Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
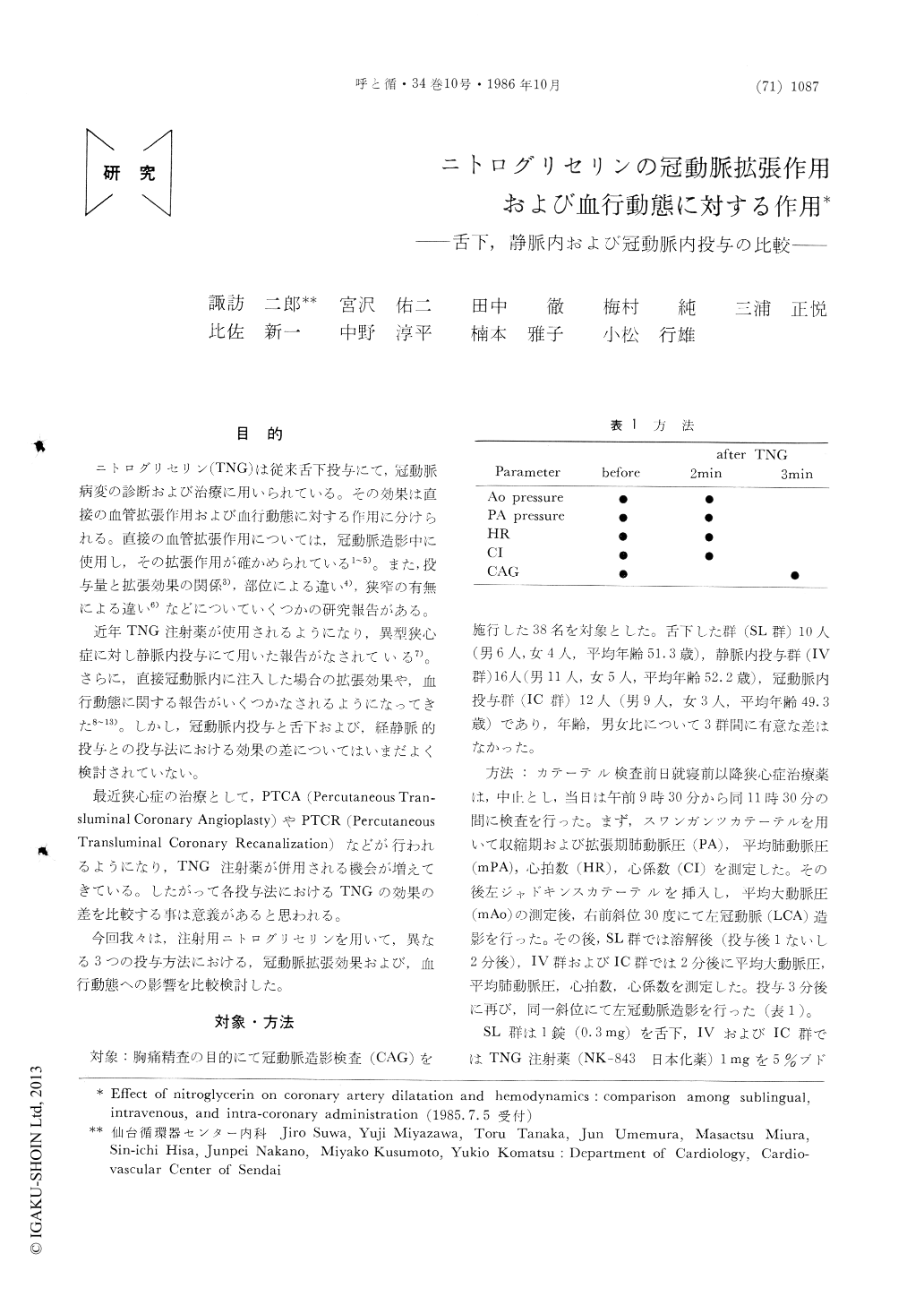
目的
ニトログリセリン(TNG)は従来舌下投与にて,冠動脈病変の診断および治療に用いられている。その効果は直接の血管拡張作用および血行動態に対する作用に分けられる。直接の血管拡張作用については,冠動脈造影中に使用し,その拡張作用が確かめられている1〜5)。また,投与量と拡張効果の関係3),部位による違い4),狭窄の有無による違い6)などについていくつかの研究報告がある。
近年TNG注射薬が使用されるようになり,異型狭心症に対し静脈内投与にて用いた報告がなされている7)。さらに,直接冠動脈内に注入した場合の拡張効果や,血行動態に関する報告がいくつかなされるようになってきた8〜13)。しかし,冠動脈内投与と舌下および,経静脈的投与との投与法における効果の差についてはいまだよく検討されていない。
To evaluate the difference of efficiency of nitrogly-cerin (TNG) among different routes of administration, we studied, the effects of TNG on the hemodynamics and coronary artery dilatation in 38 patients examined for chest pain.
Administration doses were 0.3mg in sublingual (SL) group (N=10), 0.lmgin intravenous (IV) group (N= 16) and intracoronary (IC) group (N=12). Hemodynamic studies showed significant reduction in mean aortic and pulmonary artery pressures in IV group (about 8.8mmHg, p<0.05 and about 3.5mmHg, p<0.001 respectively). On the other hand, reduction of mean aortic and pulmonary pressures was not signi-ficant in SL and IC groups.
Heart rate was increased in SL and IV groups, but decreased in IC group. As pulmonary artery pressures were under 15mmHg in almost all cases, cardiac index was reduced slightly in each group.
Magnitude of coronary artery dilatation was about 25 % in every group and no significant difference existed among the three groups.
Copyright © 1986, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


