Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
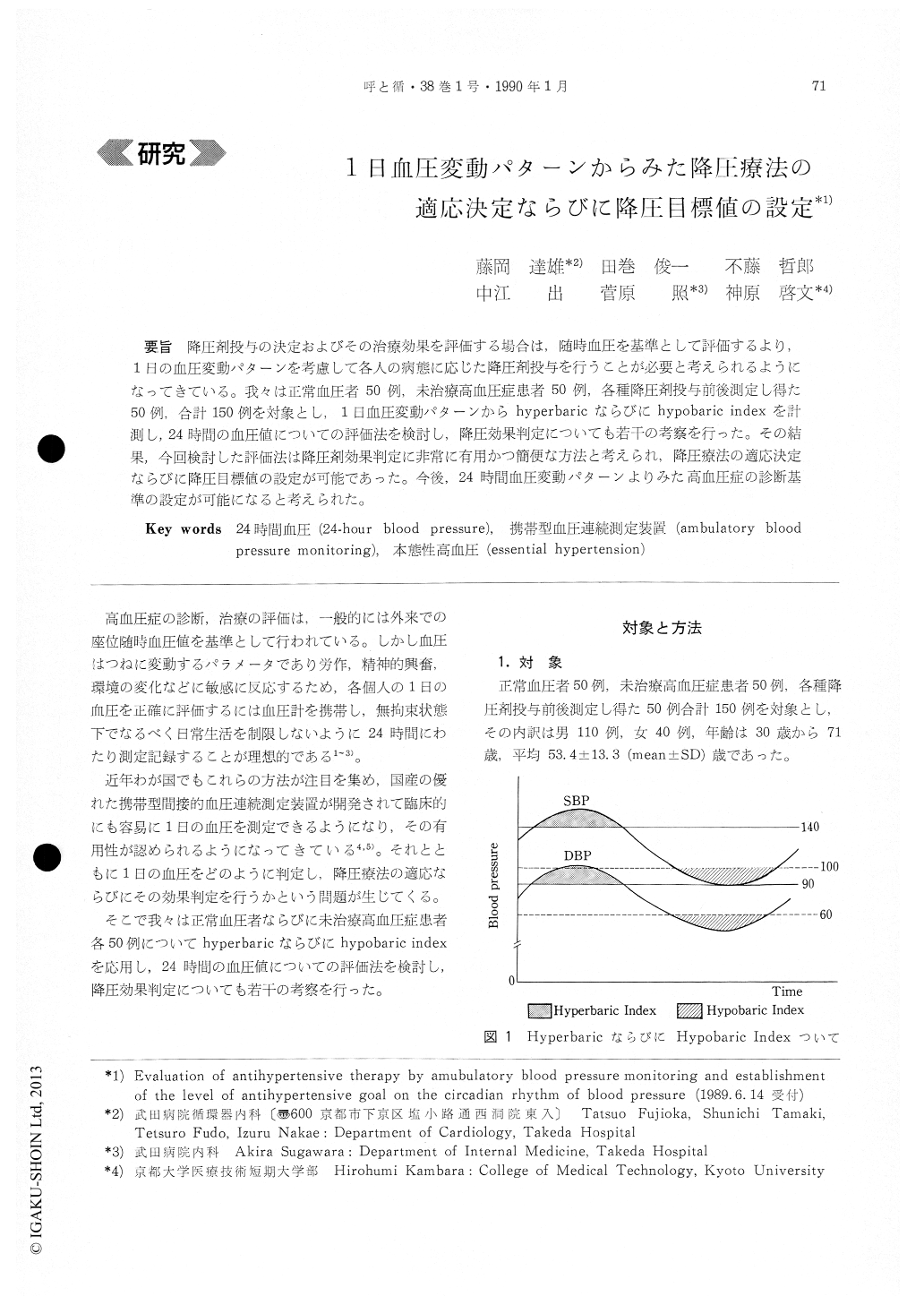
降圧剤投与の決定およびその治療効果を評価する場合は,随時血圧を基準として評価するより,1日の血圧変動パターンを考慮して各人の病態に応じた降圧剤投与を行うことが必要と考えられるようになってきている。我々は正常血圧者50例,未治療高血圧症患者50例,各種降圧剤投与前後測定し得た50例,合計150例を対象とし,1日血圧変動パターンからhyperbaricならびにhypobaric indexを計測し,24時間の血圧値についての評価法を検討し,降圧効果判定についても若干の考察を行った。その結果,今回検討した評価法は降圧剤効果判定に非常に有用かつ簡便な方法と考えられ,降圧療法の適応決定ならびに降圧目標値の設定が可能であった。今後,24時間血圧変動パターンよりみた高血圧症の診断基準の設定が可能になると考えられた。
We have developed a new method for the evalua-tion of antihypertensive therapy on the circadian rhythm of blood pressure and attempted to determine the indications for antihypertensive therapy and the level of antihypertensive goal.
Blood pressures were measured for 24 hours by the use of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring using 630 (ABPM-630) in 50 normotensives, 50 untreated hypertensives and 50 hypertensives undertreatment with various antihypertensive drugs (110 males and 40 females, with a mean age of 53. 4±13. 3 yrs). Blo-od pressure profiles were prepared for determina-tion of the hyperbaric and hypobaric indexes. Acco-rding to the WHO's definitions for blood pressure, the hyperbaric index was defined as the area above 140 mmHg in systolic blood pressure or 90 mmHg in diastolic blood pressure, and the hypobaric index, as the area below 100 mmHg or 60 mmHg, respectively.
The criteria of the hypobaric index was obtained from the mean basal blood pressure (the lowest blo-od pressure during sleep) of the 50 normotensives.
The mean hyperbaric index of the 50 normoten-sives was 20.4±40.2/5.5±15.3 (systole/diastole) mmHg・hour/day and the mean hypobaric index, 12.2 ±22.5/9. 0±24.0 mmHg・hour/day. The 50 untreated hypertensives showed a mean hyperbaric index of 281.8±197.0/156.0±126.1 mmHg・hour/day and a mean hypobaric index of 0.1±0.6/0.3±1.5 mmHg・hour/day.
Comparison of the indexes before and after treat-ment with various antihypertensives showed that a decrease in the hyperbaric index without an increase in the hypobaric index was the most optimal reduc-tion of blood pressure. The effect of antihyperten-sive therapy should not be evaluated on the basis of the hyperbaric index alone, but hypotension due to excessive antihypertensive treatment should also be taken into account. Therefore, we evaluated antihy-pertensive therapy on the basis of both hyperbaric and hypobaric indexes.
The present method is thought to be very useful and simple in the evaluation of the effect of antihy-pertensive therapy. It permitted establishment of the indications for antihypertensive therapy and the ideal level for blood pressure fall. Further studies using this method may lead to the establishment of the diagnostic criteria for hypertension on the basis of the pattern of 24-hour blood pressure monitoring.
Copyright © 1990, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


