Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
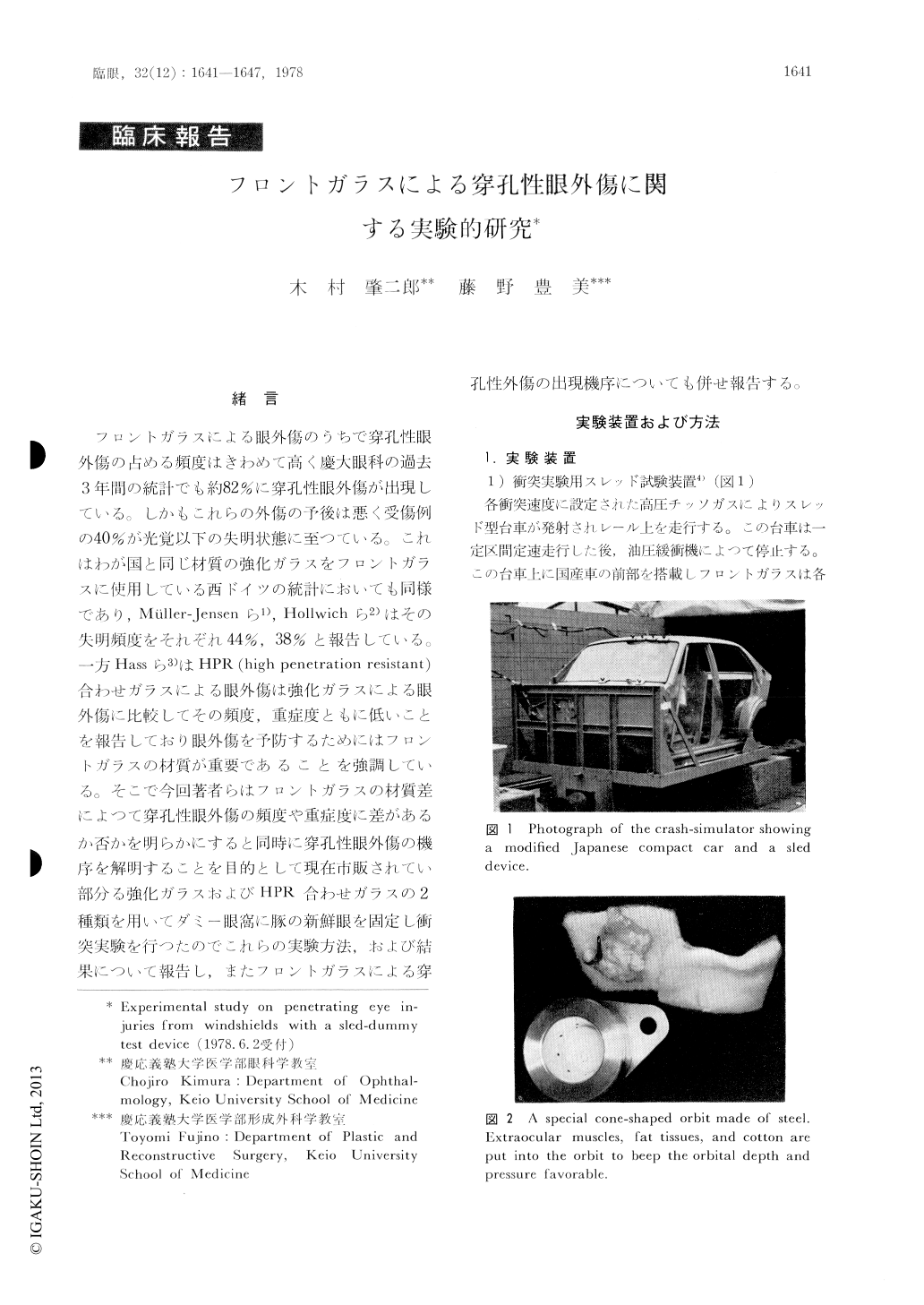
緒 言
フロントガラスによる眼外傷のうちで穿孔性眼外傷の占める頻度はきわめて高く慶大眼科の過去3年間の統計でも約82%に穿孔性眼外傷が出現している。しかもこれらの外傷の予後は悪く受傷例の40%が光覚以下の失明状態に至つている。これはわが国と同じ材質の強化ガラスをフロントガラスに使用している西ドイツの統計においても同様であり,Müller-Jensenら1),Hollwichら2)はその失明頻度をそれぞれ44%,38%と報告している。一方Hassら3)はHPR (high penetration resistant)合わせガラスによる眼外傷は強化ガラスによる眼外傷に比較してその頻度,重症度ともに低いことを報告しており眼外傷を予防するためにはフロントガラスの材質が重要であることを強調している。そこで今回著者らはフロントガラスの材質差によつて穿孔性眼外傷の頻度や重症度に差があるか否かを明らかにすると同時に穿孔性眼外傷の機序を解明することを日的として現在市販されてい部分る強化ガラスおよびHPR合わせガラスの2種類を用いてダミー眼窩に豚の新鮮眼を固定し衝突実験を行つたのでこれらの実験方法,および結果について報告し,またフロントガラスによる穿孔性外傷の出現機序についても併せ報告する。
The high incidence and the severity of penet-rating eye injuries to car occupants from the shattering of tempered windshields have been reported by numerous authors. Eye injuries frombroken tempered windshields resulted in practical blindness of the affected eyes in 40% of 22 cases in our clinic during the past 3 years.
We undertook an experimental study to compare the safety performances of differentially tempe-red glass and laminated glass with 0.76mm HPR (High Penetration Resistance) interlayer. We constructed a dummy with orbits made of steel and with fresh pig eyeballs fixed in it.
Copyright © 1978, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


