Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
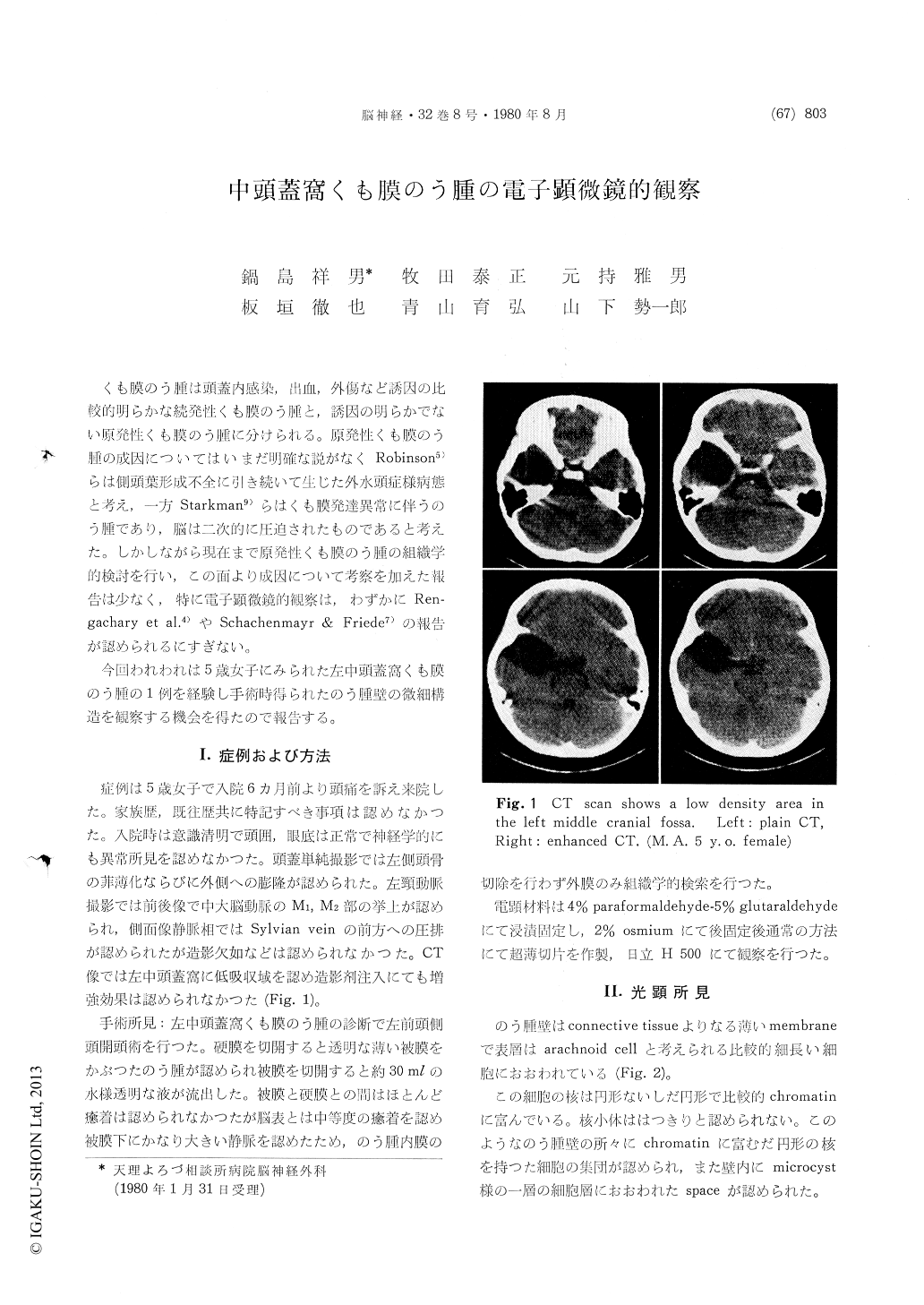
くも膜のう腫は頭蓋内感染,出血,外傷など誘因の比較的明らかな続発性くも膜のう腫と,誘因の明らかでない原発性くも膜のう腫に分けられる。原発性くも膜のう腫の成因についてはいまだ明確な説がなくRobinson5)らは側頭葉形成不全に引き続いて生じた外水頭症様病態と考え,一方Starkman9)らはくも膜発達異常に伴うのう腫であり,脳は二次的に圧迫されたものであると考えた。しかしながら現在まで原発性くも膜のう腫の組織学的検討を行い,この面より成因について考察を加えた報告は少なく,特に電子顕微鏡的観察は,わずかにRen—gachary et al.4)やSchachenmayr & Friede7)の報告が認められるにすぎない。
今回われわれは5歳女子にみられた左中頭蓋窩くも膜のう腫の1例を経験し手術時得られたのう腫壁の微細構造を観察する機会を得たので報告する。
The primary arachnoid cyst developed on the left middle cranial fossa of 5 year-old girl was examined with electron-microscope and discussed its patho-genesis.
The cyst wall was mainly composed of two dis-tinct layers, one was compact arranged flattened cells and others loosely arranged of collagen fibers and fibroblast. Various junctions were observed between those cells. Those features were similar to that was seen in normal arachnoid membrane. However, the abundant attenuated cell processes, whole formation and psammoma body were ob-served in cyst wall. Those finding suggested the cyst was congenital arachnoid malformation, result-ing from abnormal proliferation of developing arachnoid cells.
Copyright © 1980, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


