Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
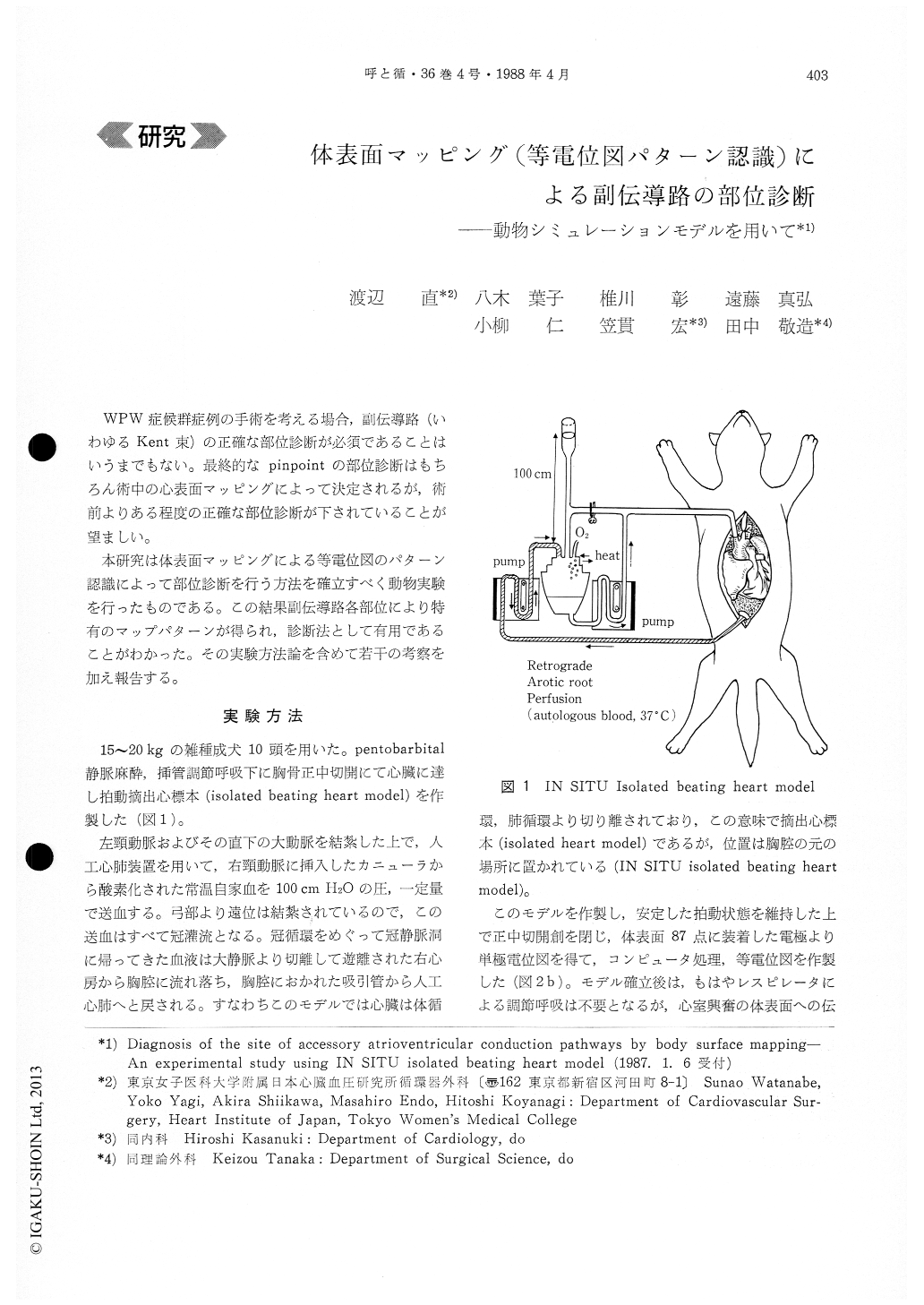
WPW症候群症例の手術を考える場合,副伝導路(いわゆるKent束)の正確な部位診断が必須であることはいうまでもない。最終的なpinpointの部位診断はもちろん術中の心表面マッピングによって決定されるが,術前よりある程度の正確な部位診断が下されていることが望ましい。
本研究は体表面マッピングによる等電位図のパターン認識によって部位診断を行う方法を確立すべく動物実験を行ったものである。この結果副伝導路各部位により特有のマップパターンが得られ,診断法として有用であることがわかった。その実験方法論を含めて若干の考察を加え報告する。
The Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome was mi-micked by stimulating nine different pre-excitation sites in the isolated beating heart of adult mongrel dog which was left in situ (IN SITU isolated beat-ing heart model). The objective was to determine specific body surface isopotential map pattern in each pre-excitation site. During early QRS (δ wave) pe-riod the site of point minimum as well as the vector of points minimum-maximum was found to be charac-teristic in each pre-excitation site. From this ex-perimental study it was concluded that the pattern of isopotential body surface map (the site of point minimum along with the vector of the axis of points minimum-maximum) could provide an easy way to noninvasively diagnose the site of accessory conduc-ion pathways in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


