Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
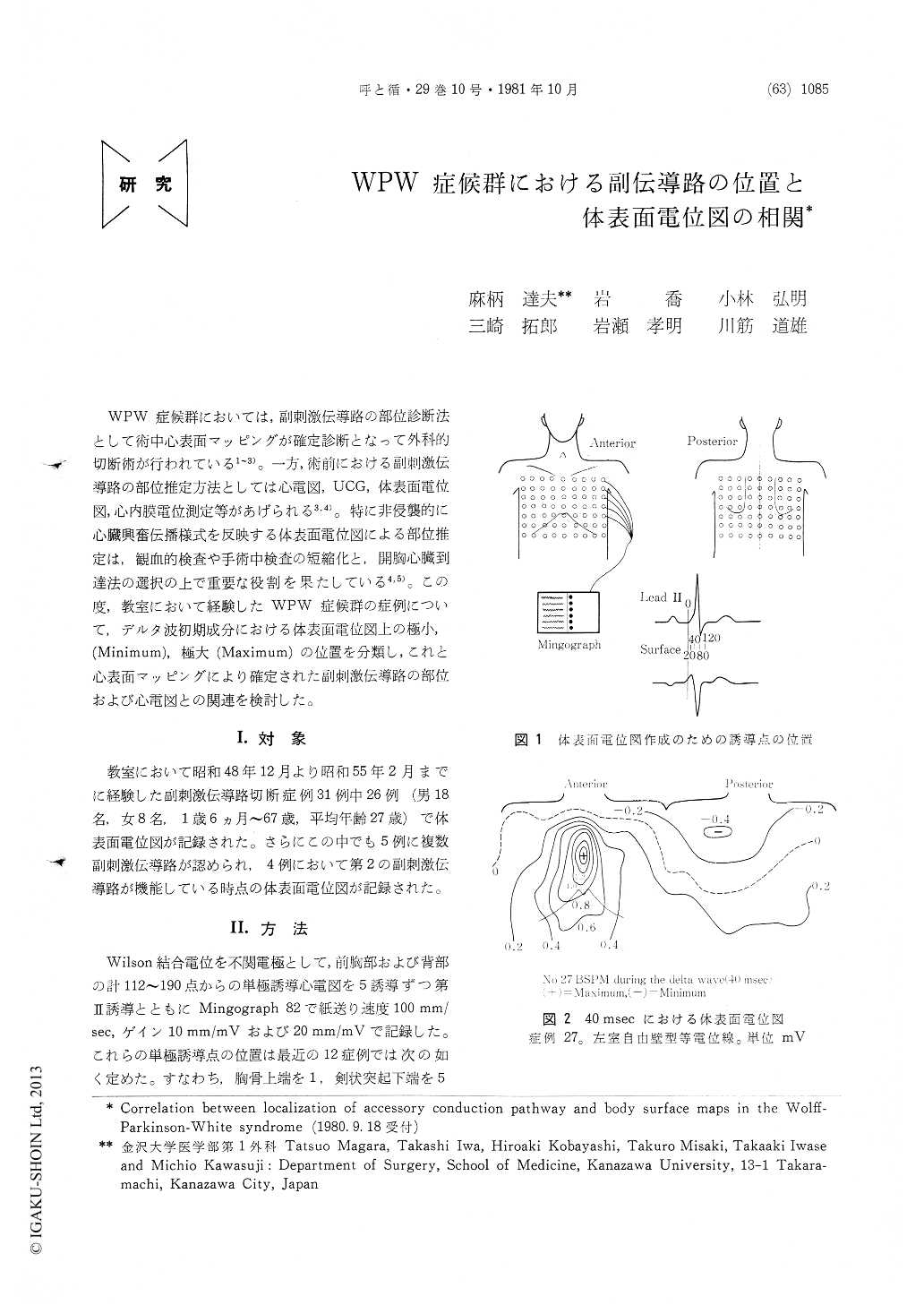
WPW症候群においては,副刺激伝導路の部位診断法として術中心表面マッピングが確定診断となって外科的切断術が行われている1〜3)。一方,術前における副刺激伝導路の部位推定方法としては心電図,UCG,体表面電位図,心内膜電位測定等があげられる3,4)。特に非侵襲的に心臓興奮伝播様式を反映する体表面電位図による部位推定は,観血的検査や手術中検査の短縮化と,開胸心臓到達法の選択の上で重要な役割を果たしている4,5)。この度,教室において経験したWPW症候群の症例について,デルタ波初期成分における体表面電位図上の極小,(Minimum),極大(Maximum)の位置を分類し,これと心表面マッピングにより確定された副刺激伝導路の部位および心電図との関連を検討した。
Body surface maps were recorded in 26 patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, who underwent successful localization and inter-ruption of the accessory conduction pathway. We could classify five types of body surface maps according to the location of the potential maximum and minimum in the delta wave. Each type correlated well with the location of the accessory pathway, which was determined intra-operatively through epicardial and/or endo-cardial maps or surgical interruption.
In the left free wall type map, the potential minimum in the delta wave was on the back and the potential maximum was on the anterior chest wall. When the potential minimum was located on the lower back, the accessory pathway was located on the posterior left ventricular wall. When the potential minimum was locat-ed on the upper back, the accessory pathway was located on the antero-lateral left ventricular wall.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


