Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
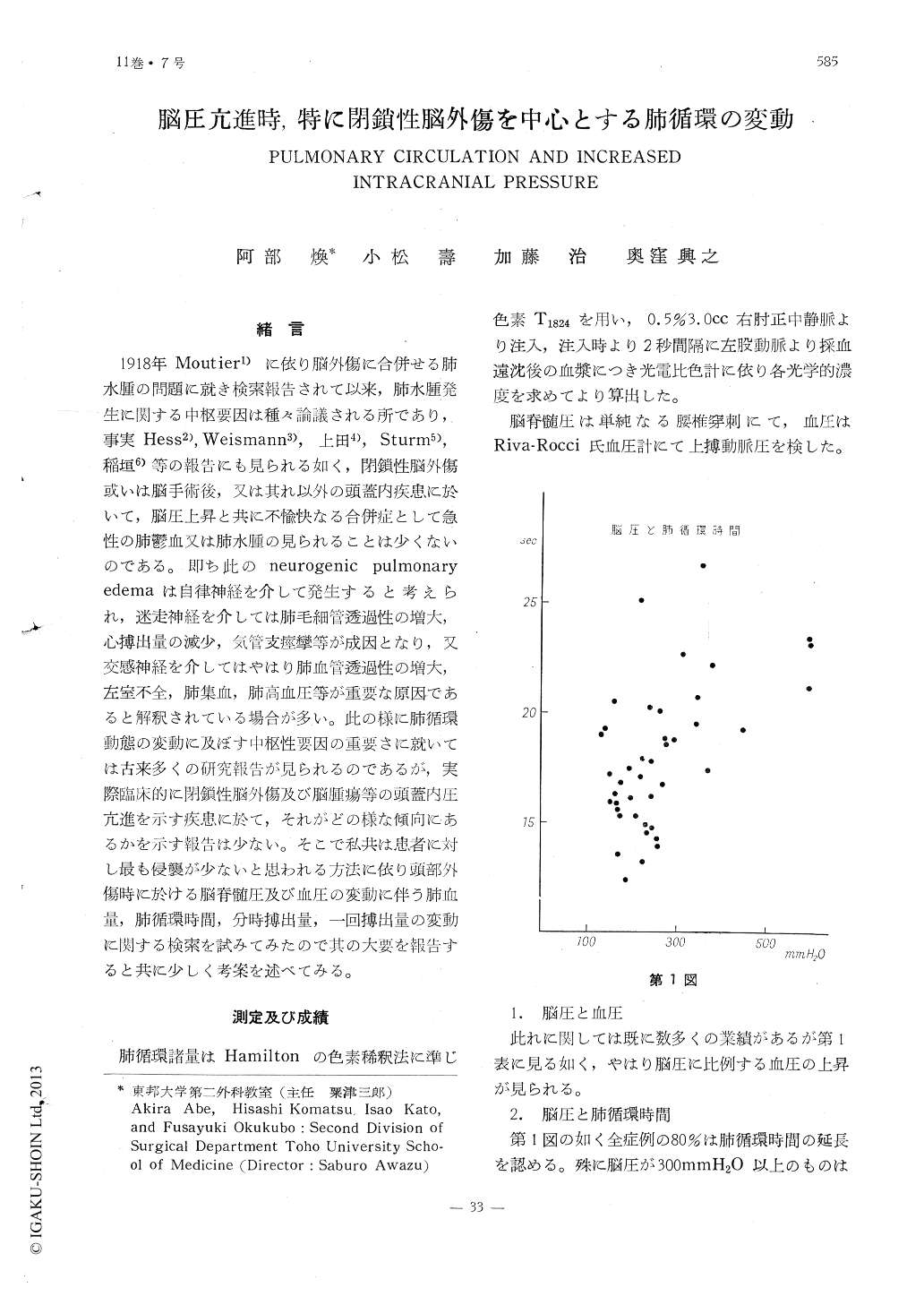
緒言
1918年Moutier1)に依り脳外傷に合併せる肺水腫の問題に就き検索報告されて以来,肺水腫発生に関する中枢要因は種々論議される所であり,事実Hess2),Weismann3),上田4),Sturm5),稲垣6)等の報告にも見られる如く,閉鎖性脳外傷或いは脳手術後,又は其れ以外の頭蓋内疾患に於いて,脳圧上昇と共に不楡快なる合併症として急性の肺欝血又は肺水腫の見られることは少くないのである。即ち此の neurogenic pulmonary edemaは自律神経を介して発生すると考えられ,迷走神経を介しては肺毛細管透過性の増大,心搏出量の減少,気管支痙攣等が成因となり,又交感神経を介してはやはり肺血管透過性の増大,左室不全,肺集血,肺高血圧等が重要な原因であると解釈されている場合が多い。此の様に肺循環動態の変動に及ぼす中枢性要因の重要さに就いては古来多くの研究報告が見られるのであるが,実際臨床的に閉鎖性脳外傷及び脳腫瘍等の頭蓋内圧亢進を示す疾患に於て,それがどの様な傾向にあるかを示す報告は少ない。そこで私共は患者に対し最も侵襲が少ないと思われる方法に依り頭部外傷時に於ける脳脊髄圧及び血圧の変動に伴う肺血量,肺循環時間,分時搏出量,一回搏出量の変動に関する検索を試みてみたので其の大要を報告すると共に少しく考案を述べてみる。
Since the Montier's report in 1918 concern-ing pulmonary edema caused by brain-injuries, there are many reports about the mechanism of this edema.
It is well known that acute pulmonary congestion occurs in the cases of head injuries or of other central nervous disease, though clinical investigation in such cases have little been performed.
In 50 cases of acute brain-injuries and brain-tumors, pulmonary circulation-time, pulm-onary blood-volume, output-volume per min-ute, stroke-volume, those by the dyedilution-method, intracranial pressure, blood piressure and clinical symptoms were observed.
Pulmonary circulation-time was delayed and pulmonary blood-volume increased in the cases of increased intracranial pressure or of high blood pressure, on the other hand, the changes of out-put-volume per minuite were insignificant even though stroke-volume in-creased slightly in those cases.
These changes were more apparent in the cases showing the signs of brain-stem-damage such as unconsciousness, high body tempera-ture and incontinence etc.
Copyright © 1959, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


