Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
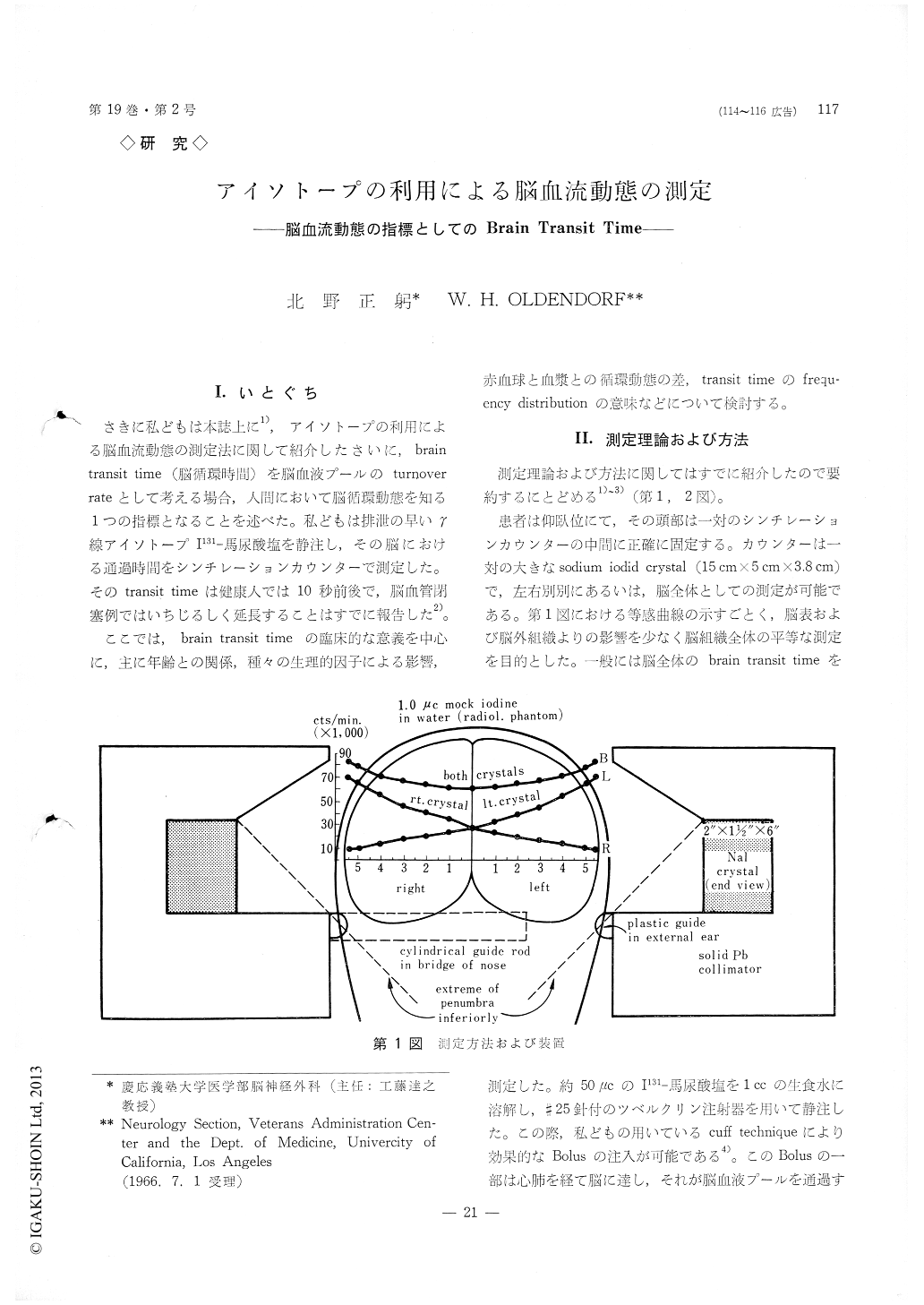
I.いとぐち
さきに私どもは本誌上に1),アイソトープの利用による脳血流動態の測定法に関して紹介したさいに,brain transit time (脳循環時間)を脳血液プールのturnover rateとして考える場合,人間において脳循環動態を知る1つの指標となることを述べた。私どもは排泄の早いγ線アイソトープI131馬尿酸塩を静注し,その脳における通過時間をシンチレーションカウンターで測定した。そのtransit timeは健康入では10秒前後で,脳血管閉塞例ではいちじるしく延長することはすでに報告した2)。
ここでは,brain transit timeの臨床的な意義を中心に,主に年齢との関係,種々の生理的因子による影響,赤血球と血漿との循環動態の差,transit timeのfrequ—ency distributionの意味などについて検討する。
1) Brain transit times were studied in normals by an intravenous radioisotope technique utilizing external monitoring of brain passage of a bolus of nondiffusible radioactive indicators. This transit time (or brain pool turnover time) was used as an index of brain blood flow.
2) Brain transit time is 10 seconds in average in healthy subjects with a general increase in advanced age. Brain transit time is also prolonged by hyper-ventilation and Valsalva effect.
3) Differential rate of passage of brain transit time of plasma and red cell were studied respectively. Red cell transit time is faster than plasma (mode value 7 seconds vs 5 second, mean value 8 seconds vs 5 second).
4) Frequency distribution of transit time of plasma and red cell were measured and its significance was discussed.
5) Clinical significance of brain transit time was discussed as an index of cerebral hemodynamics.
Copyright © 1967, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


