Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
日常容易に遭遇する外傷によって薬症した小児の脳塞栓症の3例について報告した。急に振り向く,上肢を急に引っ張られる,頭髪を後方に引っ張られるなど,頸部の回旋・伸展などに関与する運動から短時間後に塞栓によると考えられる脳梗塞が出現した。血管撮影所見では内頸動脈の壁不整,多発性の頭蓋内血管の閉塞ならびに狭窄,血管内の栓子の所見がみられ,塞栓源は頸動脈領域にあると考えられた。このような症例は小児では少なく,渉猟し得た範囲では16例を数えるのみであった。これらを基に,その臨床症状,脳血管撮影所見,成因などにつき若干の考察を行った。
Three cases of cerebral embolism secondary to trivial trauma are reported.
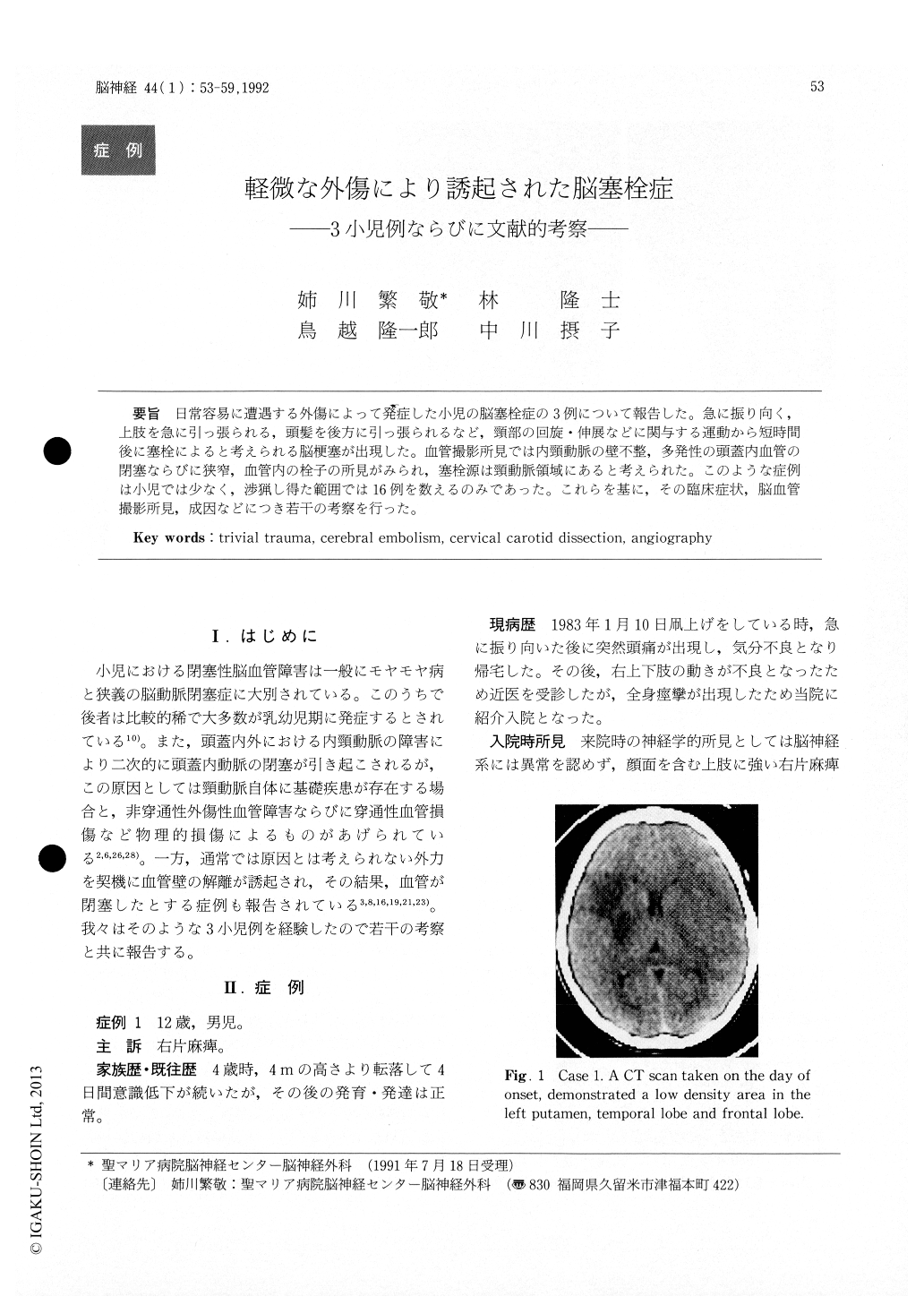
Case 1: A 12-year-old male suffered a severe headache followed by a generalized convulsion after he turned his head when he was flying a kite. A neurological examination on admission demonstrat-ed right hemiparesis and aphasia. A CT revealed a low density in the left putamen, temporal lobe and frontal lobe. Left carotid angiography (CAG) showed irregular narrowing of the internal carotid with an embolic occlusion and narrowing of the middle cerebral artery with the intraluminal pres-ence of emboli both in the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. He is now doing well but has right hemiparesis.
Case 2 : This 6-year-old female could not grasp chopsticks and had neck pain 10 munites after being pulled up by the right arm by her father. Neuro-logical examination demonstrated a right hemipa-resis and aphasia. A CT scan and magnetic resonace imaging ( MRI ) of the head showed an infarcted area in the left caudate head, anterior limb of the internal capsule and putamen. Left CAG revealed an obstruction of the trunk of the middle cerebral artery. She has slight weakness in her right extremi-ties.
Case 3: This 11-year-old female noted a weak-ness in her left lower limb soon after her hair was pulled backward. On admission, a neurological examination failed to demonstrate any abnomality. CT showed an ill defined low density lesion in the right putamen. MRI revealed a high intensity lesion in a T2 weighted image. Right CAG showed an irregularity of the arterial wall in the cavernous portion of the right internal carotid artery. She was discharged with no neurological deficit.
Most reported cases of infarction associated with trivial trauma and all our patients suffered the episode shortly after cervical rotation or extension due to trivial trauma in everyday life. Cervical and intracranial carotid dissection may result in cere-bral ischemic symptoms owing to hemodynamic compromise from stenosis or occlusion, but more often an embolism of thrombotic fragments obstructs the disital vessels. The importance of rapid body movement or trivial trauma on the pathogenesis of these lesions is stressed.
Copyright © 1992, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


