Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
前頭蓋底髄膜脳瘤は通常4型に分けられ,うちf代表的な型としてはtranssphenoidal typeとtransethmoidal typeがあげられる。極めて稀な疾患であるといえる。これらの髄膜脳瘤は他の部位におけるそれとは異なり,腫瘤が鼻・咽頭内に隠されているために,外観上の診断が困難である。しかし,本疾患には次のような症候ならびに画像上の特徴がある。すなわち,1)いびき,口呼吸,繰り返す髄膜炎,2)正中唇裂,口蓋裂,外鼻腔の変形および非対称,3)篩骨ないし蝶形骨特にトルコ鞍底部の骨欠損,それに鼻・咽頭部内の軟部組織陰影,4)CT scanにみられる水頭症とくに後角の拡大(colpocephaly),脳梁欠損それに鼻・咽頭腔内への頭蓋内組織の嵌入などの所見である。上記の顔面正中ならびに脳形成の異常の程度はtranssphenoidal typeにより顕著であるとされ,その発生時期が両者では異なると考えられる。
我々は最近2例のtransethmoidal typeを経験したので,前頭蓋底部髄膜脳瘤の臨床的特徴と発生学的考察を行い,報告する。
Transethomoidal menigoencephalocele is caused by protrusion into the nasal cavity of a part of brain and meninges through an ethomoidal defect being a subtype of basal meningoencephalocele. It is extremely rare as only a few cases have been reported so far. It gives characteristic symptoms and signs as follows : (i) mouth breathing and snoring due to intranasal tumor and obstruction from birth, (ii) pulsation of the tumor synch-ronous with pulse or respiration, (iii) complica-tion of facial deformities such as hypertelorism, cleft lip and palate, and (iv) leakage of cerebro-spinal fluid from the nose, meningitis, etc. More-over, agenesis of corpus callosum and congenital hydrocephalus are identfied, which indicate the origin of this disease as have been repored by various authors.
Recently, we experienced two cases of newborninfants with this anomaly.
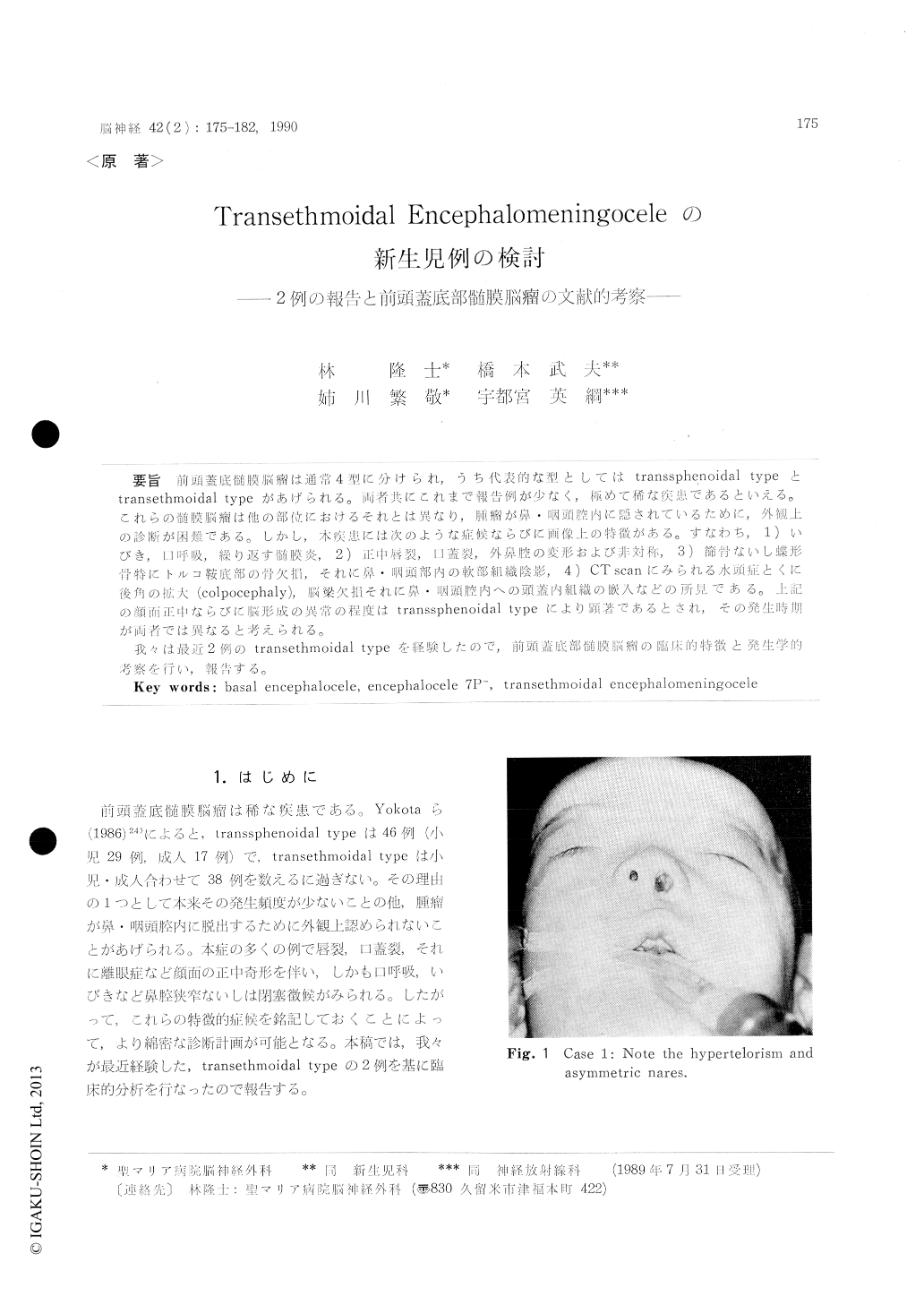
Case 1: A 1-day-old male was born by Caes-arean section at full term, body weight at birth being 3500 gm, cranial circumference 35. 2 cm, and Apgar score at 5 minutes of full. Since he was dyspneic while nursing, he was transferred to our clinic. Hypertelorism, unequal anterior nares, and micrograthia were the facial abnormalities at admission. Both nasal cavities were completely obstruced by abnormal bony tissue at about 3 cm from the anterior border of the nares. No obvious abnormality was found by neurological and bio-chemitoloical examination. A transcranial repair of the basal encephalocele was performed. The crista galli could not be seen, but the base of the frontal skull was found to be deeply depressed into the ethmoid sinus proper just as seen by CT scan. Case 2: A 4-day-old female was born by spon-taneous delivery on cephalic presentation at the 42nd week without asphyxia. Her body weight at birth was 3630 gm, and a stridor was of note. The anomalies on the skull and the face such as exophthalmos, ptosis, low set ears, small maxilla and brachicephaly were observed. The interstitial deletion of the short arm of chromosome 7 (7 p-) at the 46 XX was detected. The bicoronal syno-stosis with craniolacunia of the frontal bone was seen on craniogram. A part of the frontal lobe was herniated into the nasal cavity on a sagittal plane of the CT scan. Frontal advancement and repair of the transethmoidal encephalocele and the craniosynostosis were performed by the bicoronal craniectomy.
Both cases were exactly diagnosed prior to surgery by neuroradiological examinations. The main diagnostic problems and their importance are described together with a discussion on the embryology.
Copyright © 1990, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


