Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.いとぐち
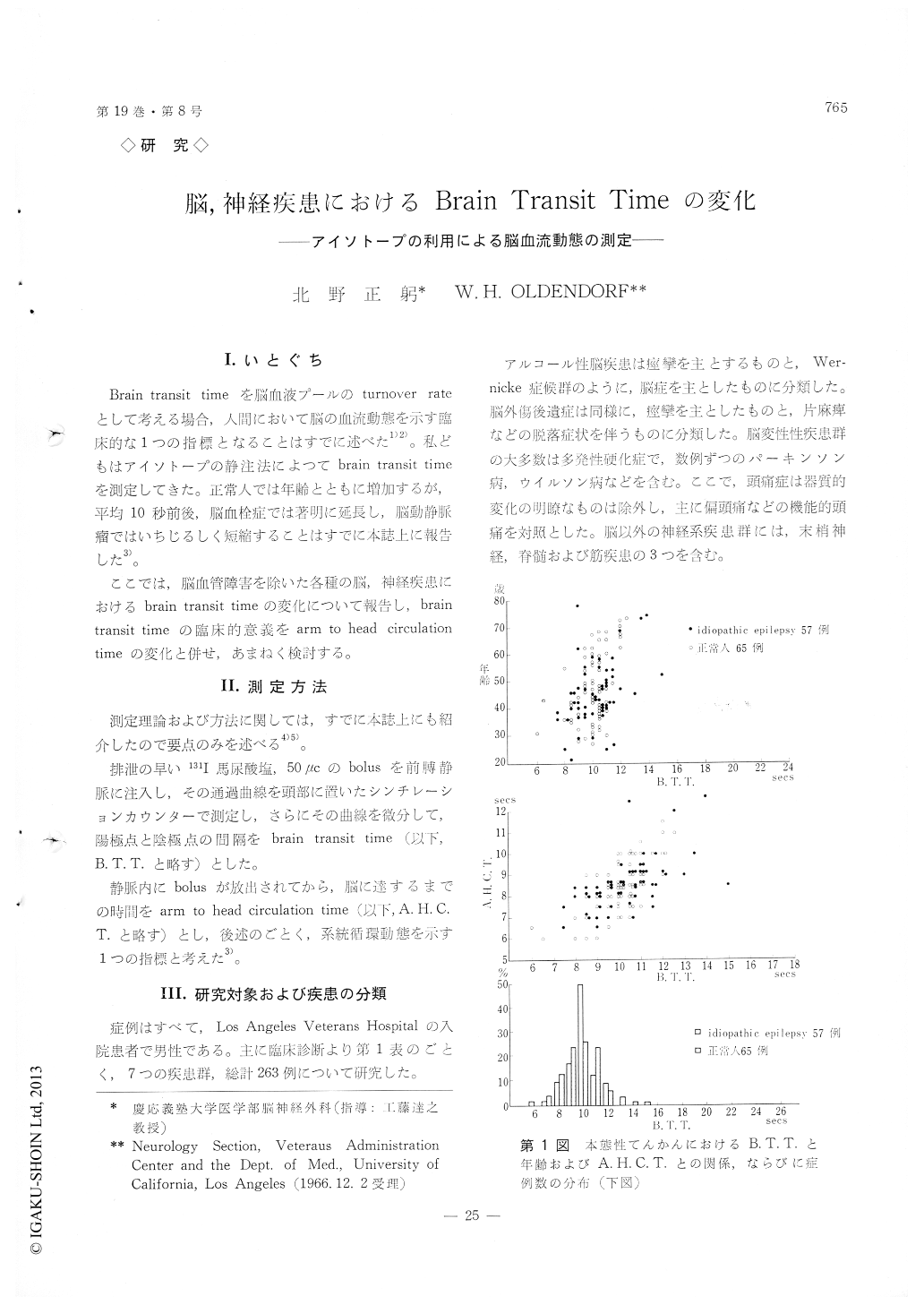
Brain transit timeを脳血液プールのturnover rateとして考える場合,人間において脳の血流動態を示す臨床的な1つの指標となることはすでに述べた1)2)。私どもはアイソトープの静注法によってbrain transit timeを測定してきた。正常人では年齢とともに増加するが,平均10秒前後,脳血栓症では著明に延長し,脳動静脈瘤ではいちじるしく短縮することはすでに本誌上に報告した3)。
ここでは,脳血管障害を除いた各種の脳,神経疾患におけるbrain transit timeの変化について報告し,brain transit timeの臨床的意義をarm to head circulation timeの変化と併せ,あまねく検討する。
Brain blood pool transit time were studied in relation to Arm to Head Circulation Time in 263 subjects of various neurological diseases. These were measured by an intravenous radioisotope technique utilizing ex-ternal monitoring of brain passage of bolus of non-diffusible radioactive indicator, I-131-Hippurate. B. T. T. is 10± 0.2 seconds in healthy subjects.
Marked prolongation of B. T. T. is seen in alcoholic and posttraumatic encephalopathy and degenerative neurological diseases. A. H. C. T. is not prolonged in comparison with B. T. T. prolongation in alcoholic encephalopathy whereas A. H. C. T. is prolonged in proportion to B. T. T. in posttraumatic encephalopathy and degenerative disease.
Seizure group such as idiopathic epilepsy, alcoholic and posttraumatic seizure, B. T. T. is in normal limits as well as A. H. C. T. except in cases with long his-tory.
Moderate prolongation is seen in brain tumor where-as B. T. T. is relatively prolonged as well as A. H. C. T. in the case with increased intracranial pressure. Slight shortning of B. T. T. is seen in headaches. In noncerebral neurological diseases, B. T. T. is in normal limits.
There is a general positive relationship between B. T. T. and A. H. C. T. except few groups such as alcoholic and traumatic encephalopathy.
Clinical significance of B. T. T. is discussed in all neurological diseases concluding this series of publica-tion on B. T. T.
Copyright © 1967, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


