- 有料閲覧
- 文献概要
- 1ページ目
緒言
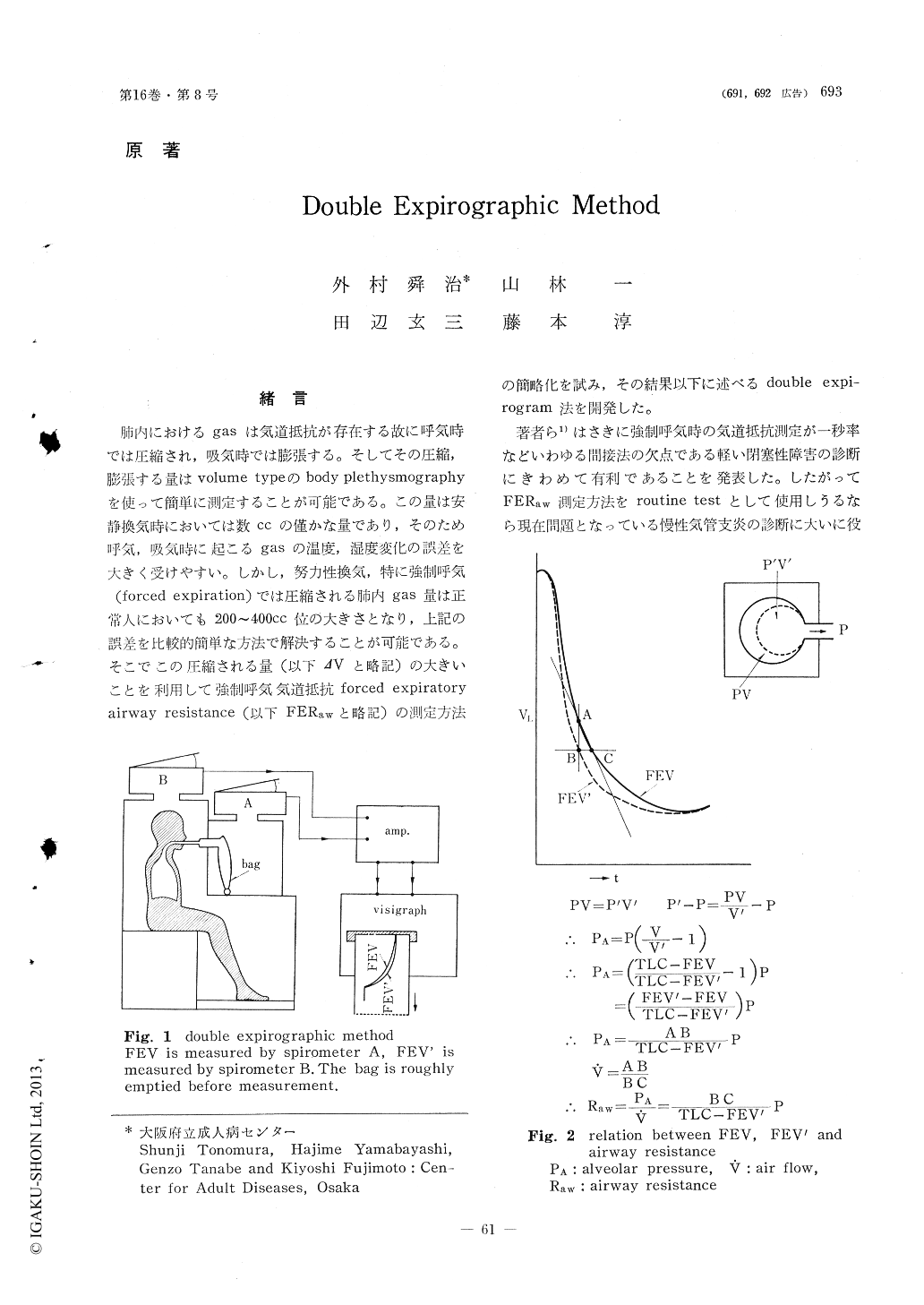
肺内におけるgasは気道抵抗が存在する故に呼気時では圧縮され,吸気時では膨張する。そしてその圧縮,膨張する量はvolume typeのbody plethysmographyを使って簡単に測定することが可能である。この量は安静換気時においては数ccの僅かな量であり,そのため呼気,吸気時に起こるgasの温度,湿度変化の誤差を大ぎく受けやすい。しかし,努力性換気,特に強制呼気(forced expiration)では圧縮される肺内gas量は正常人においても200〜400cc位の大きさとなり,上記の誤差を比較的簡単な方法で解決することが可能である。そこでこの圧縮される量(以下ΔVと略記)の大きいことを利用して強制呼気気道抵抗forced expiratory airway resistance (以下FERawと略記)の測定方法の簡略化を試み,その結果以下に述べるdouble expi—rogram法を開発した。
著者ら1)はさきに強制呼気時の気道抵抗測定が一秒率などいわゆる間接法の欠点である軽い閉塞性障害の診断にきわめて有利であることを発表した。したがってFERaw測定方法をroutine testとして使用しうるなら現在問題となっている慢性気管支炎の診断に大いに役立つことも考えられる。また間接法が強制呼気曲線を主体とした指標であるかぎり,その指標の臨床的な診断価値はFERawを基として評価すべきであるともいえる。以上の問題点を含め,double expirogram法を報告する。
A method of measurement of forced expi-ratory resistance (FERaw) was described.
1) This method was very valuable in clini- cal use because simple technique without laborious mathematical calculation. The FERaw was found as a very sensitive index in detecting the mild airway obstruction.
2) The value of FERaw at 50 % of viatl ca- pacity (FERaw 50 %) was most valuable to use.
3) The conventional spirometric technique to detect the abnormality in airway was evaluated with compairing with our new technique.
All patients with FEV1.0 % less than 69 % had the abnormal FERaw 50 % while the most of subjects with FEV1.0 % more than 85% had the normal FERaw 50%.
In the cases with FEV1.0% between 70 and 84 % the normal and abnormal FERaw 50% were overlapped.
Copyright © 1968, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


