Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
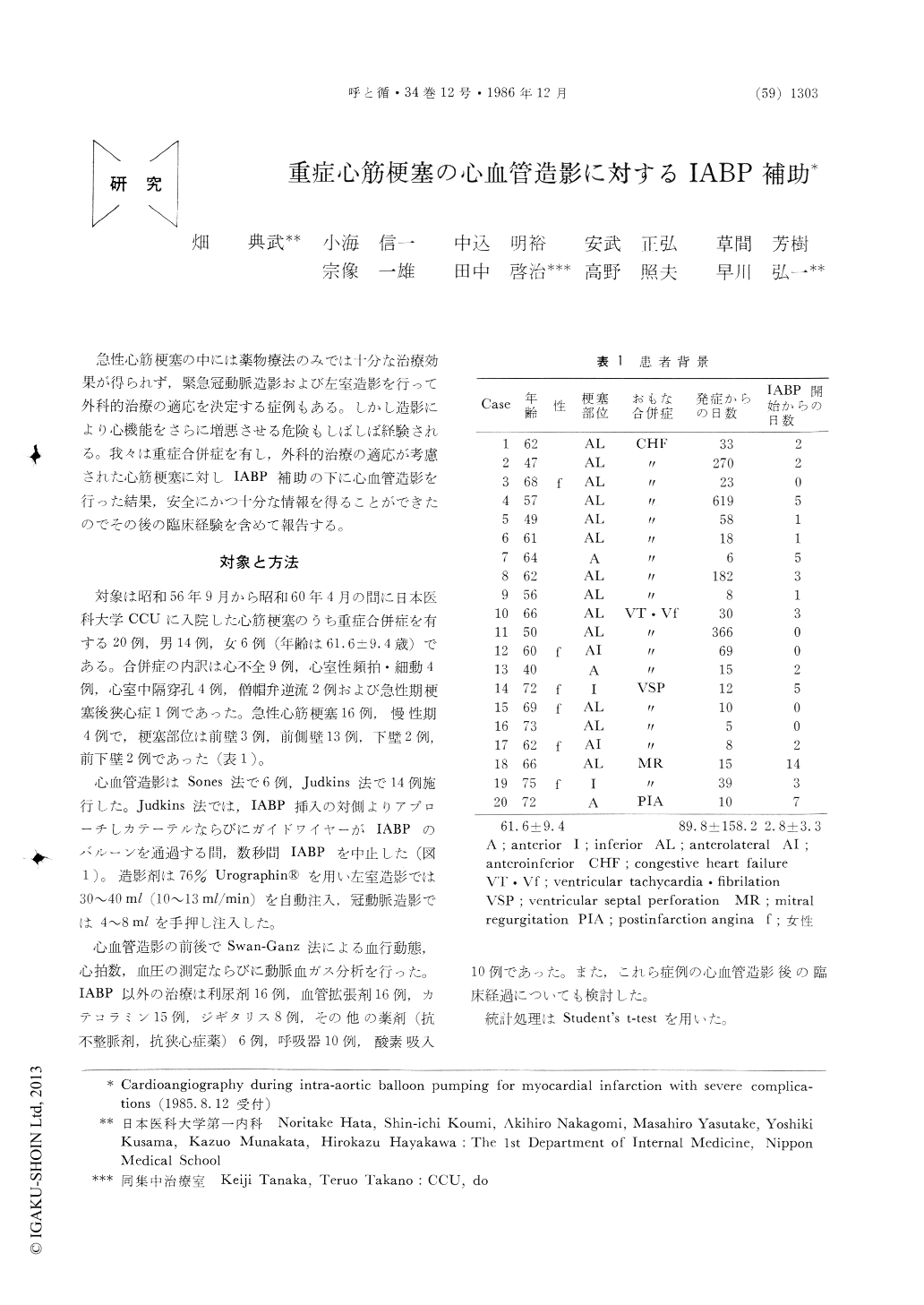
急性心筋梗塞の中には薬物療法のみでは十分な治療効果が得られず,緊急冠動脈造影および左室造影を行って外科的治療の適応を決定する症例もある。しかし造影により心機能をさらに増悪させる危険もしばしば経験される。我々は重症合併症を有し,外科的治療の適応が考慮された心筋梗塞に対しIABP補助の下に心血管造影を行った結果,安全にかつ十分な情報を得ることができたのでその後の臨床経験を含めて報告する。
In order to clarify the significance and safety of cardioangiography during intra-aortic balloon pumping (IABP) in patients with severely complicated myo-cardial infarction (MI), we evaluated hemodynamic change and blood gas analysis before and after car-dioangiography, and also their clinical course in 20 MI patients (14 males and 6 females, 61.6±9.4 years old). Severe complications were intractable congestive heart failure (CHF) in 9 cases, recurrent ventricular tachycardia and/or fibrillation (VT Vf) in 4 cases, ventricular septal perforation (VSP) in 4 cases, mitral regurgitation (MR) in 2 cases and unstable pcstin-farction angina (PIA) in 1 case. Cardioangiography was performed by Sones technique in 6 cases and by Judkins technique in 14 cases. The time from the starting of IABP to cardioangiography was 2.8±3.3 days (0~14 days).
Mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPA), pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) and cardiac index (CI) did not change significantly (26.2±7.3→24.3± 9.4mmHg, 17.4± 7.0→17.1±8.0mmHg and 2.32± 0.85→2.27±0.72l/min/m2, respectively) before and after cardicangiography. h Systolic blood pressure (sBP), heart rate (HR) and central venous pressure (CVP) also did not change significantly either (111.9±12.9?.107.7±12.1mmHg, 99.3±13.6→98.3±13.1 beats/min, and 11.0±4.6→ 10.2±5. 6cmH2O, respectively).
VT and, or Vf occurred in 2 cases with previous recurrent VT・Vf, and atrioventricular dissociation occurred in 1 case with CHF while in the catheteri-zation laboratory. But, all recovered immediately with countershock or intravenous injection of atropin sulfate. h After cardioangiography, 17 of the 20 cases had surgical treatment. The remaining 3 cases with CHF were not candidates for surgery because of diffuse hypokinesis and a large area of akinesis or aneurysm of the left ventricle. 8 of the 17 surgical patients and 2 of the 3 medical patients died. The mortality was high in CHF patients (6 out of 9) ; on the other hand in VSP and PIA, the prognosis was relatively good (3 out of 4 VSP and 1 PIA survived).
In non-survival cases in whom poor left ventricular function and multivessel disease were found, hemody-namic data tended to worsen gradually after cardio-angiography ; PCWP elevated and CI decreased.
In conclusion, cardioangiography for determination of surgical indication of severely complicated MI could be carried out without seriously dangerous complications when performed during IABP. Its clinical benefit might be superior to the risk in such patients.
Copyright © 1986, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


