Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
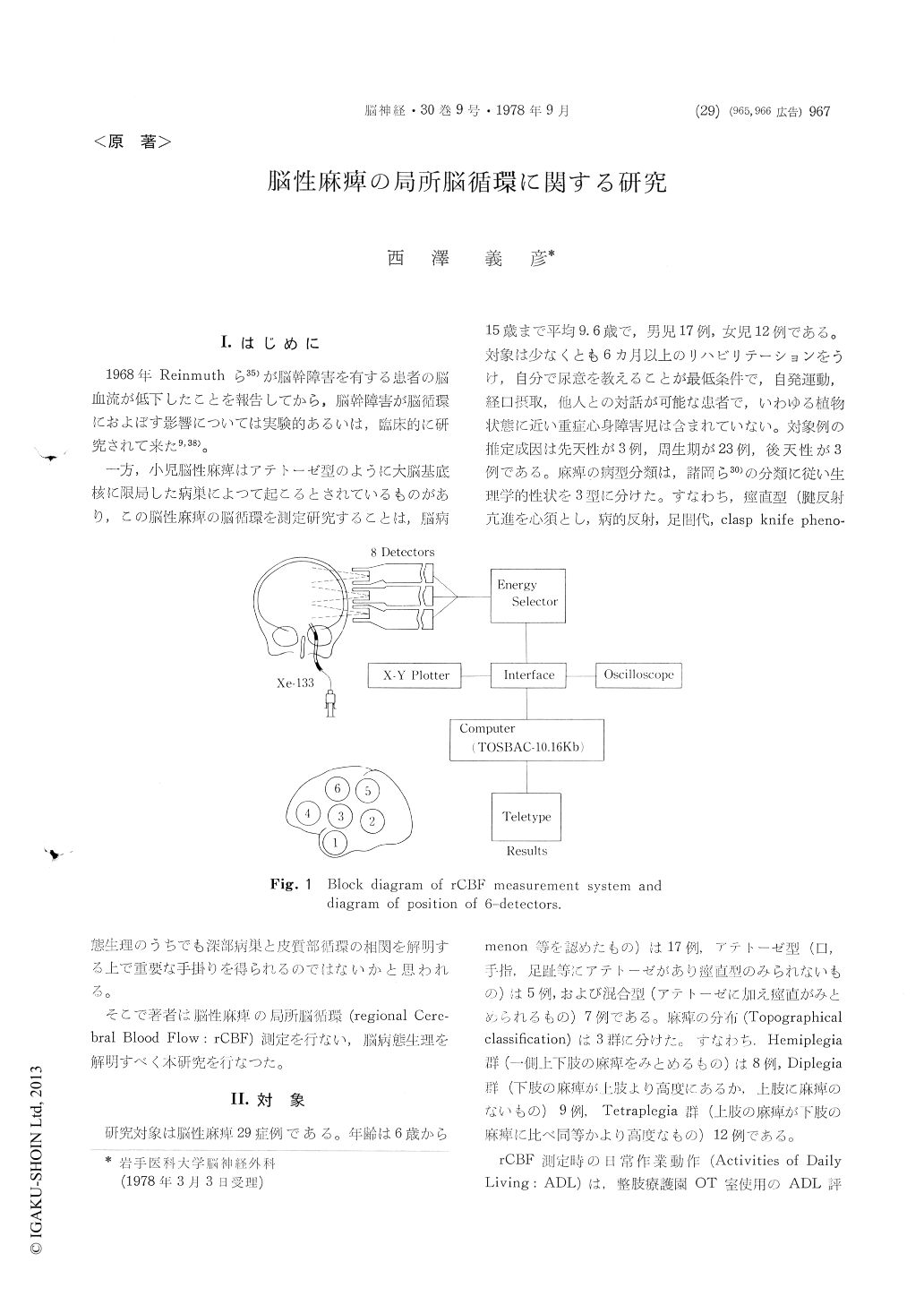
1968年Reinmuthら35)が脳幹障害を有する患者の脳血流が低下したことを報告してから,脳幹障害が脳循環におよぼす影響については実験的あるいは,臨床的に研究されて来た9,38)。
一方,小児脳性麻癖はアテトーゼ型のように大脳基底核に限局した病巣によつて起こるとされているものがあり,この脳性麻痺の脳循環を測定研究することは,脳病態生理のうちでも深部病巣と皮質部循環の相関を解明する上で重要な手掛りを得られるのではないかと思われる。
29 patients with cerebral palsy composed of 17 cases of the spastic type, 5 cases of the athetoid type, and 7 cases of the mixed type. The regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) was studied bilateraly by 133-Xe clearance method under general anes-thesia. The following results were obtained.
1) In 7 cases with spastic hemiplegia, the mean rCBF (MrCBF) of diseased hemispheres showed a significant low value compared with that of the intact hemisheres. In 5 cases of the athetoid typehad a decreased MrCBF in the bilateral hemispheres. In 7 cases of the mixed type, a significantly high value of the MrCBF was shown in the diseased hemispheres compared with that of the intact hemispheres.
2) In the 7 cases with spastic hemiplegia, a good correlation was seen between the MrCBF of the intact hemisphere and the activity of daily living (ADL), while that of the diseased hemisphere was not correlated with ADL. In patients of the athetoid and the mixed type, the MrCBF of the deseased hemisphere showed an inverse correlation with the ADL.
3) Among 7 cases with spastic hemiplegia, 3 cases showed a glodal ischemia, while other 3 cases showed a focal ischemia confined in the sensory motor area in the diseased hemisphere. On the other hand, 6 cases of all patients with the mixedtype showed a global hyperemia.
4) Abnormal CO2 response of the cerebral circ-ulation were obsereved in the diseased hemispheres of tne following 3 cases; 1. The hemiplegic spastic type exibiting low ADL score. 2. The sensory motor ares of the athetoid type. 3. The sensory motor area of the mixed type demonstrating athe-tosis of the lighter degree.
5) It was concluded that the extent of extra-pyramidal injuries involved may produced different patterns of the abnormal vascular reaction; a res-tricted and lighter degree of injuries may cause a local ischemic reaction or a paradoxical CO2 reaction, whereas a diffuse and severe degree of injuries may cause a total vasoparalysis leading to the global hyperemia.
Copyright © 1978, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.