Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
Aprindine hydrochloride (以下aprindineと略す)はVaughan Williams分類のclass Iに属する抗不整脈薬で,1973年Kestelootらによって臨床応用されて1)以来,主としてヨーロッパで使用されてきた。本邦でも1987年3月に発売され,広く臨床に使用されつつある。
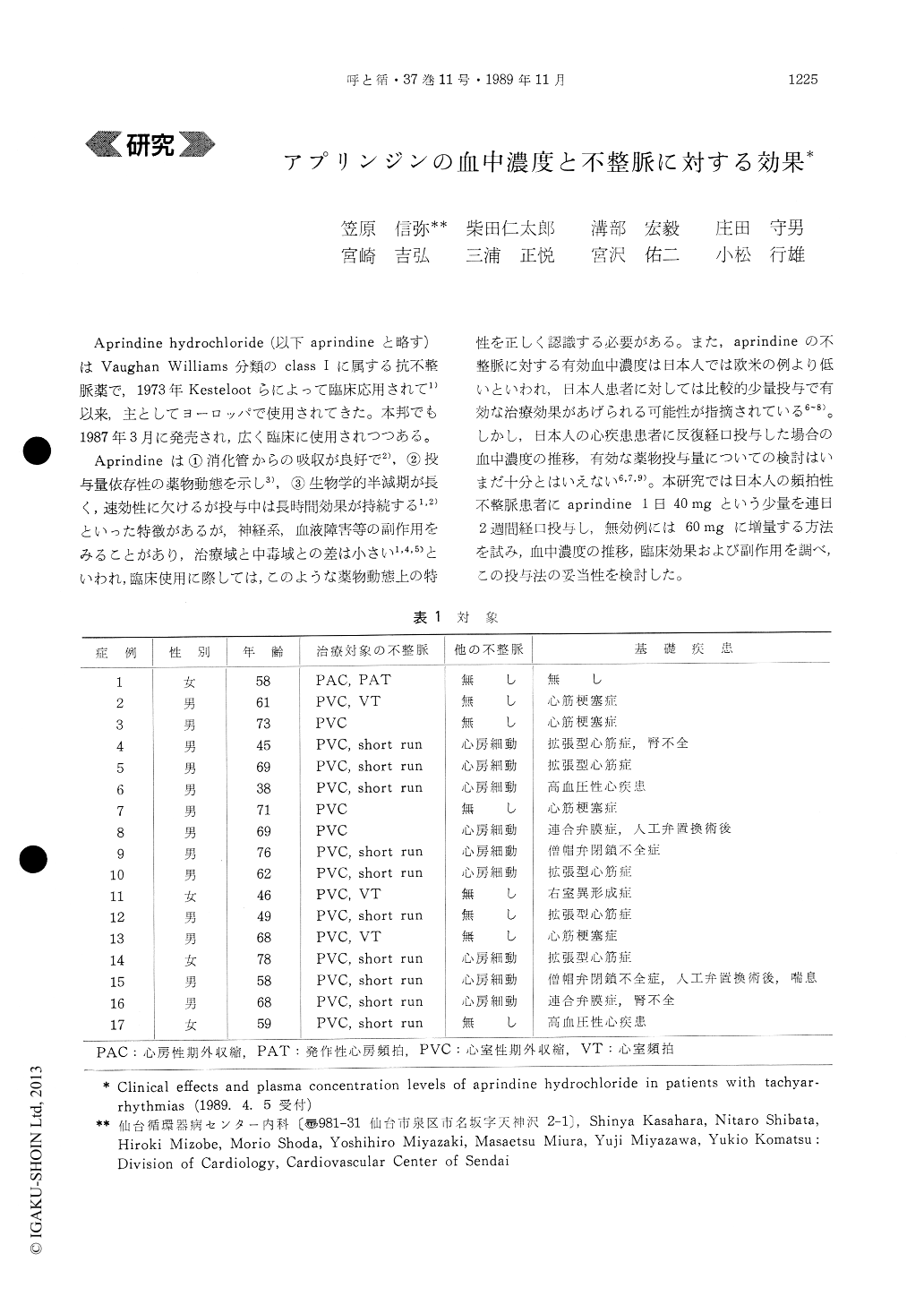
Aprindineは①消化管からの吸収が良好で2),②投与量依存性の薬物動態を示し3),③生物学的半減期が長く,速効性に欠けるが投与中は長時間効果が持続する1,2)といった特徴があるが,神経系,血液障害等の副作用をみることがあり,治療域と中毒域との差は小さい1,4,5)といわれ,臨床使用に際しては,このような薬物動態上の特性を正しく認識する必要がある。また,aprindineの不整脈に対する有効血中濃度は日本人では欧米の例より低いといわれ,日本人患者に対しては比較的少量投与で有効な治療効果があげられる可能性が指摘されている6〜8)。しかし,日本人の心疾患患者に反復経口投与した場合の血中濃度の推移,有効な薬物投与量についての検討はいまだ十分とはいえない6,7,9)。本研究では日本人の頻拍性不整脈患者にaprindine 1日40mgという少量を連日2週間経口投与し,無効例には60mgに増量する方法を試み,血中濃度の推移,臨床効果および副作用を調べ,この投与法の妥当性を検討した。
Aprindine hydrochloride (aprindine) was admini-stered orally in 17 Japanese patients with supraven-tricular or ventricular tachyarrhythmias, and the clinical effects and plasma concentration levels were evaluated.
The antiarrhythmic effects were defined using Hol-ter ECG recordings. Aprindine was administered orally with a daily dose of 40 mg for 2 weeks in all cases, and aprindine, 60 mg daily, was administeredfor the next 2 weeks in patients who did not show sufficient antiarrhythmic effects with 40 mg of the drug.
Aprindine was effective in 9 of 17 patients, and the mean plasma concentration level reached 0. 6μg/ ml 2 weeks after the administration was started. Effective results were seen in 2 of the 4 patients receiving a daily dose of 60 mg, and the mean plasma concentration level reached 1.0μg/ml 2 weeks after the administration was started.
Transient mild elevations of liver transaminases were observed in one patient and mild transient anemia was observed in another. These abnormal data disappeared although the drug administration was continued.
In conclusion, the administration of a relatively small dose of aprindine and, consequently, low pla-sma concentration levels, are effective for cardiac tachyarrhythmias in Japanese patients.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


