Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
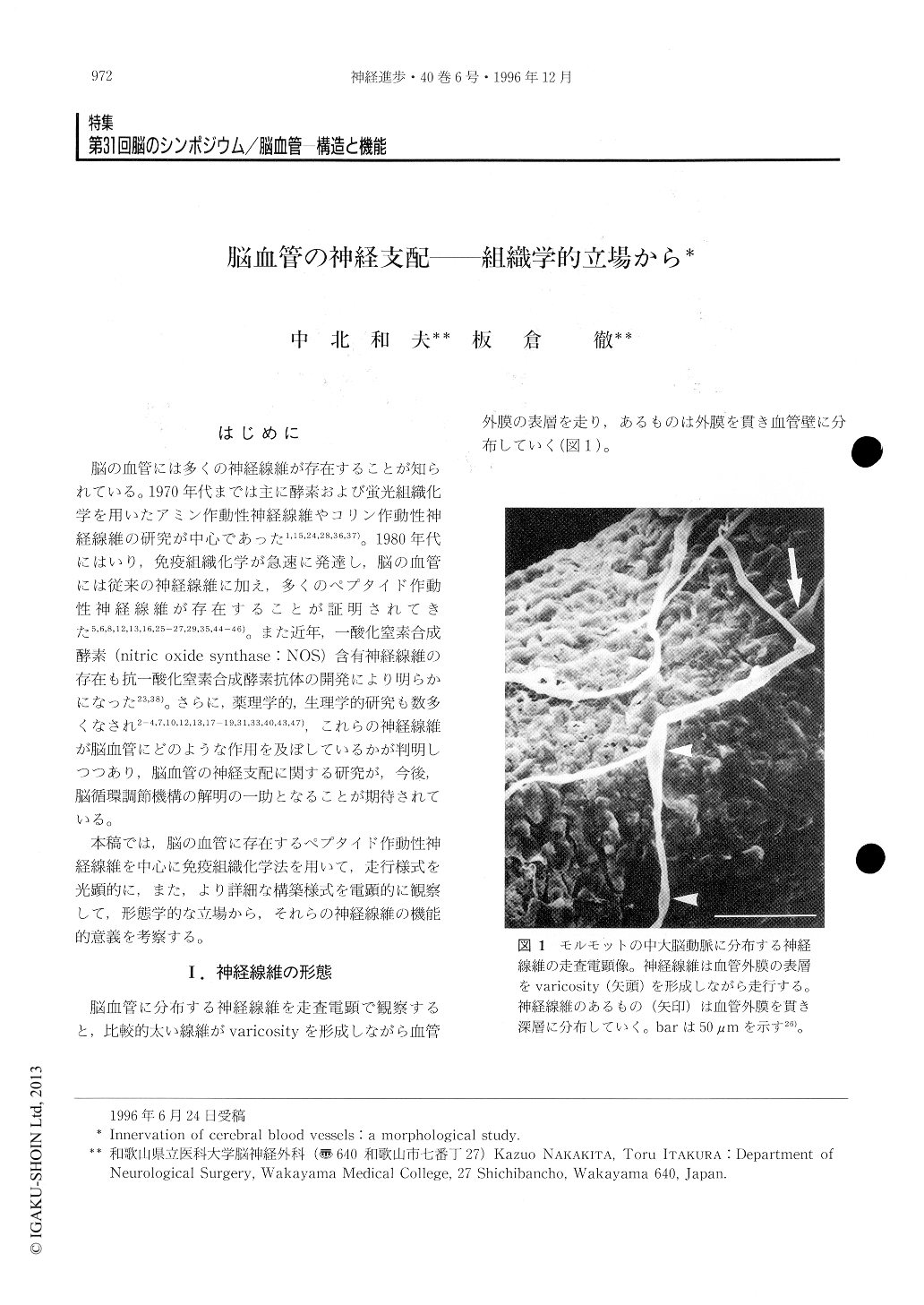
脳の血管には多くの神経線維が存在することが知られている。1970年代までは主に酵素および蛍光組織化学を用いたアミン作動性神経線維やコリン作動性神経線維の研究が中心であった1,15,24,28,36,37)。1980年代にはいり,免疫組織化学が急速に発達し,脳の血管には従来の神経線維に加え,多くのペプタイド作動性神経線維が存在することが証明されてきた5,6,8,12,13,16,25-27,29,35,44-46)。また近年,一酸化窒素合成酵素(nitric oxide synthase:NOS)含有神経線維の存在も抗一酸化窒素合成酵素抗体の開発により明らかになった23,38)。さらに,薬理学的,生理学的研究も数多くなされ2-4,7,10,12,13,17-19,31,33,40,43,47),これらの神経線維が脳血管にどのような作用を及ぼしているかが判明しつつあり,脳血管の神経支配に関する研究が,今後,脳循環調節機構の解明の一助となることが期待されている。
本稿では,脳の血管に存在するペプタイド作動性神経線維を中心に免疫組織化学法を用いて,走行様式を光顕的に,また,より詳細な構築様式を電顕的に観察して,形態学的な立場から,それらの神経線維の機能的意義を考察する。
The distribution of peptidergic nerve fibers containing substance P (SP) , calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) , vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) and neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the cerebral artery and vein of the guinea pig was studied using immunohistochemical techniques. Nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-containing fibers in the cerebral artery of the cat were also observed immunohistochemically. The ultrastructures of these immunoreactive peptidergic nerve terminals were moreover compared.
Copyright © 1996, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


