Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
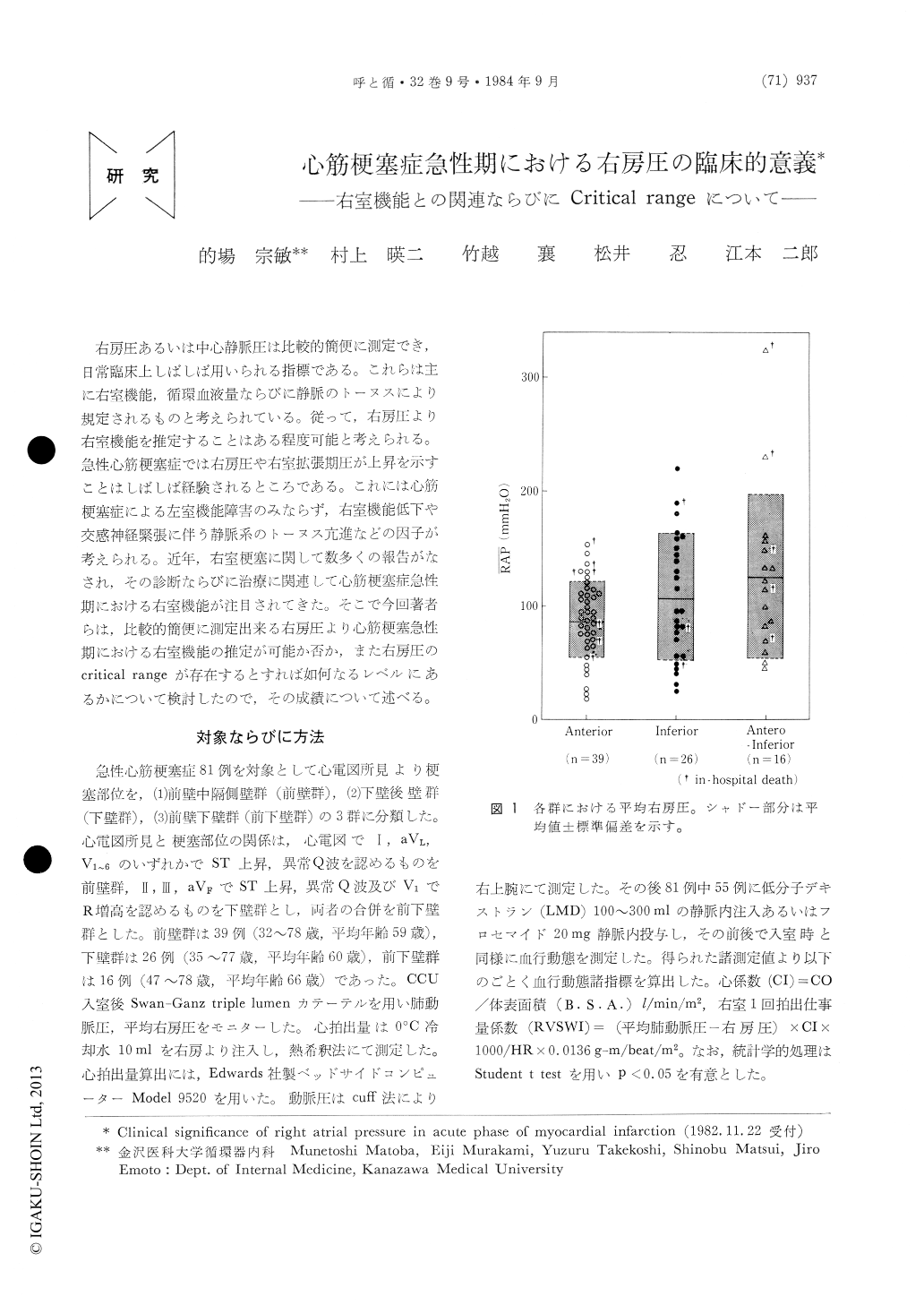
右房圧あるいは中心静脈圧は比較的簡便に測定でき,日常臨床上しばしば用いられる指標である。これらは主に右室機能,循環血液量ならびに静脈のトーヌスにより規定されるものと考えられている。従って,右房圧より右室機能を推定することはある程度可能と考えられる。急性心筋梗塞症では右房圧や右室拡張期圧が上昇を示すことはしばしば経験されるところである。これには心筋梗塞症による左室機能障害のみならず,右室機能低下や交感神経緊張に伴う静脈系のトーヌス亢進などの因子が考えられる。近年,右室梗塞に関して数多くの報告がなされ,その診断ならびに治療に関連して心筋梗塞症急性期における右室機能が注目されてきた。そこで今回著者らは,比較的簡便に測定出来る右房圧より心筋梗塞急性期における右室機能の推定が可能か否か,また右房圧のcritical rangeが存在するとすれば如何なるレベルにあるかについて検討したので,その成績について述べる。
To investigate the clinical significance of right atrial pressure (RAP) in acute phase of myocardial infarction, resting hemodynamics using Swan-Ganz triple lumen catheter was measured in 81 patients with acute myocardial infarction (anterior infarc-tion : 39 patients, inferior infarction : 26, antero-inferior infarction : 16). Thereafter, low molecular dextran or furosemide were adminstered in 55 of 81 patients and right ventricular stroke work index (RVSWI)-RAP (=right ventricular function curve), cardiac index (CI)-RAP and pulmonary arterial end-diastolic pressureg (PAEDP)-R AP rela-tionships were examined. In patients of inferior infarction with RAP higher than 140-150 mmH2O and patients of antero-inferior infarction with RAP higher then 140 mmH2O RVSWI was decreased markedly. In inferior infarction, right ventricular function curves were shifted to right and lower position when the RAP exceeded 140 mmH2O, CI was decreased accompanied with an increase in RAP higher than 140 mmH2O and PAEDP did not elevate beyond 18 mmHg in spite of the eleva-tion of RAP. These results indicate that patients of inferior infarction with RAP higher than 140-150 mmH2O and patients of antero-posterior infarction with RAP higher than 140 mmH2O show the depressed right ventricular function and critical range of RAP is 140-150 mmH2O in patients of inferior infarction.
Copyright © 1984, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


