Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
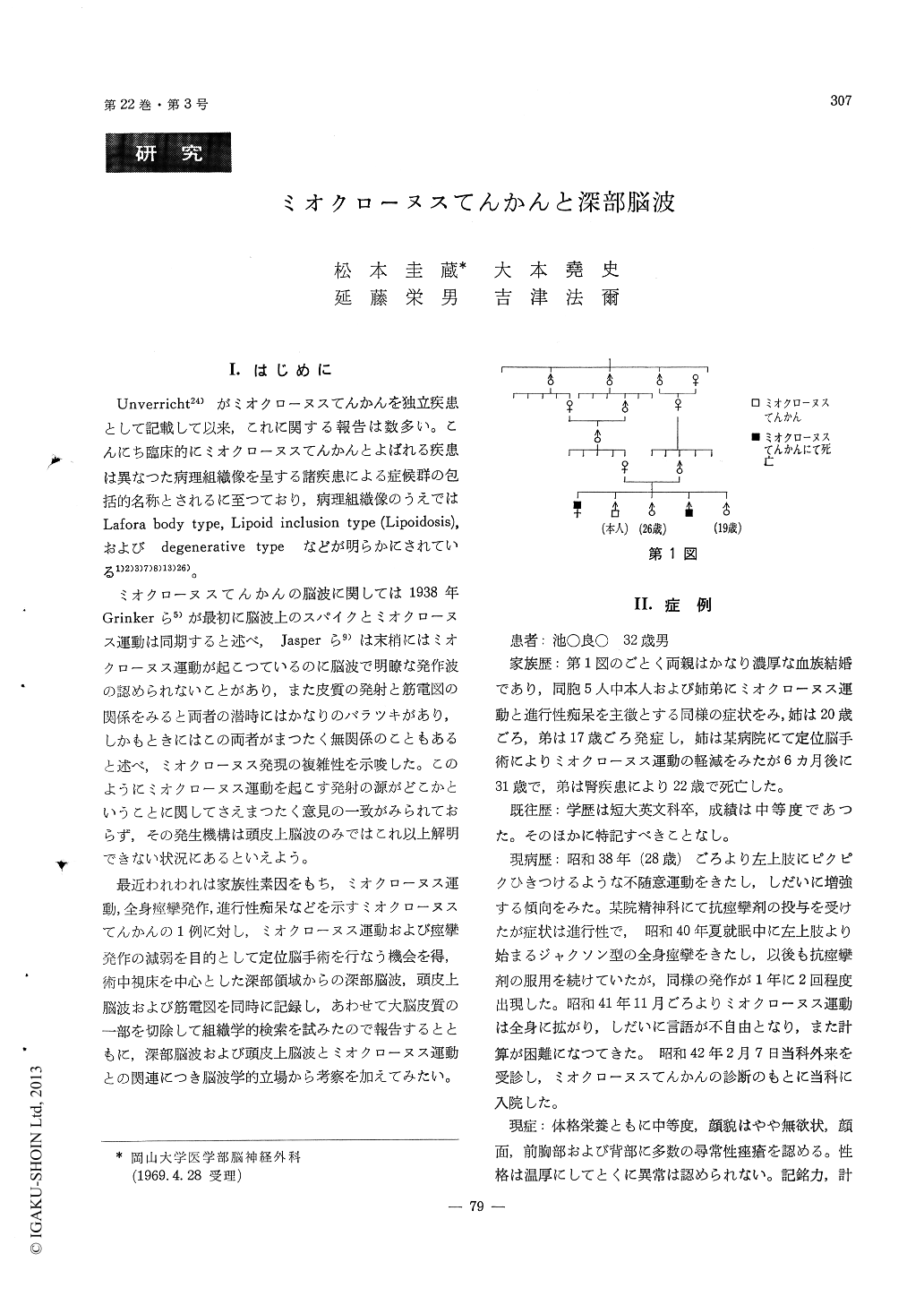
I.はじめに
Unverricht24)がミオクローヌスてんかんを独立疾患として記載して以来,これに関する報告は数多い。こんにち臨床的にミオクローヌスてんかんとよばれる疾患は異なつた病理組織像を呈する諸疾患による症候群の包括的名称とされるに至つており,病理組織像のうえではLafora body type, Lipoid inclusion type (Lipoidosis),およびdegenerative typeなどが明らかにされている1)2)3)7)8)13)26)。
ミオクローヌスてんかんの脳波に関しては1938年Grinkerら5)が最初に脳波上のスパイクとミオクローヌス運動は同期すると述べ,Jasperら9)は末梢にはミオクローヌス運動が起こつているのに脳波で明瞭な発作波の認められないことがあり,また皮質の発射と筋電図の関係をみると両者の潜時にはかなりのバラツキがあり,しかもときにはこの両者がまつたく無関係のこともあると述べ,ミオクローヌス発現の複雑性を示唆した。このようにミオクローヌス運動を起こす発射の源がどこかということに関してさえまつたく意見の一致がみられておらず,その発生機構は頭皮上脳波のみではこれ以上解明できない状況にあるといえよう。
A 32-year-old male, who had an episode of general convulsions, signs of general myoclonic jerkings, progressive dementia, and positive family history,was admitted to our hospital and was diagnosed a slowly progressive form of myoclonus epilepsy.
The ventro-lateral thalamotomy and the destruc-tion of the field of Forel-H were performed on his right side under local anesthesia. A probe with five silver ring electrodes separating 4mm distance and the sixth electrode 36mm distance from the tip was inserted into the ventro-lateral nucleus of the thala-mus at the time of surgery. Electrical activities from the thalamus as well as the scalp and electromyo-gram of the left brachial biceps muscle were re-corded simultaneously with EEG machine.
Background electrical activity of the thalamus was similar to the scalp one in amplitude, frequency, and configuration. However, predominant spikes and waves of irregular spike and wave bursts were re-cognized in the thalamic recording, and the pa-roxysmal bursts often preceded with period of a few hundreds milliseconds in the thalamic lead. Simul-taneous EMG recordings revealed that the discharge on EMG were often synchronous with the spike of the spike and wave bursts in the thalamic lead. The case was photosensitive electroencephalographically, and the polyspike and wave bursts were readily evoked in the thalamic lead. Clinical and electro-encephalographic observations were made immedi-ately after right ventro-lateral thalamotomy during surgery. There was no change electromyographically ane electroencephalographically.
Then, the destruction of the field of Forel-H was performed on the right side and the depth-electrode was inserted again into the previous recording point of the thalamus. The depth-recordings demonstrated marked diminution of paroxysmal bursts in the tha-lamic lead after the destruction. Polyspike and wave bursts were no more evoked by photic stimulation. There was nearly no change with some build up of slow waves. His myoclonic movements slightly decreased clinically as well. The destruction of the field of Forel-H brought an improvement of clinical myoclonic movement and a decrement of the ex-citability of the thalamus and the neighboring struc-tures.
A brain biopsy was obtained from a frontal cortex during surgery. The specimen revealed a type of myoclonus epilepsy with neuronal lipoidosis histo-logically.
Copyright © 1970, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


