2と呼んだ。一方Kornhuberら(196523),19698))は,N2成分のみが錐体路細胞の興奮を直接反映するものとしてこれを"motor potential"と呼び,N1を"Bereitschaftspotential,readiness potential",P1を"Premotion positivity",P2を"reafferente Potentiale"と呼んだ。
Normal findings on the movement-related cortical potentials (MP) were reviewed, based on the author's own previous studies as well as on review of the relevant literature. MP consists of 4 components. The N1 component (readiness potential) seems to reflect the preparatory event of cerebral cortex, especially of the motor cortex, for a voluntary movement. Physiological significance of the P1 and N2 components still remains controversial.
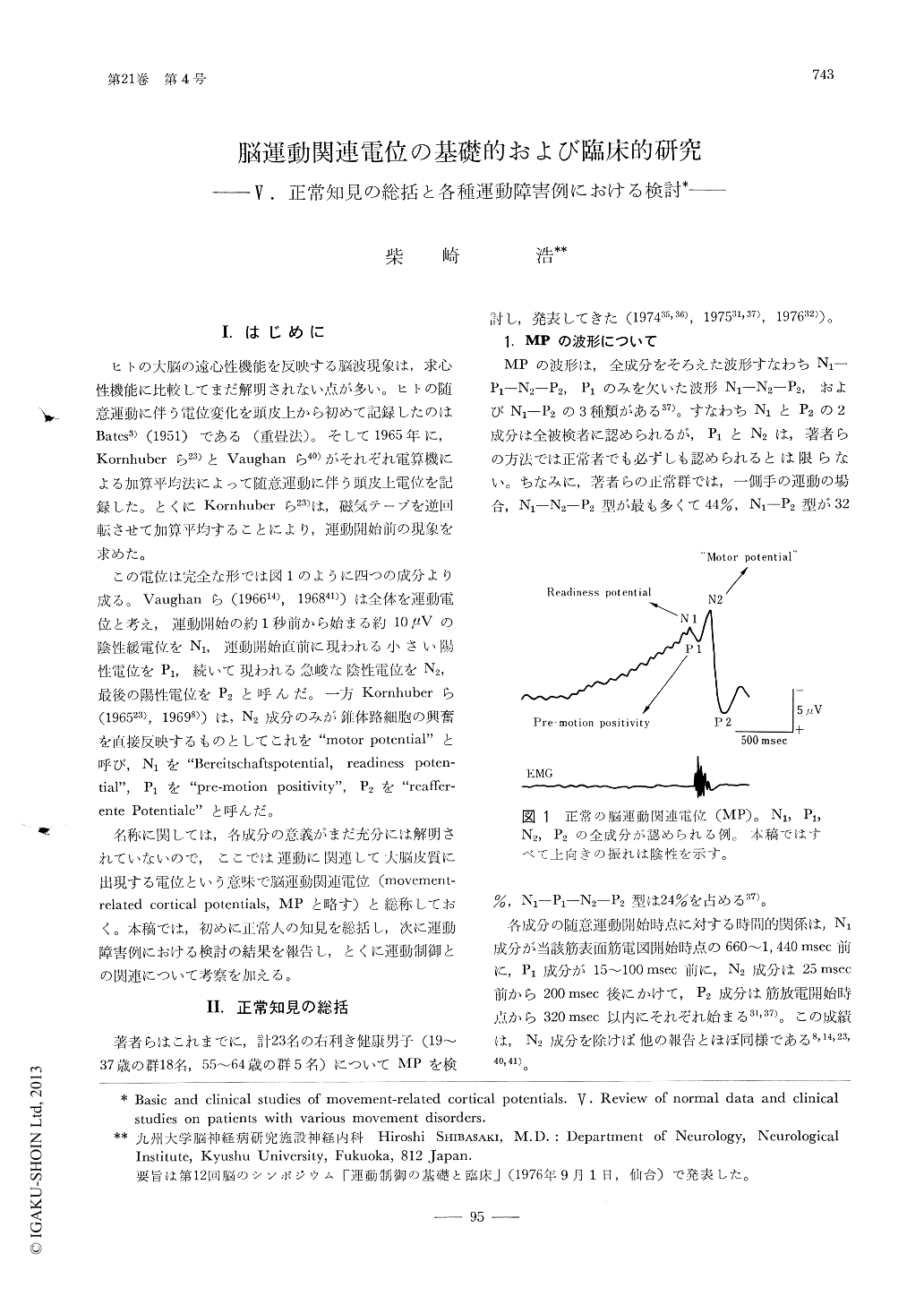
Copyright © 1977, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


